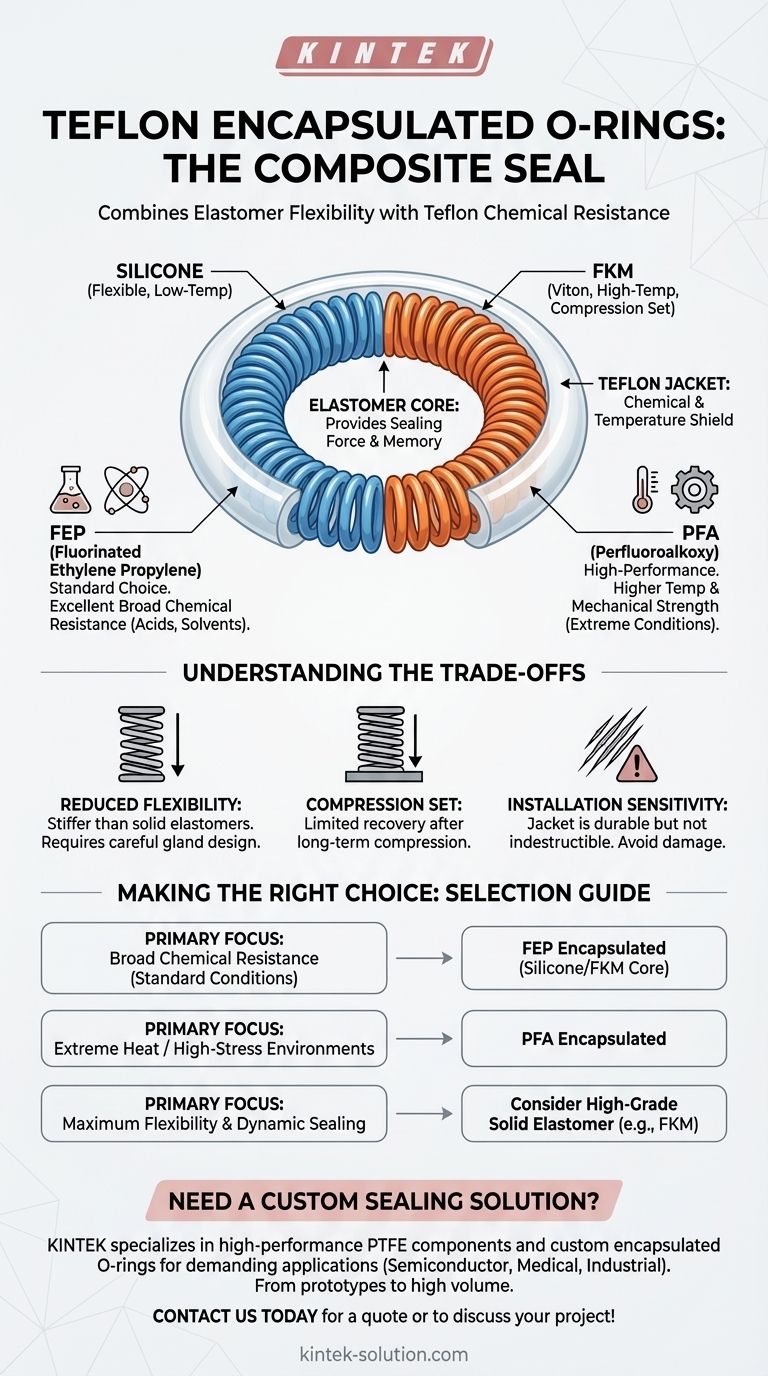
At its core, a Teflon encapsulated O-ring is a composite seal. It consists of an inner elastomeric core, typically made of Silicone or FKM, which is then completely encased in a seamless outer jacket made from one of two Teflon resins: FEP or PFA.
The fundamental principle behind this design is to combine the best properties of two distinct material families: the superior chemical and temperature resistance of a Teflon jacket is paired with the essential flexibility and sealing force of an elastomer core.
The Anatomy of an Encapsulated O-Ring
To understand why these materials are chosen, it's crucial to see the O-ring as a system where each component serves a distinct purpose. This composite structure solves a problem that neither material could solve on its own.
The Elastomer Core: Providing the Sealing Force
The inner core is the engine of the seal. Its primary job is to provide the elasticity and "memory" required to maintain pressure and create a tight, effective barrier against leaks.
The two most common core materials are:
- Silicone: Chosen for its excellent flexibility over a wide temperature range, particularly in low-temperature applications.
- FKM: Often known by its brand name Viton, FKM is selected for its superior compression set resistance and good performance at higher temperatures.
The Seamless Jacket: The Chemical Shield
The outer jacket is the O-ring's protective armor. It is what comes into direct contact with the process media, shielding the sensitive elastomer core from chemical attack and extreme temperatures.
This jacket is always made from a seamless sheath of thermoplastic Teflon resin, which prevents any potential leak paths.
A Closer Look at the Jacket Materials
The choice between FEP and PFA for the outer jacket depends entirely on the specific demands of the application, primarily concerning temperature and mechanical stress.
FEP (Fluorinated Ethylene Propylene)
FEP is the standard material for Teflon encapsulation. It provides a remarkable defense against a broad spectrum of aggressive chemicals, including acids, solvents, and petroleum spirits.
It is the go-to choice for the majority of applications where extreme chemical inertness is the primary requirement.
PFA (Perfluoroalkoxy)
PFA is the high-performance option. While it shares the same outstanding chemical resistance as FEP, it offers two key advantages.
PFA delivers higher mechanical strength and, most importantly, increased temperature resistance. It is specified for applications involving extreme thermal cycling, high pressure, or where maximum durability is non-negotiable.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While offering a unique solution, the composite nature of encapsulated O-rings introduces specific considerations that are critical for proper application.
Reduced Flexibility
The primary trade-off is a reduction in elasticity. The Teflon jacket makes the entire O-ring significantly stiffer than a standard, solid elastomer O-ring. This must be accounted for in gland design and installation procedures.
Compression Set
These O-rings do not have the same "rebound" or compression set resistance as high-performance solid elastomers. The rigid jacket can limit the core's ability to fully recover after being compressed for long periods.
Installation Sensitivity
The Teflon jacket is durable but not indestructible. Care must be taken during installation to avoid scratching or nicking the surface, as any breach in the jacket will compromise the seal and expose the core to chemical attack.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct encapsulated O-ring requires aligning the material properties with your primary operational goal.
- If your primary focus is broad chemical resistance in standard conditions: An FEP encapsulated O-ring with either a Silicone or FKM core is the most effective and economical choice.
- If your primary focus is performance in extreme heat or high-stress environments: A PFA encapsulated O-ring provides the necessary thermal stability and mechanical strength to ensure reliability.
- If your primary focus is maximum flexibility and dynamic sealing: An encapsulated O-ring may not be the ideal solution; a high-grade solid elastomer like FKM should be considered if it meets your chemical compatibility needs.
Ultimately, understanding this combination of a resilient core and an inert shield empowers you to engineer a sealing solution for some of the most demanding industrial environments.
Summary Table:
| Component | Material Options | Key Function |
|---|---|---|
| Inner Core | Silicone, FKM (Viton) | Provides elasticity and sealing force |
| Outer Jacket | FEP, PFA | Acts as a chemical and temperature shield |
Need a custom sealing solution for a demanding application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components, including custom encapsulated O-rings. Our expertise in precision production ensures you get a seal perfectly matched to your requirements, whether you're in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, or industrial sector.
We offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders. Let us help you solve your toughest sealing challenges.
Contact us today for a quote or to discuss your project!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech



















