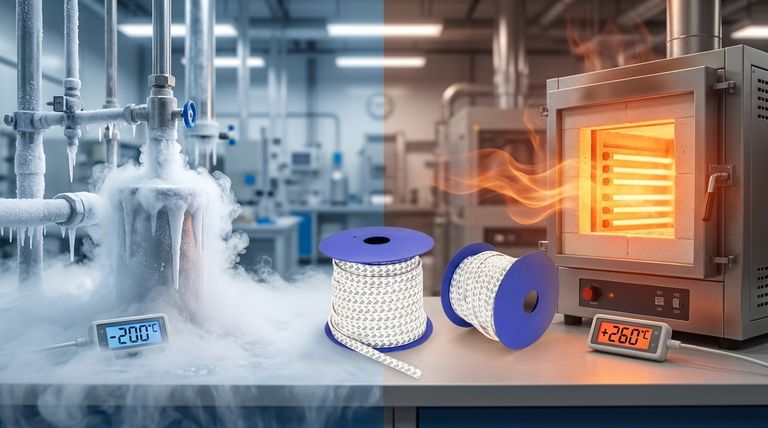
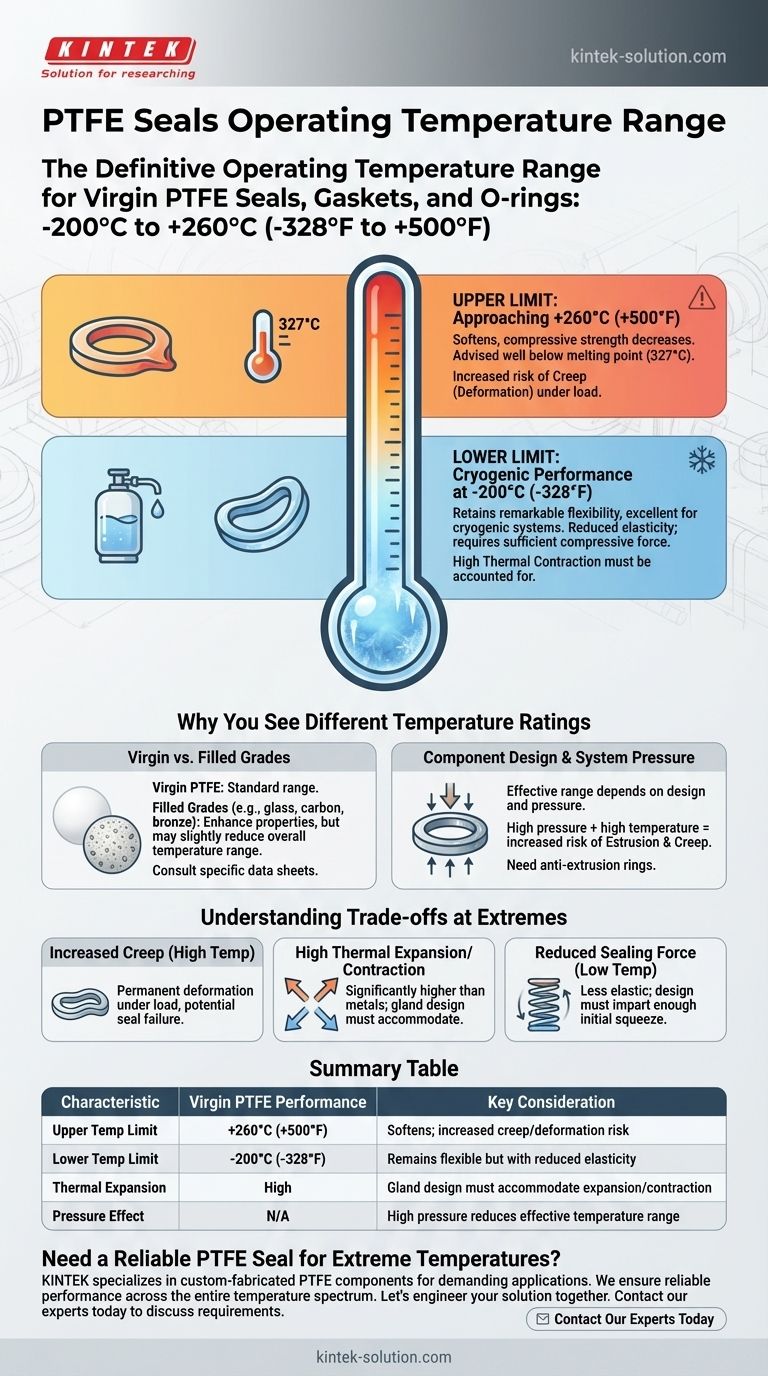
The definitive operating temperature range for seals, gaskets, and O-rings made from virgin Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is -200°C to +260°C (-328°F to +500°F). This exceptionally wide range makes PTFE a highly versatile material suitable for everything from cryogenic systems to high-heat industrial processes. While this is the standard range, the material's specific grade and the application's mechanical stresses will influence its practical performance limits.
Understanding PTFE's temperature range isn't just about memorizing the numbers. The core challenge is recognizing how the material's physical properties—like strength, flexibility, and expansion rate—change at these extremes, which directly impacts seal design and long-term reliability.

Deconstructing the Temperature Range
PTFE's performance is not uniform across its entire operating spectrum. Its behavior at the upper and lower limits is fundamentally different, and understanding these characteristics is critical for proper engineering design.
The Upper Limit: Approaching 260°C (500°F)
As PTFE approaches its maximum continuous service temperature, its mechanical properties begin to change. The material softens, and its compressive strength and wear resistance decrease.
It is critical to note that the operating limit of 260°C (500°F) is well below PTFE's actual melting point of approximately 327°C (621°F). Approaching the melting point is not advised, as the material will lose all structural integrity.
The Lower Limit: Cryogenic Performance at -200°C (-328°F)
Unlike most polymers that become extremely brittle at low temperatures, PTFE retains a remarkable degree of flexibility. This property makes it an excellent choice for sealing applications in cryogenic environments, such as those involving liquid nitrogen or other liquefied gases.
While it remains flexible, its elasticity is reduced. A successful cryogenic seal relies on a design that accounts for thermal contraction and ensures sufficient compressive force is maintained on the sealing surfaces.
Why You See Different Temperature Ratings
You may encounter slightly different temperature ratings for PTFE components across various datasheets. These discrepancies are not errors; they reflect the nuances of material composition and application-specific demands.
Virgin PTFE vs. Filled Grades
The standard -200°C to +260°C range applies to virgin PTFE. However, various fillers—such as glass fiber, carbon, or bronze—are often added to enhance specific properties like wear resistance, compressive strength, or thermal conductivity.
These fillers can sometimes slightly reduce the overall operating temperature range of the compound. Therefore, when using a filled PTFE, you must consult the manufacturer's specific data sheet for that grade.
Component Design and System Pressure
The stated temperature range is for the material itself. The effective operating range of a seal also depends on its design and the system pressure it must contain.
High pressure combined with high temperature creates the most demanding environment for a PTFE seal. This combination increases the risk of extrusion (the seal being forced into the clearance gap) and creep (permanent deformation under load).
Understanding the Trade-offs at Temperature Extremes
Simply staying within the temperature limits is not enough. A successful design must account for the material's inherent trade-offs, particularly at the far ends of its operating range.
Increased Creep and Deformation (High Temperatures)
PTFE is susceptible to a phenomenon known as creep or cold flow. At elevated temperatures, this tendency is magnified, and a seal under a constant load can slowly deform, potentially leading to a loss of sealing force and eventual failure.
High Thermal Expansion and Contraction
PTFE has a significantly higher coefficient of thermal expansion than most metals. This means it expands and contracts much more with temperature changes.
Hardware design must account for this. The gland or housing for the seal needs to have the correct dimensions to accommodate this expansion without over-compressing the seal or allowing it to become too loose.
Reduced Sealing Force (Low Temperatures)
At cryogenic temperatures, the material is less elastic. To maintain a reliable seal, the initial design must impart enough "squeeze" or compression to compensate for this reduced resiliency and for the thermal contraction of the material.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right material and design requires matching your primary goal to the properties of PTFE.
- If your primary focus is the widest possible temperature range: Virgin PTFE offers the best performance, particularly for cryogenic applications.
- If your primary focus is high wear resistance or load-bearing capacity: A filled grade of PTFE is likely superior, but you must verify its specific temperature rating, as it may be slightly narrower than that of virgin PTFE.
- If your primary focus is a high-pressure, high-temperature environment: You must carefully consider creep and extrusion, potentially using a filled PTFE grade and incorporating anti-extrusion (backup) rings into your design.
Ultimately, successful sealing with PTFE depends on a holistic understanding of how temperature influences the material's behavior within your specific system.
Summary Table:
| Characteristic | Virgin PTFE Performance | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Upper Temp Limit | +260°C (+500°F) | Softens; increased creep/deformation risk |
| Lower Temp Limit | -200°C (-328°F) | Remains flexible but with reduced elasticity |
| Thermal Expansion | High | Gland design must accommodate expansion/contraction |
| Pressure Effect | N/A | High pressure reduces effective temperature range |
Need a Reliable PTFE Seal for Extreme Temperatures?
PTFE's performance is highly dependent on precise manufacturing and design. KINTEK specializes in custom-fabricated PTFE components—including seals, gaskets, liners, and labware—for the most demanding applications in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
We ensure your components perform reliably across the entire temperature spectrum, from cryogenic systems to high-heat processes.
Let's engineer your solution together. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements, from prototype to high-volume production.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- How do FEP and PTFE encapsulated O-rings contribute to equipment longevity? Prevent Costly Downtime with Superior Seals
- What are the key properties of PTFE that make it suitable for sealing applications? | High-Performance Seals for Extreme Conditions
- What are the benefits of using PTFE seals? Unmatched Chemical & Temperature Resistance
- What are some common PTFE seal types used in industrial applications? Explore Solutions for Every Motion & Environment
- What are the key properties of PTFE that make it suitable for seals? Unlock Reliability in Extreme Conditions



















