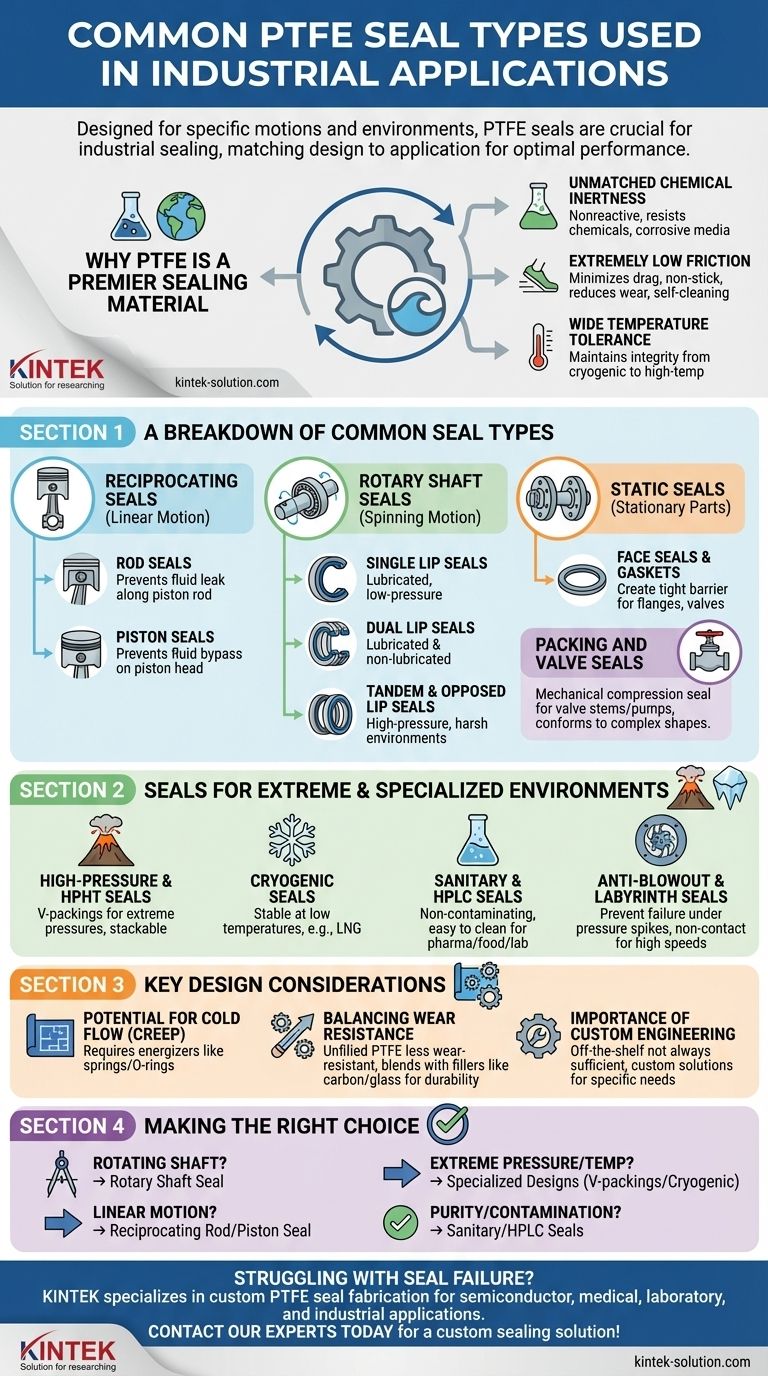
The most common PTFE seal types are designed around specific industrial motions and environments. These primarily include reciprocating seals for linear movement (rod and piston seals), rotary shaft seals for spinning components, and static seals like face seals and gaskets for stationary parts. Specialized versions also exist for extreme conditions such as high pressure (HPHT), cryogenic temperatures, and sanitary applications.
The core challenge in industrial sealing isn't just finding a durable material, but matching the seal's design to the specific application. While PTFE's properties make it a superior material, its effectiveness is entirely dependent on selecting the correct seal type for the motion, pressure, and environment it will face.
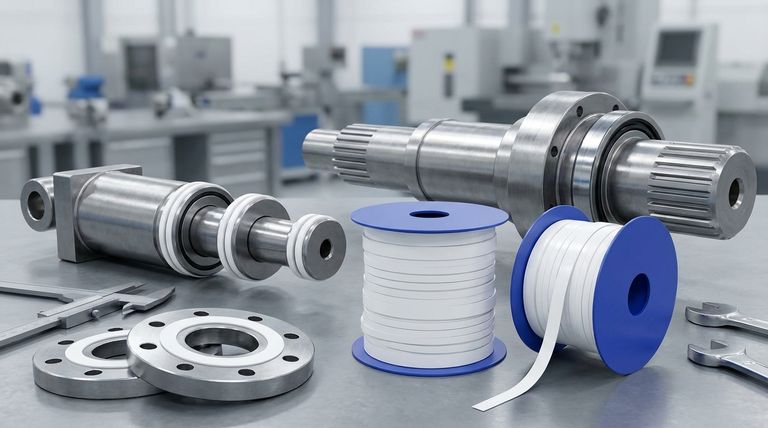

Why PTFE is a Premier Sealing Material
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a synthetic fluoropolymer prized for a unique combination of properties. These inherent characteristics make it an exceptionally versatile and reliable choice for the most demanding sealing applications across industries.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
PTFE is nonreactive and resistant to nearly all industrial chemicals and corrosive media. This makes it invaluable for sealing systems in chemical synthesis, pharmaceuticals, and processing plants where aggressive substances are common.
Extremely Low Friction
With one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid, PTFE minimizes drag and wear in dynamic applications. This non-stick property reduces energy consumption and prevents material buildup, contributing to longer component life and self-cleaning capabilities.
Wide Temperature Tolerance
PTFE maintains its integrity and sealing performance across a vast temperature range, from cryogenic lows to high-temperature highs. This stability makes it suitable for applications that experience significant thermal cycling.
A Breakdown of Common Seal Types
PTFE seals are not a one-size-fits-all solution. They are engineered to solve specific problems, which are best understood by categorizing them based on their intended motion and application.
Reciprocating Seals (Rod & Piston)
These seals are designed for dynamic, back-and-forth linear motion. Rod seals prevent fluid from leaking out of a cylinder along the piston rod, while piston seals prevent fluid from bypassing the piston head itself.
Rotary Shaft Seals
Used to seal rotating or spinning shafts, these are critical for protecting bearings and retaining lubricants. Common designs include:
- Single Lip Seals: Best for lubricated, low-pressure environments.
- Dual Lip Seals: Suitable for both lubricated and non-lubricated conditions.
- Tandem & Opposed Lip Seals: Engineered for high-pressure or harsh environments, providing more robust sealing action.
Static Seals (Face Seals & Gaskets)
Unlike dynamic seals, static seals are used between two non-moving surfaces. PTFE gaskets and face seals create a tight barrier in applications like pipe flanges, valve bodies, and equipment housings, leveraging PTFE's chemical resistance and flexibility.
Packing and Valve Seals
PTFE packing is a form of mechanical compression seal often used to seal valve stems and pumps. Its malleability allows it to conform to complex shapes, providing a reliable seal in equipment handling corrosive or high-purity media.
Seals for Extreme and Specialized Environments
Beyond standard applications, specialized PTFE seals are engineered to perform under the most severe operating conditions.
High-Pressure & HPHT Seals
For High-Pressure/High-Temperature (HPHT) environments, designs like V-packings are used. These are chevron-shaped seals that can be stacked to handle extreme pressures that would destroy a standard single seal.
Cryogenic Seals
The inherent stability of PTFE at very low temperatures makes it a primary choice for sealing valves and fittings in cryogenic applications, such as those involving liquefied natural gas (LNG).
Sanitary and HPLC Seals
In pharmaceutical, food processing, and laboratory settings (like HPLC chromatography), seals must be non-contaminating. Sanitary PTFE seals are designed to prevent product contamination and are easy to clean.
Anti-Blowout and Labyrinth Seals
Anti-blowout seals are a critical safety feature designed to prevent catastrophic failure under sudden pressure spikes. Labyrinth seals are non-contacting seals that use a complex path to prevent leakage, often used in high-speed rotary applications where friction is unacceptable.
Key Design Considerations
While PTFE offers significant advantages, its physical properties introduce important design considerations that must be addressed to ensure long-term reliability.
Potential for Cold Flow (Creep)
PTFE can slowly deform or "creep" over time when subjected to a constant compressive load. Seal design must account for this by incorporating energizers (like springs or O-rings) that maintain a constant sealing force even if the PTFE element deforms slightly.
Balancing Wear Resistance
Unfilled PTFE has lower wear resistance compared to harder materials. For high-wear dynamic applications, PTFE is often blended with fillers (like carbon, glass, or bronze) to improve durability, a key factor in creating custom-engineered seals.
Importance of Custom Engineering
The wide variety of seal types highlights a crucial point: off-the-shelf solutions are not always sufficient. Many demanding applications require custom or engineered seals where the geometry and material composition are tailored to specific pressure, temperature, and media requirements.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct seal involves a clear understanding of your primary operational challenge.
- If your primary focus is sealing a rotating shaft: Your choice will be a rotary shaft seal, with the lip configuration (single, dual, tandem) dictated by pressure and lubrication.
- If your primary focus is sealing linear motion: You require a reciprocating rod or piston seal designed to handle dynamic back-and-forth movement.
- If your primary focus is extreme pressure or temperature: Look to specialized designs like V-packings for high pressure or cryogenic-grade seals for extreme cold.
- If your primary focus is purity and preventing contamination: Your best options are sanitary seals or those specifically designed for applications like HPLC.
Ultimately, matching the seal's engineering to the demands of the application is the key to leveraging PTFE's remarkable properties and achieving a reliable, long-lasting solution.
Summary Table:
| Seal Type | Primary Application | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Reciprocating Seals | Linear back-and-forth motion (cylinders) | Handles dynamic movement, low friction |
| Rotary Shaft Seals | Spinning or rotating shafts | Retains lubricants, protects bearings |
| Static Seals (Gaskets) | Stationary surfaces (flanges, housings) | Excellent chemical resistance, creates tight barrier |
| High-Pressure (HPHT) Seals | Extreme pressure environments | Stackable design (e.g., V-packings) for reliability |
| Sanitary Seals | Pharmaceutical, food, lab (HPLC) | Non-contaminating, easy to clean |
Struggling with seal failure in extreme conditions? KINTEK specializes in custom PTFE seal fabrication for semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial applications. We engineer seals to handle high pressure, extreme temperatures, and corrosive media, ensuring long-lasting performance and reliability. From prototypes to high-volume orders, our precision manufacturing delivers the exact solution you need. Contact our experts today for a custom sealing solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are some unique features of expanded PTFE gaskets? Superior Conformability & Creep Resistance
- What are some innovative applications of CNC machined PTFE in product design? Unlock Extreme Performance in Medical, Aerospace & Electronics
- What are PTFE envelope gaskets? The Ultimate Sealing Solution for Corrosive Environments
- What is Expanded PTFE joint sealant used for? Seal Imperfect Flanges in Extreme Conditions
- How often should PTFE butterfly valves be maintained? Optimize Your Maintenance Schedule
- What are the common applications of PTFE in industrial components? Seals, Bearings & More
- What design considerations are important for PTFE lip seals in extreme temperatures? | Material, Geometry & Energizer
- How do custom Teflon rotary shaft seals contribute to operational efficiency? Maximize Reliability & Cut Costs



















