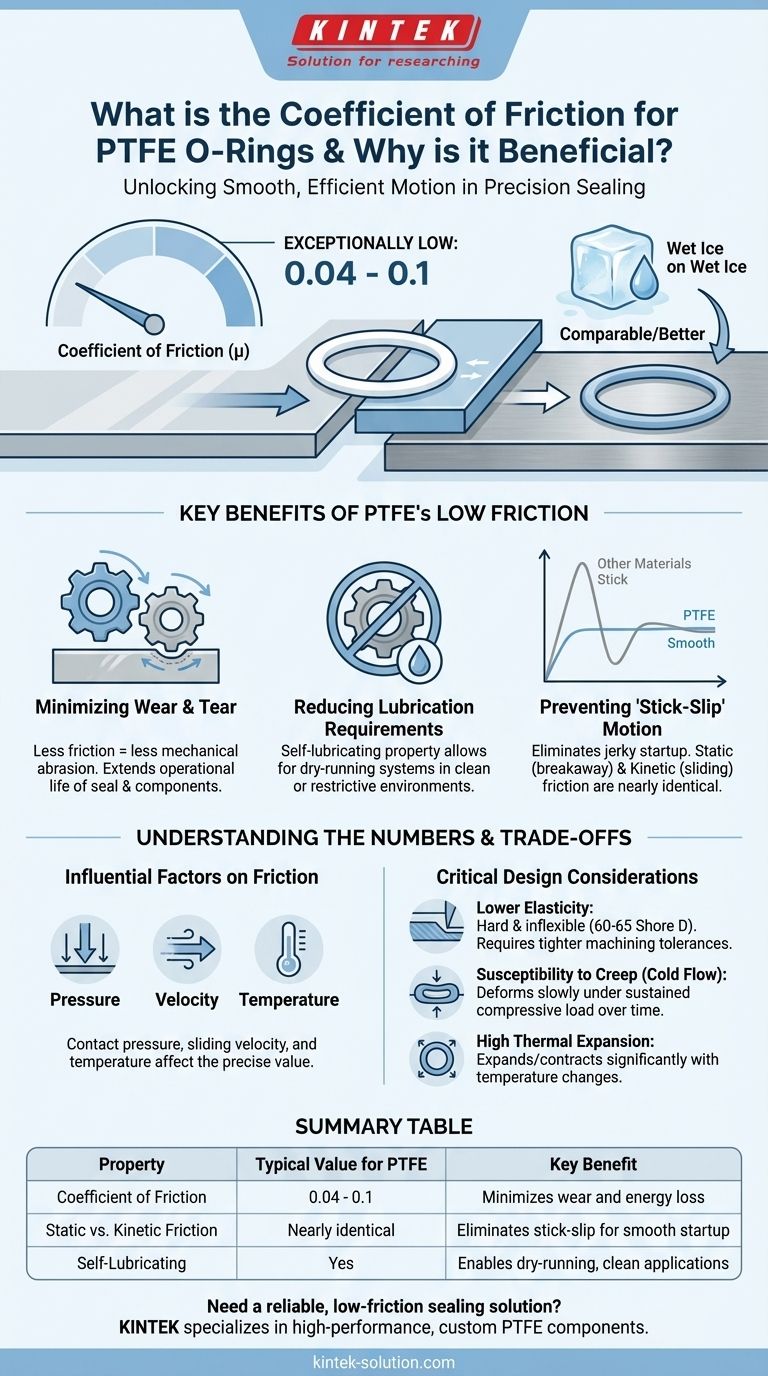
The coefficient of friction for PTFE O-Rings is exceptionally low, typically cited in the range of 0.04 to 0.1. This value is one of the lowest of any solid material, comparable to or even better than wet ice on wet ice. This inherent lubricity is the material's defining mechanical advantage, allowing it to significantly reduce operational resistance and wear between moving surfaces.
The core benefit of PTFE's low coefficient of friction is not just reduced wear, but its ability to deliver exceptionally smooth, predictable motion. Because its static (breakaway) friction is nearly identical to its kinetic (sliding) friction, it eliminates the "stick-slip" phenomenon that plagues many dynamic sealing applications.

What a Low Coefficient of Friction Means in Practice
The theoretical number for friction only matters because of its real-world impact on system performance, longevity, and design possibilities. PTFE's unique frictional properties create several distinct advantages.
Minimizing Wear and Tear
Less friction directly translates to less mechanical abrasion. In dynamic applications, where a seal is constantly moving against a housing, PTFE O-rings reduce the rate of wear on both the seal and the surrounding components, extending the operational life of the entire assembly.
Reducing Lubrication Requirements
PTFE is often described as self-lubricating. This property allows for the design of "dry-running" systems where traditional liquid or grease lubricants are impractical or undesirable, such as in food processing, medical devices, or cleanroom environments.
Preventing "Stick-Slip" Motion
This is perhaps the most critical advantage in precision applications. Many materials have a static coefficient of friction that is significantly higher than their kinetic coefficient. This difference causes a jerky, stuttering motion at low speeds as the seal repeatedly sticks and breaks free.
Because PTFE's static and kinetic friction values are nearly the same, it provides a smooth, fluid transition from a standstill to motion, ensuring high predictability and control.
Understanding the Numbers: Why Values Vary
You will see different values cited for PTFE's coefficient of friction because it is not a single, constant number. It is a system-dependent property that changes based on several key factors.
The Influence of Operating Conditions
The precise friction value is influenced by variables like contact pressure, sliding velocity, and temperature. Generally, higher pressures and lower speeds tend to result in a lower coefficient of friction for PTFE.
Static vs. Kinetic Friction
Static friction is the force required to initiate movement from a resting state. Kinetic friction is the resistance during continuous motion. For lubricated steel, the static value can be double the kinetic value (e.g., 0.1 vs. 0.05). For PTFE, both are cited as low as 0.04, highlighting its exceptionally smooth startup characteristics.
A Practical Range
For general engineering purposes, assuming a coefficient of friction between 0.04 and 0.1 is a safe and reliable starting point for design calculations.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While its low friction is a tremendous asset, PTFE is not a universal solution. Its mechanical properties introduce critical design considerations that must be respected.
Lower Elasticity
Compared to common elastomers like Nitrile (Buna-N) or Viton, PTFE is a relatively hard and inflexible material (typically 60-65 Shore D). It does not compress and rebound as effectively, requiring tighter machining tolerances on glands and mating surfaces to ensure a proper seal.
Susceptibility to Creep (Cold Flow)
Under sustained compressive load, PTFE can slowly deform over time, a phenomenon known as creep or cold flow. This can lead to a loss of sealing force in long-term static applications, particularly at elevated temperatures.
High Thermal Expansion
PTFE expands and contracts more significantly with temperature changes than most metals. The seal's housing (the gland) must be designed to accommodate this change to prevent O-ring failure or extrusion in systems with wide operating temperature ranges.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting a PTFE O-ring should be a deliberate decision based on the primary challenge you are trying to solve.
- If your primary focus is dynamic sealing with minimal wear: PTFE is an ideal candidate for high-speed or long-life applications where you need to minimize friction-induced material loss.
- If your primary focus is eliminating "stick-slip" and ensuring smooth startup: PTFE's near-identical static and kinetic friction provides the highly predictable, smooth motion required in precision control systems.
- If your primary focus is chemical compatibility or temperature range: While its friction is a bonus, you must design around PTFE's mechanical inflexibility and potential for creep to ensure a reliable seal.
By understanding both the unparalleled benefits and the inherent trade-offs of PTFE's low friction, you can design more reliable and efficient mechanical systems.
Summary Table:
| Property | Typical Value for PTFE | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Coefficient of Friction | 0.04 - 0.1 | Minimizes wear and energy loss |
| Static vs. Kinetic Friction | Nearly identical | Eliminates stick-slip for smooth startup |
| Self-Lubricating | Yes | Enables dry-running, clean applications |
Need a reliable, low-friction sealing solution? KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-performance, custom PTFE components like O-rings, seals, and liners. Our precision production ensures your designs benefit from PTFE's low friction while overcoming its mechanical challenges. We serve the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors with prototypes to high-volume orders. Contact our experts today to discuss how our PTFE components can enhance your application's efficiency and longevity.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs



















