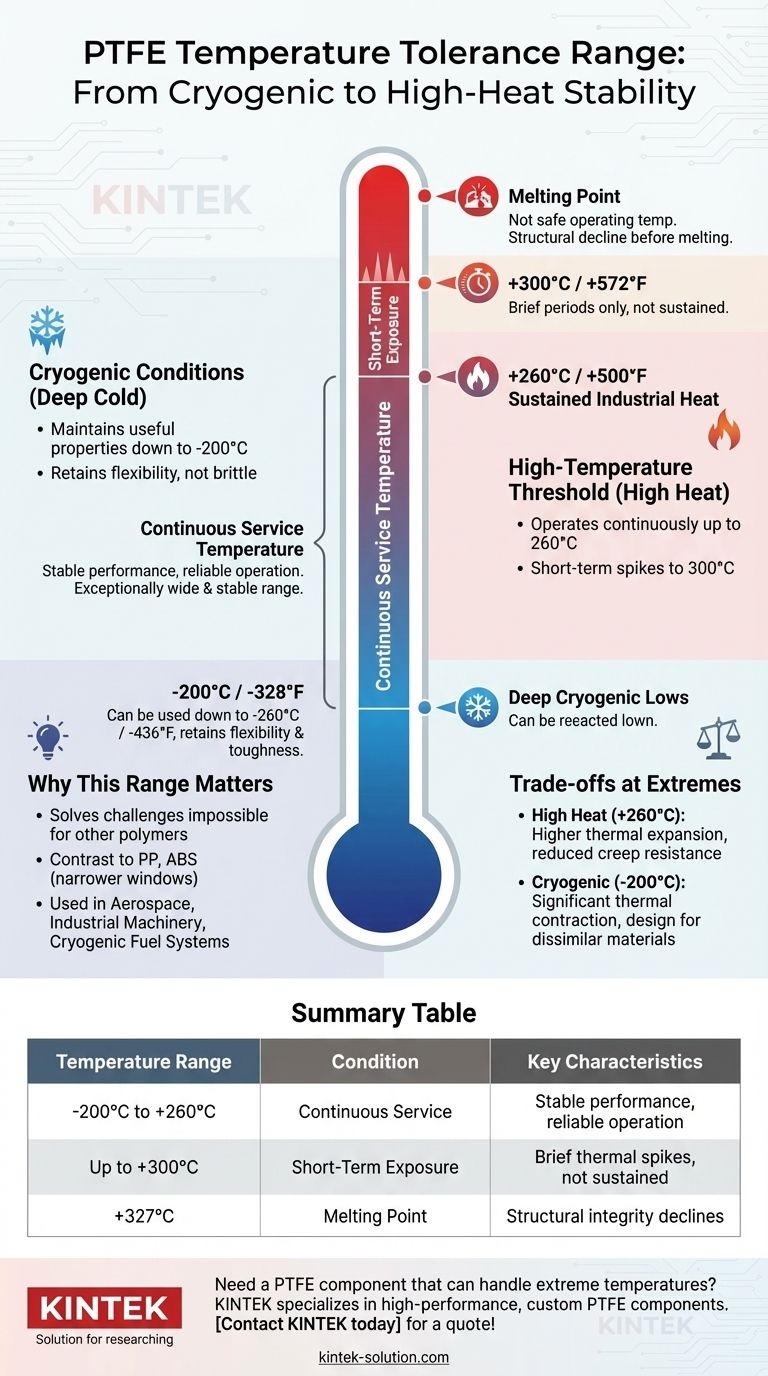
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) has an exceptionally wide and stable operating temperature range. Its thermal performance is one of its most defining characteristics, allowing it to function reliably in environments where most other polymers would fail. The generally accepted continuous service temperature for PTFE is from -200°C to +260°C (-328°F to +500°F).
PTFE's true value lies not just in its resistance to high heat, but in its consistent and reliable performance across an enormous spectrum, from deep cryogenic lows to sustained industrial heat, a level of thermal stability that few other materials can match.

Deconstructing PTFE's Thermal Limits
To apply PTFE correctly, it is crucial to understand the nuances of its performance at both ends of its temperature range and to distinguish its operating limits from its physical melting point.
The High-Temperature Threshold
PTFE can operate continuously at temperatures up to 260°C (500°F) without significant degradation. This makes it a premier choice for high-heat applications.
For brief periods, it can even withstand temperatures as high as 300°C (572°F). However, prolonged exposure above 260°C will begin to compromise its mechanical properties.
Understanding the Melting Point
The actual melting point of PTFE is approximately 327°C (621°F). It is critical to recognize that this is not a safe operating temperature.
Long before it melts, PTFE's structural integrity and key properties like tensile strength will decline as it approaches this threshold. The 260°C service limit provides a necessary safety margin.
Performance in Cryogenic Conditions
At the other extreme, PTFE maintains its useful properties in deep cold. It performs exceptionally well down to -200°C (-328°F).
Some data suggests it can be used in even colder environments, with certain sources citing a lower limit of -260°C (-436°F). Unlike many plastics that become extremely brittle at low temperatures, PTFE retains a degree of flexibility and toughness.
Why This Range Matters in Practice
The sheer breadth of PTFE's thermal tolerance allows it to solve engineering challenges that are impossible for most other common plastics and elastomers.
A Stark Contrast to Other Polymers
Materials like Polypropylene or ABS have much narrower operating windows and would fail catastrophically in the conditions where PTFE excels. This makes PTFE essential for applications demanding extreme thermal stability.
Enabling Critical Applications
This unique property profile is why PTFE is specified for demanding components in aerospace, high-pressure seals in industrial machinery, and parts used in cryogenic fuel systems. It ensures reliability whether the component is in a hot engine compartment or handling liquefied gases.
Understanding the Trade-offs at Temperature Extremes
While its performance is remarkable, designing for applications at the edge of PTFE's thermal range requires awareness of potential trade-offs.
The Impact of High Heat
As PTFE approaches its upper service limit of 260°C, it will experience a higher rate of thermal expansion and a reduction in its resistance to creep (deformation under load). These factors must be accounted for in precise mechanical designs.
Considerations for Cryogenic Use
Although PTFE remains ductile in the cold, its coefficient of thermal contraction is significant. When designing assemblies with dissimilar materials, this contraction must be calculated to avoid stress and sealing failures.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Use these guidelines to determine if PTFE's thermal profile aligns with your project's specific requirements.
- If your primary focus is sustained high-heat industrial processes: Rely on the continuous operating limit of 260°C (500°F) for long-term reliability and performance.
- If your application involves short thermal spikes: You can design for brief excursions up to 300°C (572°F), but this should never be the sustained operating temperature.
- If your primary focus is cryogenic systems: PTFE is a premier choice for its impressive ductility and stability at temperatures down to -200°C (-328°F) and below.
Understanding these thermal boundaries allows you to leverage PTFE's remarkable stability for the most demanding engineering challenges.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Range | Condition | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| -200°C to +260°C | Continuous Service | Stable performance, reliable operation |
| Up to 300°C | Short-Term Exposure | Brief thermal spikes, not for sustained use |
| 327°C | Melting Point | Structural integrity declines before melting |
Need a PTFE component that can handle extreme temperatures?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-performance, custom PTFE components—from seals and liners to complex labware—that deliver unwavering reliability from deep cryogenic conditions to sustained high-heat environments.
Our precision production and custom fabrication services ensure your parts meet exact specifications, whether you need prototypes or high-volume orders for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, or industrial sectors.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your project's thermal requirements and get a quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Volumetric Flasks for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Use
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- In which industries is PTFE commonly used? Key Applications for Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- Why is chemical compatibility important when choosing a PTFE-coated septum? Avoid Sample Contamination and Data Loss
- What are the unique properties of PTFE that make it commercially valuable? Unlock Unmatched Performance
- What are some exceptional properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Extreme Environments
- What industrial applications does PTFE have? Unlock Performance in Extreme Environments



















