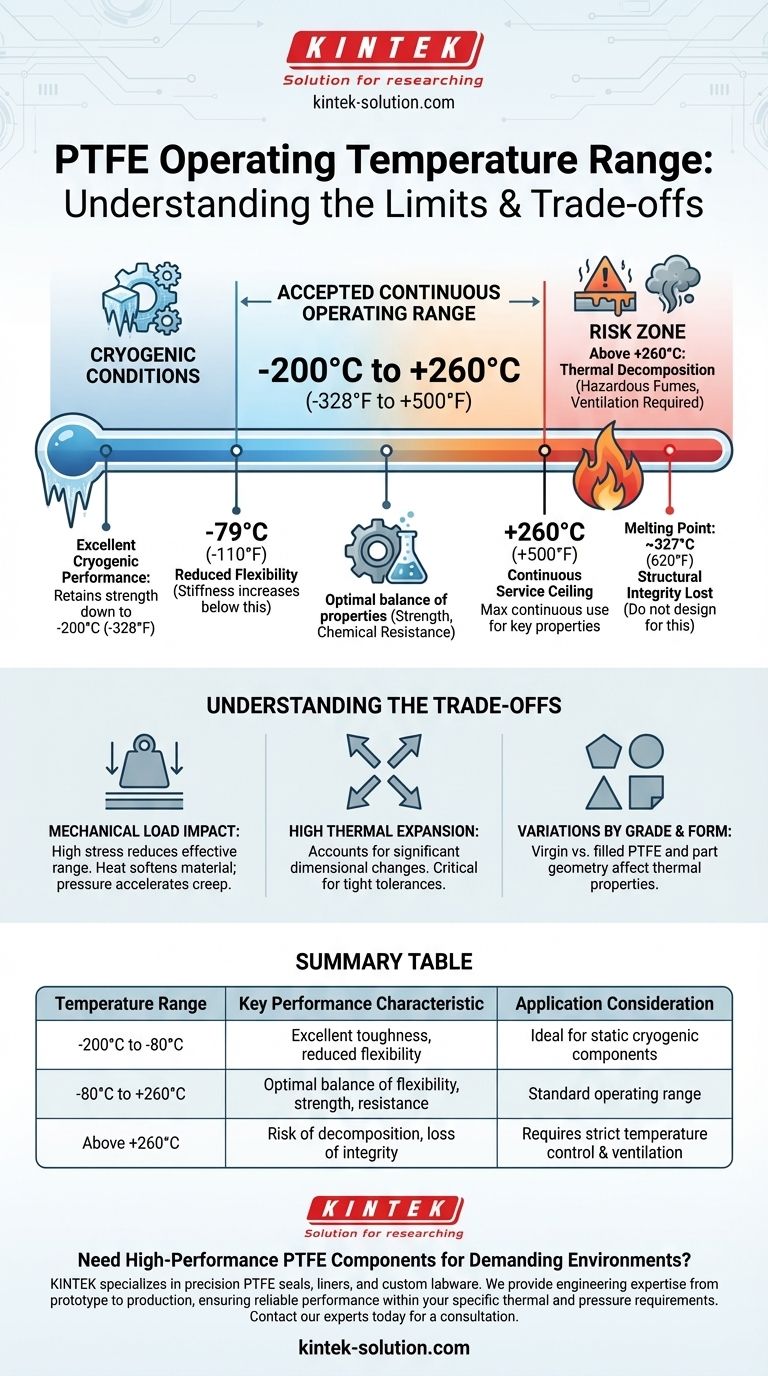
In short, the accepted continuous operating temperature range for PTFE is from approximately -200°C to +260°C (-328°F to +500°F). While this range is exceptionally wide, the material's mechanical properties change significantly at these extremes, and the precise limits depend heavily on the application's specific pressures and stresses.
The core challenge is not just knowing PTFE's temperature range, but understanding how its performance—particularly its strength and flexibility—degrades as it approaches the upper and lower limits of that range.

Understanding the High-Temperature Limit
The upper temperature limit is where most engineers focus, as exceeding it can lead to irreversible failure. The distinction between continuous service temperature and the material's actual melting point is critical.
The Continuous Service Ceiling
For most applications, +260°C (500°F) is the maximum temperature at which PTFE can operate continuously without significant degradation of its key properties, such as its chemical resistance and low friction.
Approaching the Melting Point
PTFE’s actual melting point is much higher, around 327°C (620°F). However, long before it reaches this temperature, the material loses its structural integrity and load-bearing capabilities. Relying on the melting point for design is a critical mistake.
The Risk of Thermal Decomposition
As temperatures begin to significantly exceed the 260°C service limit, PTFE will begin to decompose. This process, known as pyrolysis, can release hazardous fumes, making proper ventilation and temperature control an essential safety consideration in high-heat applications.
Navigating the Low-Temperature Spectrum
PTFE is renowned for its performance in cryogenic conditions, but its behavior changes as temperatures drop. It doesn't become brittle in the same way many other plastics do, but its flexibility is reduced.
Excellent Cryogenic Performance
PTFE maintains high strength and toughness at extremely low temperatures, even down to -200°C (-328°F). Some data shows it retains useful properties as low as 5°K (-268°C), making it a suitable choice for cryogenic and space applications.
The Point of Reduced Flexibility
While it remains tough, PTFE's flexibility diminishes at very low temperatures. It exhibits good flexibility down to around -79°C (-110°F). Below this, it becomes increasingly stiff. This is a crucial factor for dynamic applications like seals that must flex, but less of a concern for static components.
Understanding the Trade-offs
A material's datasheet temperature range is a guideline, not a guarantee. Real-world conditions dictate the true performance limits.
The Impact of Mechanical Load
The effective temperature range of PTFE shrinks significantly under high mechanical stress. A PTFE seal under high pressure will fail at a lower temperature than an unloaded component because the heat softens the material and makes it more susceptible to creep and deformation.
High Thermal Expansion
PTFE has a high coefficient of thermal expansion compared to metals. In designs with tight tolerances, engineers must account for how much a PTFE part will expand or contract with temperature changes to avoid component failure or seizure.
Variations by Grade and Form
The stated temperature range is for pure, or "virgin," PTFE. Different grades (e.g., filled with glass or carbon) can have slightly different thermal properties. Similarly, the form factor matters; a thin liner may perform differently than a thick, structural O-ring, which might have a more conservative temperature rating.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To apply this information effectively, match the material's properties to the specific demands of your operating environment.
- If your primary focus is high-heat industrial processes: Use 260°C (500°F) as a firm upper limit for continuous service and always factor in the mechanical loads involved.
- If your primary focus is cryogenic sealing: PTFE is an excellent choice, but ensure your design can tolerate reduced flexibility for any dynamic components operating below -80°C.
- If your primary focus is an application with wide temperature swings: Account for thermal expansion in your design to maintain proper clearances and prevent stress-related failures.
Ultimately, selecting the right material requires looking beyond a single number and considering the entire engineering system.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Range | Key Performance Characteristic | Application Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| -200°C to -80°C (-328°F to -110°F) | Excellent toughness, but flexibility decreases. | Ideal for static cryogenic components. |
| -80°C to +260°C (-110°F to +500°F) | Optimal balance of flexibility, strength, and chemical resistance. | Standard operating range for most applications. |
| Above +260°C (Above +500°F) | Risk of decomposition and loss of mechanical integrity. | Requires strict temperature control and ventilation. |
Need High-Performance PTFE Components for Demanding Environments?
Understanding the precise thermal limits of PTFE is critical for the success and safety of your project. At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
We go beyond just supplying parts; we provide engineering expertise to ensure your PTFE solution performs reliably within its specific temperature and pressure requirements, from prototypes to high-volume production.
Let's engineer a solution for your unique challenges. Contact our experts today for a consultation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the base characteristics of PTFE? Unlocking Extreme Performance in Friction, Temperature, and Chemical Resistance
- What is PTFE commonly known as and what are its unique properties? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What are the primary applications of PTFE fasteners and custom parts? Critical Solutions for Extreme Environments
- What is the working temperature range of PTFE? Master Extreme Heat and Cryogenic Applications
- Why is PTFE suitable for cryogenic or high-temperature applications? Unmatched Thermal Stability from -450°F to 500°F



















