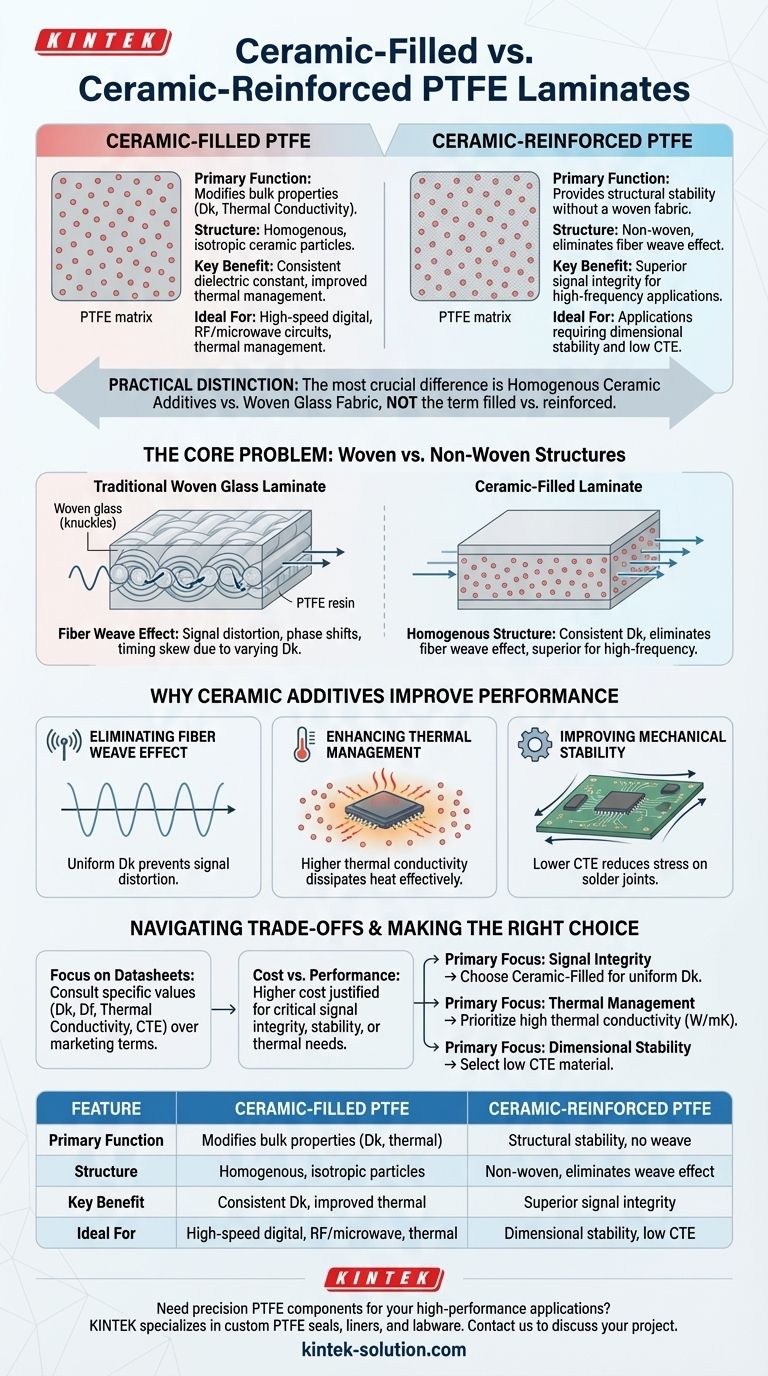
The fundamental difference between ceramic-reinforced and ceramic-filled PTFE laminates lies in the primary function of the ceramic component. A ceramic-filled laminate uses ceramic particles as an additive mixed into the PTFE to modify bulk properties like dielectric constant and thermal conductivity. The term ceramic-reinforced implies the ceramic provides structural integrity, but critically, it does so without the woven fabric structure found in traditional glass-reinforced materials.
In practice, the terms are often used interchangeably. The most important distinction for engineers is not "filled vs. reinforced," but the contrast between laminates with homogenous ceramic additives and those with woven glass fabric. Ceramic additives eliminate the signal integrity issues inherent in a woven structure.

The Core Problem: Woven vs. Non-Woven Structures
The primary reason to use ceramic additives in PTFE is to overcome the limitations of woven glass fabric, which has long been the standard for reinforcing circuit board laminates.
Defining Ceramic-Filled Laminates
A ceramic-filled laminate contains fine ceramic particles, like a powder, dispersed evenly throughout the Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) resin.
The goal is not primarily structural strength, but to precisely engineer the material's electrical and thermal characteristics. This creates a uniform, or isotropic, medium for signals to travel through.
Understanding the "Reinforcement" Ambiguity
The term ceramic-reinforced can be confusing. While ceramics do add rigidity and mechanical stability, their key advantage in this context is providing that stability without a weave.
This avoids the negative electrical effects of woven glass, making it a superior choice for high-frequency applications. The "reinforcement" is the improvement in mechanical and thermal stability over pure, unfilled PTFE.
Why Ceramic Additives Improve High-Frequency Performance
Moving from a woven glass structure to a homogenous ceramic-filled material solves several critical problems for high-speed digital and RF/microwave circuits.
Eliminating the Fiber Weave Effect
In a traditional laminate, the signal path alternates between traveling over glass fiber bundles ("knuckles") and the resin-filled gaps between them.
Glass and resin have different dielectric constants (Dk). This constant variation causes signal distortion, phase shifts, and timing skew, which is detrimental to high-frequency performance. Ceramic-filled materials have a consistent Dk throughout, eliminating this effect entirely.
Enhancing Thermal Management
PTFE on its own is a poor thermal conductor. High-power or high-density components can easily create hotspots.
Ceramic particles have significantly higher thermal conductivity. Dispersing them in the PTFE creates a pathway for heat to spread away from components, improving the reliability and performance of the entire system.
Improving Mechanical Stability
Ceramic fillers lower the material's Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (CTE). A lower CTE means the circuit board expands and contracts less during temperature changes.
This is crucial for the long-term reliability of solder joints and plated through-holes, especially in environments with significant temperature cycling.
Navigating the Practical Trade-offs
While ceramic-loaded PTFE offers superior electrical performance, it's essential to understand the complete picture.
Focus on Datasheets, Not Marketing Terms
As vendors often use "filled" and "reinforced" interchangeably, you cannot rely on the product name alone.
Always consult the material datasheet. Look for the specific values for dielectric constant (Dk), dissipation factor (Df), thermal conductivity, and CTE to determine if a material meets your design requirements.
Cost vs. Performance
High-performance, ceramic-filled laminates are typically more expensive than standard FR-4 or even basic glass-reinforced PTFE materials.
However, for applications where signal integrity, phase stability, or thermal management are critical, the added cost is often justified by the significant performance gains and improved reliability.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your specific design objective should guide your material selection.
- If your primary focus is signal integrity for high-frequency signals: Choose a ceramic-filled laminate to ensure a uniform dielectric constant and eliminate fiber weave effects.
- If your primary focus is thermal management for high-power components: Prioritize laminates with the highest thermal conductivity (W/mK) listed on their datasheet, which is a direct benefit of the ceramic filler.
- If your primary focus is dimensional stability across temperatures: Select a material with a low CTE, which reduces stress on vias and solder joints during thermal cycling.
Ultimately, your decision should be driven by the specific material properties documented on the datasheet, not by the ambiguous marketing distinction between "filled" and "reinforced."
Summary Table:
| Feature | Ceramic-Filled PTFE | Ceramic-Reinforced PTFE |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Modifies bulk properties (Dk, thermal conductivity) | Provides structural stability without a woven fabric |
| Structure | Homogenous, isotropic ceramic particles | Non-woven, eliminates fiber weave effect |
| Key Benefit | Consistent dielectric constant, improved thermal management | Superior signal integrity for high-frequency applications |
| Ideal For | High-speed digital, RF/microwave circuits, thermal management | Applications requiring dimensional stability and low CTE |
Need precision PTFE components for your high-performance applications? KINTEK specializes in manufacturing custom PTFE seals, liners, and labware for the semiconductor, medical, and industrial sectors. Our expertise in material science ensures your components meet exacting standards for signal integrity and thermal management. Contact us today to discuss your project requirements—from prototypes to high-volume production—and let us help you optimize your design with the right material solution.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the base characteristics of PTFE? Unlocking Extreme Performance in Friction, Temperature, and Chemical Resistance
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Demanding Applications
- What are some common applications of machined PTFE? Leverage its Unique Properties for Demanding Applications
- What are the material advantages of machining Teflon? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What is PTFE commonly known as and what are its unique properties? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance



















