The fundamental reason PTFE extruded rods are exceptionally suitable for bearings and bushings is their uniquely low coefficient of friction, which is the lowest of any known solid material. This creates a self-lubricating surface that drastically reduces wear, requires no external lubrication, and ensures smooth, quiet operation even under demanding chemical and thermal conditions.
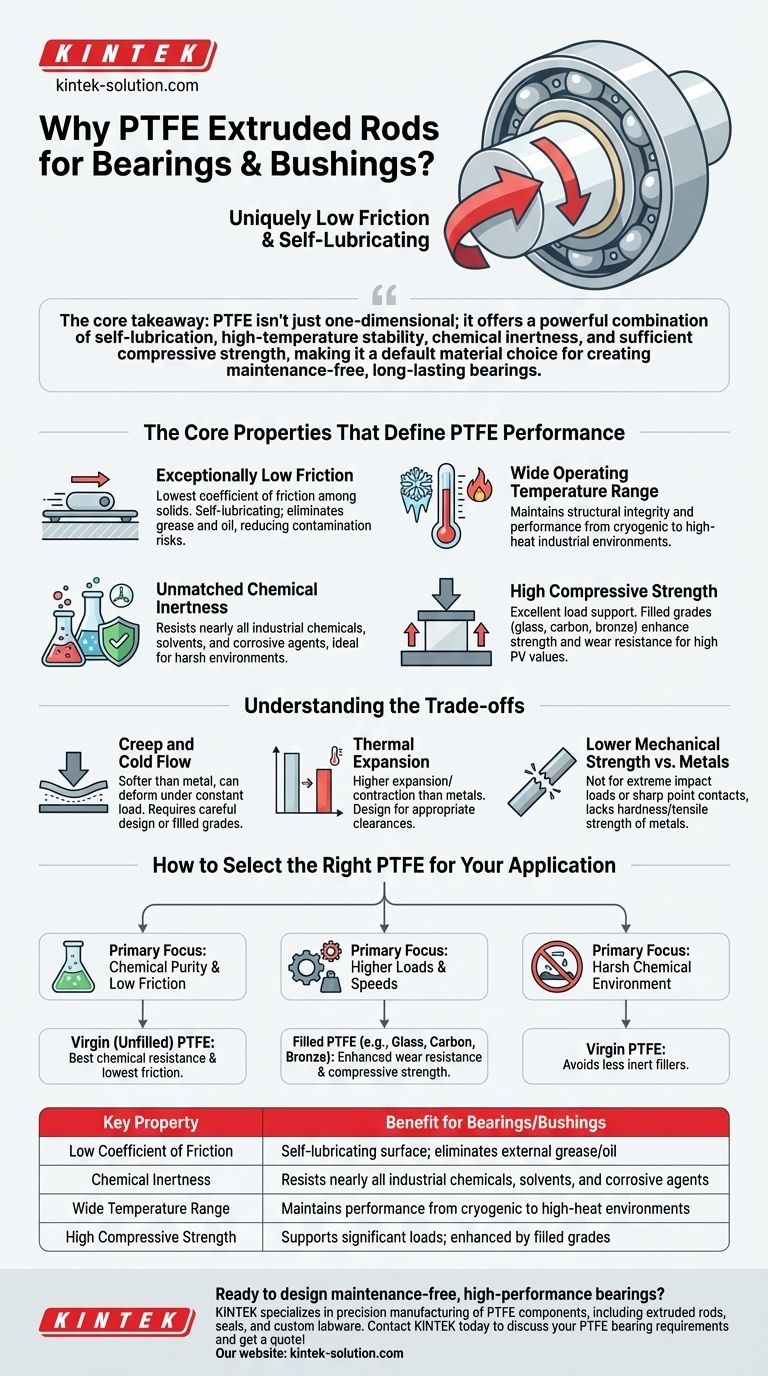
The core takeaway is that PTFE isn't just one-dimensional; it offers a powerful combination of self-lubrication, high-temperature stability, chemical inertness, and sufficient compressive strength, making it a default material choice for creating maintenance-free, long-lasting bearings.
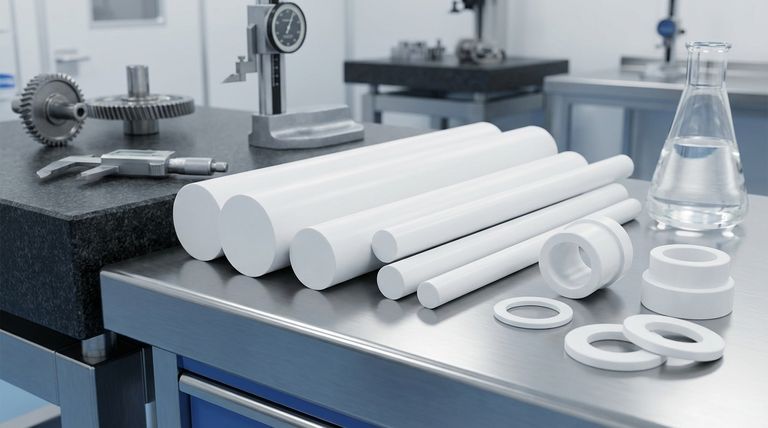

The Core Properties That Define PTFE Performance
To understand why PTFE excels, we must look at its key material characteristics. These properties work in concert to create a superior bearing surface.
Exceptionally Low Friction
PTFE’s most famous attribute is its incredibly low coefficient of friction. This means surfaces slide against it with minimal resistance.
This property is inherent to the material itself, allowing it to function as a self-lubricating surface. This eliminates the need for grease or oil, which can attract contaminants, degrade over time, or fail in extreme temperatures.
Wide Operating Temperature Range
Bearings and bushings often operate in environments with significant heat generation. PTFE maintains its structural integrity and low-friction properties across a vast temperature range.
This ensures consistent, reliable performance whether the application is in a cryogenic environment or a high-heat industrial machine.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
PTFE is famously resistant to nearly all industrial chemicals, solvents, and corrosive agents.
This makes it the ideal choice for bearings used in chemical processing, food and beverage, or any environment where exposure to moisture or harsh substances would cause a traditional metal bearing to fail.
High Compressive Strength
A bearing must support a load without being crushed. PTFE possesses excellent compressive strength, capable of absorbing significant pressure.
For applications involving very high loads and speeds (high PV values), filled PTFE grades—which include additives like glass, carbon, or bronze—are used to enhance compressive strength and wear resistance even further.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While PTFE is an exceptional material, objectivity requires acknowledging its limitations. Understanding these trade-offs is crucial for proper application design.
Creep and Cold Flow
Compared to metals, PTFE is a softer material. Under a high, constant load, it can slowly deform over time in a phenomenon known as creep or "cold flow."
This must be accounted for in design, especially for applications with high static loads. Using filled grades can significantly mitigate this issue.
Thermal Expansion
PTFE has a higher coefficient of thermal expansion than metals. This means it expands and contracts more with temperature changes.
Engineers must design for appropriate clearances to prevent binding or failure when significant temperature swings are expected.
Lower Mechanical Strength vs. Metals
While strong enough for countless bearing applications, PTFE does not possess the hardness or tensile strength of steel or bronze. It is not suitable for applications involving extreme impact loads or sharp-point contacts.
How to Select the Right PTFE for Your Application
Choosing the correct material formulation is critical to success. Your decision should be guided by the specific demands of your operating environment.
- If your primary focus is chemical purity and low friction: Virgin (unfilled) PTFE is the ideal choice, offering the best chemical resistance and lowest coefficient of friction.
- If your primary focus is handling higher loads and speeds: A filled PTFE grade (e.g., glass, carbon, or bronze-filled) will provide the necessary wear resistance and compressive strength.
- If your primary focus is operating in a harsh chemical environment: Stick with virgin PTFE, as some fillers can be less inert than the PTFE matrix itself.
Ultimately, understanding these core properties allows you to specify a PTFE bearing that delivers reliable, silent, and maintenance-free performance for its intended application.
Summary Table:
| Key Property | Benefit for Bearings/Bushings |
|---|---|
| Low Coefficient of Friction | Self-lubricating surface; eliminates need for external grease/oil |
| Chemical Inertness | Resists nearly all industrial chemicals, solvents, and corrosive agents |
| Wide Temperature Range | Maintains performance from cryogenic to high-heat environments |
| High Compressive Strength | Supports significant loads; enhanced by filled grades (glass, carbon, bronze) |
Ready to design maintenance-free, high-performance bearings?
KINTEK specializes in precision manufacturing of PTFE components, including extruded rods, seals, and custom labware. Whether you need the ultimate chemical resistance of virgin PTFE or the enhanced strength of filled grades for high-load applications, we provide custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Our expertise ensures your bearings and bushings deliver reliable, silent operation in the most demanding semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial environments.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your PTFE bearing requirements and get a quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- How are PTFE extruded rods applied in the food processing industry? Enhancing Hygiene and Efficiency
- What are the machining advantages of PTFE rod? Achieve Cost-Effective, Complex Parts
- Can PTFE rods be machined into complex shapes? Yes, with precision engineering for custom parts.
- What industries commonly use PTFE extruded rods? Key Applications in High-Performance Sectors
- What are the mechanical applications of PTFE rods? Solve Friction and Corrosion Problems



















