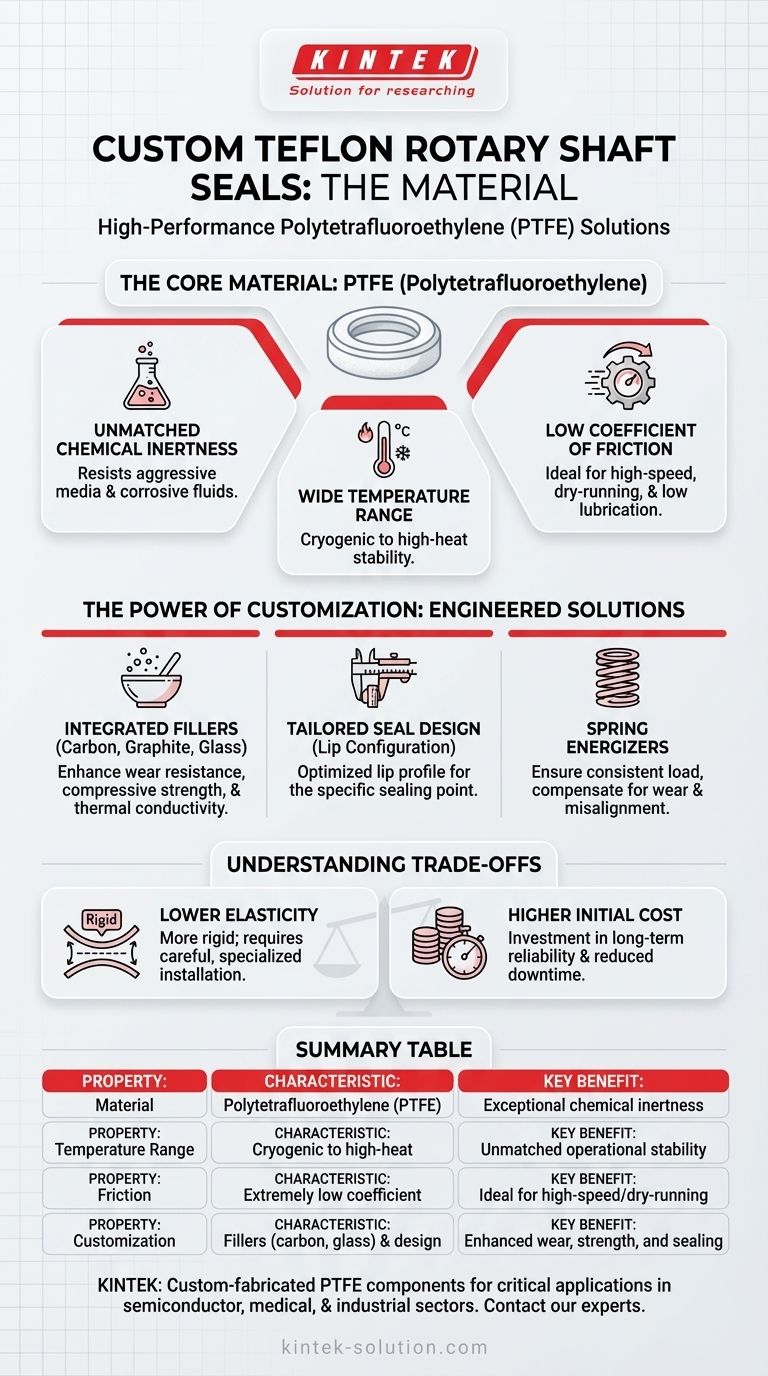
At their core, custom Teflon rotary shaft seals are made from a high-performance fluoropolymer called Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE). This material, widely known by the brand name Teflon, is chosen for its exceptional chemical resistance, ability to withstand extreme temperatures, and an extremely low coefficient of friction.
The essential takeaway is not just the base material (PTFE), but the ability to precisely customize its composition with fillers and its physical design to solve demanding sealing challenges where standard seals would fail.

Why PTFE is the Material of Choice
The fundamental properties of PTFE make it the ideal foundation for seals used in critical applications across the aerospace, automotive, and chemical processing industries.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
PTFE is virtually inert and does not react with the vast majority of industrial chemicals and corrosive media. This makes it a reliable choice for sealing aggressive fluids that would degrade traditional elastomer seals.
Wide Temperature Range
These seals maintain their integrity and performance across an exceptionally broad temperature spectrum. They can operate effectively in both cryogenic conditions and high-heat environments where other materials become brittle or break down.
Low Coefficient of Friction
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material. This "slipperiness" is critical for high-speed rotary applications, as it minimizes heat generation, reduces torque requirements, and allows for effective sealing even with poor lubrication or in dry-running conditions.
The Power of Customization: Beyond Base PTFE
The term "custom" is key. A manufacturer doesn't just use pure PTFE; they engineer a complete sealing solution tailored to a specific operational environment.
Integrating Fillers for Enhanced Properties
While pure PTFE is excellent, its mechanical properties can be significantly enhanced. Fillers like carbon, graphite, or glass fibers can be blended into the PTFE to improve wear resistance, increase compressive strength, and enhance thermal conductivity.
Tailoring the Seal Design
The physical shape of the seal is engineered for the application. This includes customizing the lip configuration to optimize the sealing point against the shaft, ensuring a perfect balance between sealing effectiveness and minimal friction.
Integrating Spring Energizers
Many custom PTFE seals incorporate a metal spring energizer. This spring provides a consistent, resilient load on the seal lips, ensuring reliable sealing at low pressures, compensating for wear over time, and accommodating minor shaft misalignments.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While PTFE seals offer superior performance in many areas, it's important to understand their specific characteristics.
Lower Elasticity
Compared to rubber (elastomer) seals, PTFE is a much more rigid material. It has less elasticity, which means installation requires more care to avoid damaging the seal lip. Specialized installation tools are often recommended.
Cost Considerations
Due to the advanced material and custom engineering involved, PTFE seals typically have a higher initial cost than standard off-the-shelf elastomer seals. However, this cost is often justified by improved reliability, reduced downtime, and a longer service life in challenging applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting a custom PTFE seal is about matching its unique capabilities to your most critical operational demands.
- If your primary focus is sealing in corrosive chemical environments: A custom PTFE seal is the definitive choice due to its superior chemical inertness.
- If your primary focus is reliability in extreme temperatures: PTFE's exceptionally wide operating range makes it far more durable than traditional elastomers.
- If your primary focus is managing high-speed or poorly lubricated shafts: The low-friction nature of PTFE minimizes wear and heat, extending the life of both the seal and the shaft.
Ultimately, choosing a custom PTFE seal is an investment in operational reliability for your most critical equipment.
Summary Table:
| Property | PTFE Seal Characteristic | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) | Exceptional chemical inertness |
| Temperature Range | Cryogenic to high-heat | Unmatched operational stability |
| Friction | Extremely low coefficient | Ideal for high-speed/dry-running |
| Customization | Fillers (carbon, glass) & design | Enhanced wear, strength, and sealing |
Facing a sealing challenge that standard seals can't handle? KINTEK specializes in custom-fabricated PTFE components, including precision rotary shaft seals for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We engineer solutions from prototype to high-volume production to deliver the reliability your critical equipment demands. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application requirements.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support



















