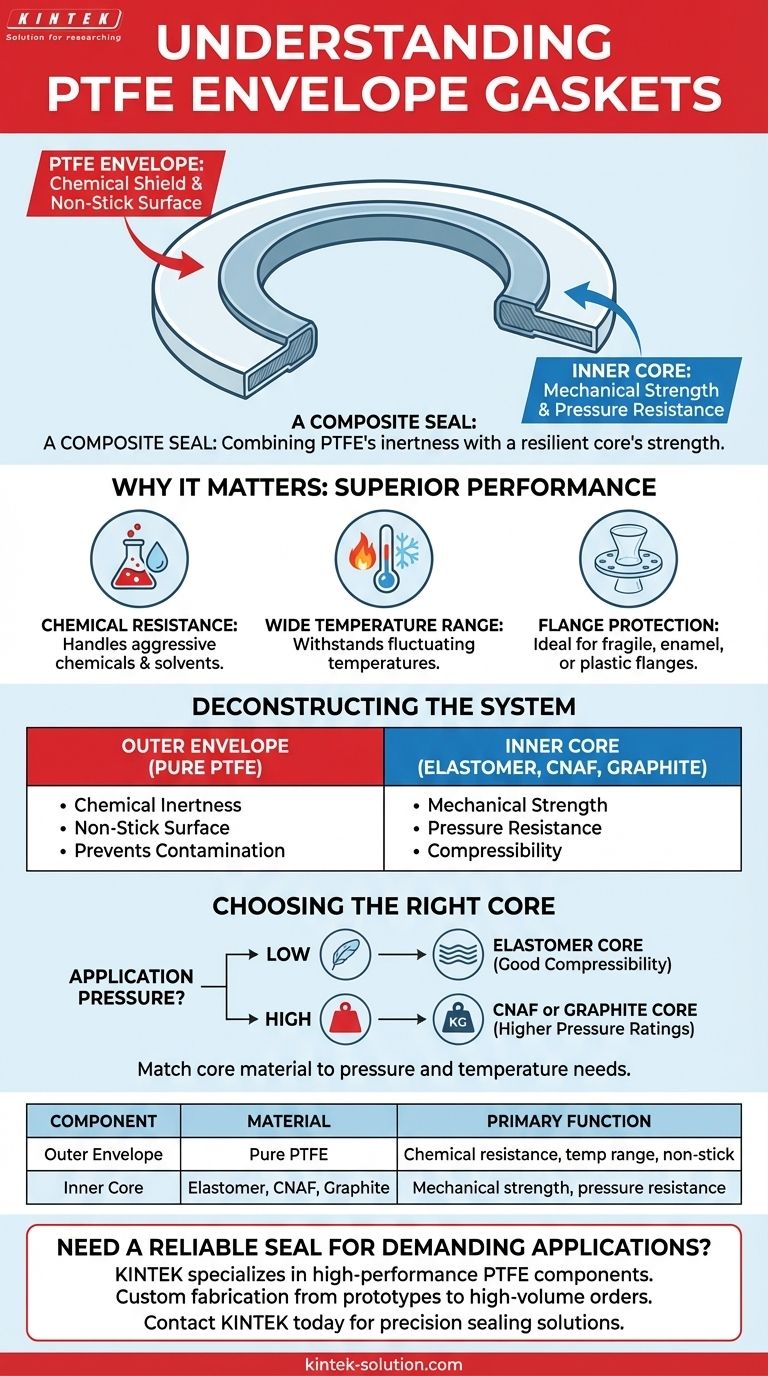
At its core, a PTFE envelope gasket is a composite seal, not a single material. It consists of an outer "envelope" made of pure Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) that encases a separate, more resilient inner core material. This clever design combines the unparalleled chemical resistance of PTFE with the mechanical strength and compressibility of the chosen insert.
The essential takeaway is that a PTFE envelope gasket leverages a two-part construction to solve a classic engineering problem: it uses a PTFE exterior for chemical inertness while relying on an internal core material to provide the mechanical strength and pressure resistance that pure PTFE lacks.

Deconstructing the PTFE Envelope Gasket
To understand its performance, you must look at the gasket as a system of two distinct components working together. Each part serves a specific and critical function.
The PTFE Envelope: Your Chemical Shield
The outer layer is the component that comes into direct contact with the process media. It is made from high-density polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE).
This material provides the gasket's signature properties: exceptional chemical resistance, a wide temperature range, and a non-stick surface. Because PTFE is virtually inert, it can handle aggressive chemicals and solvents without degrading, making it ideal for corrosive environments.
The Inner Core: The Source of Mechanical Strength
Inside the PTFE envelope lies an insert or core material. This is the structural backbone of the gasket.
The core provides the mechanical properties—such as pressure resistance, compressibility, and elastic recovery—that PTFE alone cannot offer. Common insert materials include elastomers, compressed non-asbestos fiber (CNAF), or graphite, with the selection depending entirely on the application's demands.
Why This Composite Design Matters
The dual-material construction is not an accident; it is a targeted solution for specific industrial challenges where a single material would fail.
Superior Sealing in Demanding Environments
This design creates a robust and reliable seal capable of withstanding fluctuating temperatures and harsh media. The PTFE handles the chemical attack, while the core maintains the compressive load needed to prevent leaks, exhibiting minimal creep relaxation over its lifespan.
Preventing Product Contamination
The non-stick, chemically inert surface of the PTFE envelope is critical in industries like pharmaceuticals and food processing. It ensures that the gasket material does not leach into or adhere to the product, simplifying cleaning and maintaining purity.
Protecting Sensitive Flanges
PTFE envelope gaskets are often the preferred choice for sealing fragile or sensitive flange types. They are particularly effective on enamel, plastic, or rubber-lined steel flanges, where a hard or aggressive gasket material could cause damage.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Choosing the Right Insert
The primary decision point when specifying a PTFE envelope gasket is the selection of the core material. This choice is not arbitrary and directly impacts the gasket's performance limits.
The Critical Role of Application Pressure
The insert material is chosen almost exclusively based on the required pressure resistance. An elastomer core might be suitable for low-pressure applications requiring good compressibility, while a compressed fiber or graphite core would be specified for higher-pressure duties.
Matching Core to Media and Temperature
While the PTFE envelope protects the core from direct chemical contact, the insert must still be able to withstand the system's operating temperature. The choice of insert dictates the gasket's overall temperature and pressure rating, creating a performance envelope that must match the application's needs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To select the correct gasket, you must evaluate both the chemical environment and the mechanical demands of the joint.
- If your primary focus is aggressive chemical resistance: The PTFE envelope provides the necessary protection, making this gasket type a superior choice over standard elastomeric or fiber gaskets.
- If your primary focus is high-pressure sealing: Your decision must center on specifying the correct insert material, as this component provides the gasket's mechanical integrity.
- If your primary focus is protecting fragile flanges: The soft, conformable nature of the PTFE envelope makes it an ideal solution for preventing damage to enamel or plastic surfaces.
Ultimately, understanding this gasket's composite nature is the key to deploying it effectively in your specific application.
Summary Table:
| Component | Material | Primary Function |
|---|---|---|
| Outer Envelope | Pure PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) | Chemical resistance, wide temperature range, non-stick surface |
| Inner Core | Elastomer, CNAF, or Graphite | Mechanical strength, pressure resistance, compressibility |
Need a reliable, chemically inert seal for a demanding application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components, including custom envelope gaskets. Our expertise ensures you get a seal perfectly matched to your specific pressure, temperature, and chemical requirements, whether for semiconductor, medical, laboratory, or industrial use.
We prioritize precision production and offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Contact KINTEL today to discuss your sealing challenge and get a solution that delivers superior performance and reliability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- What is PTFE commonly known as and what are its unique properties? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Demanding Applications
- What are some common applications of machined PTFE? Leverage its Unique Properties for Demanding Applications
- What are the primary applications of PTFE fasteners and custom parts? Critical Solutions for Extreme Environments



















