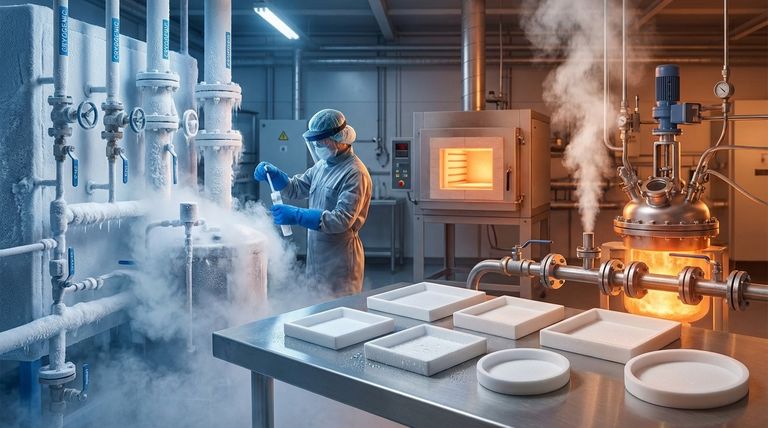
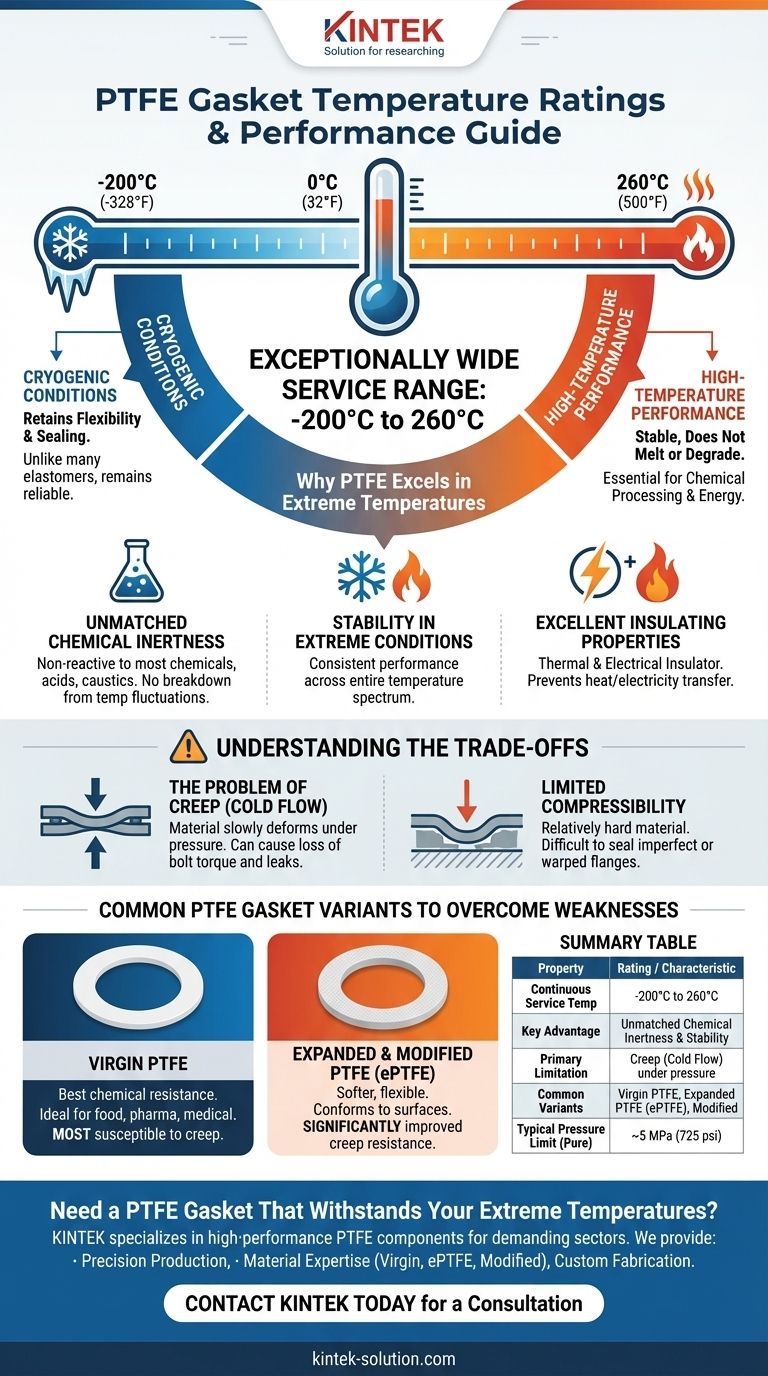
In short, PTFE gaskets have an exceptionally wide service temperature range. They are generally rated for continuous use in environments from -200°C (-328°F) to 260°C (500°F). This makes them a default choice for applications involving everything from cryogenic fluids to high-temperature chemical processing.
While PTFE's temperature range is its most famous attribute, the real challenge is understanding its mechanical limitations. The key to a successful seal is not just temperature, but managing the material's tendency to deform under pressure over time, a phenomenon known as creep.

Why PTFE Excels in Extreme Temperatures
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a fluoropolymer with unique properties that give it one of the widest temperature ranges of any sealing material. This performance stems directly from its molecular structure.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
PTFE is non-reactive and resistant to nearly all industrial chemicals, acids, and caustics. This inertness means that temperature fluctuations won't cause the gasket material to break down or react with the media it is sealing.
Stability in Cryogenic Conditions
At the low end of its range, down to -200°C (-328°F), PTFE retains its flexibility and sealing capability. Unlike many elastomers that become brittle and fail at low temperatures, PTFE remains a reliable sealing material.
High-Temperature Performance
At the upper limit of 260°C (500°F), PTFE remains stable and does not melt or degrade. This makes it essential for chemical processing, energy, and industrial sectors where high heat is a constant.
Excellent Insulating Properties
In its virgin (pure) form, PTFE is an excellent electrical and thermal insulator. This property adds value in applications where you need to prevent electrical conductivity or heat transfer across a flanged joint.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Despite its superb temperature and chemical resistance, pure PTFE is not a perfect sealing material. Its mechanical properties introduce critical trade-offs that must be managed for a reliable, long-term seal.
The Problem of Creep and Cold Flow
This is the most significant limitation of PTFE. Creep, or cold flow, is the tendency of the material to slowly deform and "flow" away from a compressed area over time. This can cause a loss of bolt torque, reducing sealing pressure and potentially leading to leaks.
Limited Compressibility
Pure PTFE is a relatively hard material with poor "memory" or elasticity. It does not compress easily, making it difficult to create a tight seal on flange surfaces that are warped, scratched, or otherwise imperfect.
Pressure Limitations
While the temperature range is wide, pure PTFE gaskets have modest pressure ratings, often around 5 MPa (725 psi). The combination of high temperature and high pressure can accelerate creep, making it a critical failure point to consider.
Common PTFE Gasket Variants
To overcome these mechanical weaknesses, several types of PTFE gaskets have been developed.
Virgin PTFE
This is pure, unfilled PTFE. It offers the best chemical resistance and is free from contaminants, making it ideal for the food, pharmaceutical, and medical industries. However, it is the most susceptible to creep.
Expanded & Modified PTFE
These materials (like ePTFE) have been processed to create a softer, more flexible structure. They conform much better to irregular surfaces and have significantly improved creep resistance, making them a better choice for demanding industrial applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct PTFE gasket requires balancing the need for temperature and chemical resistance with the mechanical demands of the joint.
- If your primary focus is chemical purity and moderate pressure: Virgin PTFE is an excellent choice, especially in food, pharmaceutical, or laboratory settings.
- If your primary focus is sealing imperfect flanges or high-pressure service: Choose an expanded or modified PTFE gasket for superior compressibility and creep resistance.
- If your primary focus is extreme temperature cycling: Proper bolt torque and re-torquing procedures are critical for any PTFE gasket to counteract the effects of material flow.
Ultimately, choosing the right PTFE variant ensures you can leverage its exceptional temperature range without compromising the mechanical integrity of your seal.
Summary Table:
| Property | Rating / Characteristic |
|---|---|
| Continuous Service Temperature | -200°C to 260°C (-328°F to 500°F) |
| Key Advantage | Unmatched chemical inertness & extreme temperature stability |
| Primary Limitation | Creep (cold flow) under sustained pressure |
| Common Variants | Virgin PTFE, Expanded PTFE (ePTFE), Modified PTFE |
| Typical Pressure Limit (Pure PTFE) | ~5 MPa (725 psi) |
Need a PTFE Gasket That Withstands Your Extreme Temperatures?
Leveraging PTFE's full potential requires expert knowledge of its properties and limitations. KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components—including seals, gaskets, liners, and custom labware—for the most demanding environments in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
We provide:
- Precision Production: Ensuring reliable performance from cryogenic to high-temperature processes.
- Material Expertise: Guidance on selecting the right PTFE variant (Virgin, ePTFE, Modified) to balance chemical resistance, temperature stability, and creep resistance for your specific application.
- Custom Fabrication: From prototypes to high-volume orders, we create solutions tailored to your exact requirements.
Don't let temperature extremes compromise your seal. Contact KINTEB today for a consultation and let our experts help you design the perfect sealing solution.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the key benefits of PTFE in custom fabrication? Unlock Performance in Extreme Conditions
- What are some common applications of machined PTFE? Leverage its Unique Properties for Demanding Applications
- What are the primary applications of PTFE fasteners and custom parts? Critical Solutions for Extreme Environments
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Demanding Applications
- What are the base characteristics of PTFE? Unlocking Extreme Performance in Friction, Temperature, and Chemical Resistance



















