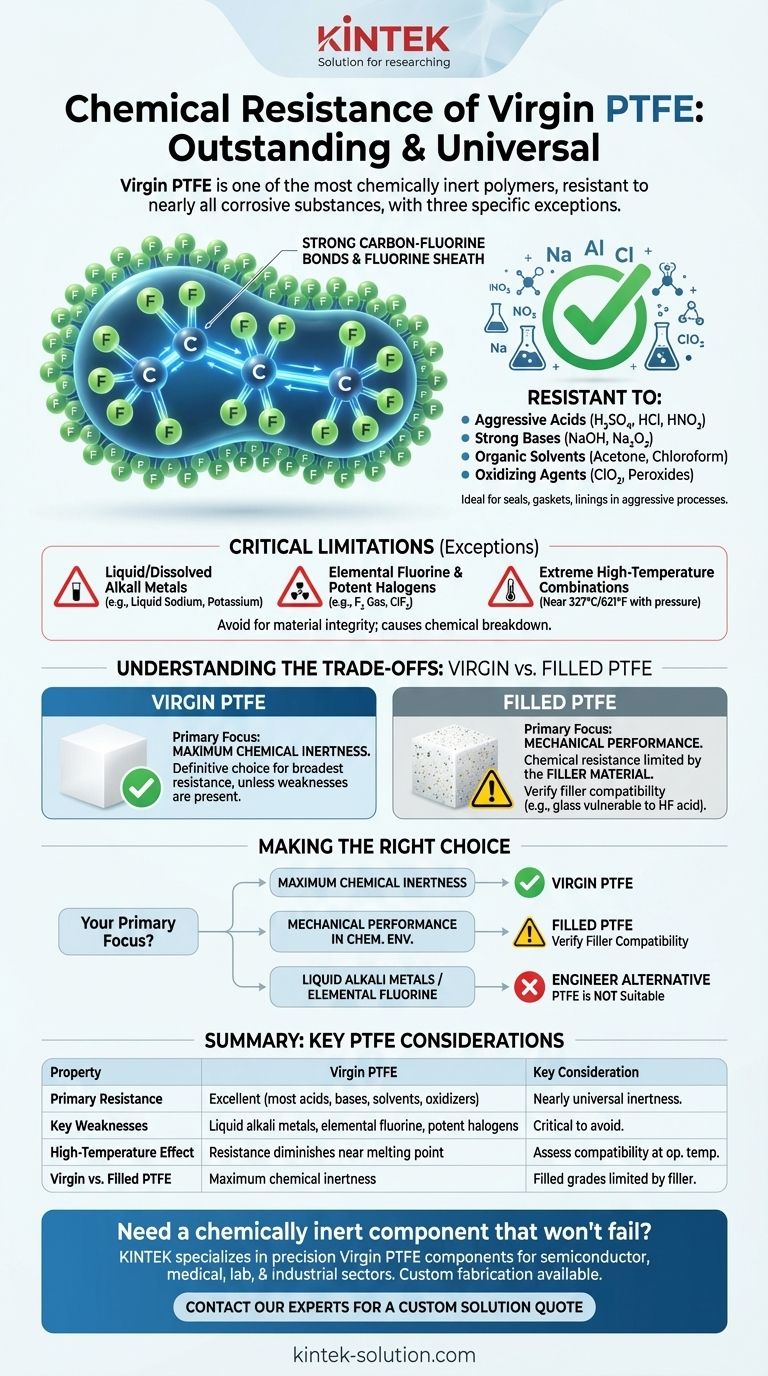
In short, the chemical resistance of Virgin PTFE is outstanding. It is one of the most chemically inert polymers known and is resistant to the vast majority of corrosive acids, bases, solvents, and aggressive chemicals. However, its near-universal resistance has three well-defined exceptions: liquid or dissolved alkali metals, elemental fluorine, and certain other extremely potent oxidizers.
The core reason for PTFE's exceptional performance is its stable molecular structure, built on powerful carbon-fluorine bonds. This makes it the default choice for highly aggressive environments, but its few, specific vulnerabilities must be respected to prevent material failure.

Why PTFE is So Chemically Resistant
The remarkable inertness of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is not an accident; it is a direct result of its unique molecular architecture. Understanding this foundation is key to using the material effectively.
The Power of the Carbon-Fluorine Bond
Virgin PTFE is a fluorocarbon, composed entirely of carbon and fluorine atoms. The bond between carbon and fluorine is exceptionally strong and stable.
This molecular backbone is shielded by a dense, continuous sheath of fluorine atoms. This sheath effectively protects the carbon chain from attack by outside chemical agents.
A Broad Spectrum of Inertness
Because of this structure, PTFE remains unaffected by a wide range of substances that degrade other materials.
This includes nearly all industrial chemicals, such as:
- Aggressive Acids: Sulfuric acid, hydrochloric acid, nitric acid
- Strong Bases: Sodium hydroxide, sodium peroxide
- Organic Solvents: Acetone, chloroform, hydrocarbons
- Oxidizing Agents: Chlorine dioxide, peroxides
This stability makes it a premier material for seals, gaskets, linings, and components in chemically aggressive processes.
The Critical Limitations of Virgin PTFE
No material is universally impervious. While PTFE's list of weaknesses is extremely short, they are absolute and critical to acknowledge in any design or application.
Liquid or Dissolved Alkali Metals
Substances like liquid sodium or potassium can attack the PTFE polymer, defluorinating it and causing a chemical breakdown. This reaction is a significant limitation in specific high-temperature or nuclear applications.
Elemental Fluorine and Potent Halogens
High-pressure fluorine gas, particularly at elevated temperatures, is one of the few substances that can react with and degrade PTFE. Other highly reactive halogen compounds, such as chlorine trifluoride, can also attack the material.
High-Temperature Considerations
While PTFE has a high melting point of around 327°C (621°F), its resistance to certain chemicals can diminish as it approaches these extreme temperatures. A chemical that is compatible at room temperature may become reactive under conditions of both high heat and high pressure.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Virgin vs. Filled PTFE
While this discussion focuses on Virgin PTFE, you will often encounter "filled" grades in industrial applications. Understanding the difference is crucial.
What is Filled PTFE?
Fillers such as glass, carbon, graphite, or bronze are added to the PTFE base to improve specific mechanical properties. These enhancements often include better wear resistance, reduced creep (deformation under load), and higher compressive strength.
The Impact on Chemical Resistance
Adding a filler fundamentally changes the material's chemical profile. The overall chemical resistance of the composite is limited by the resistance of the filler material.
For example, a glass-filled PTFE will have poor resistance to hydrofluoric acid or strong alkalis because the glass itself is attacked by these chemicals, even though the PTFE resin remains inert. The filler creates a vulnerability that does not exist in the virgin material.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct grade of PTFE requires matching its properties to your specific operational environment.
- If your primary focus is maximum chemical inertness: Virgin PTFE is the definitive choice. It provides the broadest possible resistance, as long as you avoid its specific weaknesses.
- If your primary focus is mechanical performance in a chemical environment: A filled PTFE may be necessary, but you must first verify the chemical compatibility of the filler material with your media.
- If your application involves liquid alkali metals or elemental fluorine: PTFE is not the correct material, and a suitable alternative must be engineered.
Ultimately, understanding both the exceptional inertness and the precise limitations of PTFE is the key to successful and safe material selection.
Summary Table:
| Property | Virgin PTFE | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Resistance | Excellent resistance to most acids, bases, solvents, and oxidizers. | Nearly universal inertness. |
| Key Weaknesses | Liquid/dissolved alkali metals, elemental fluorine, potent halogen compounds. | Critical to avoid for material integrity. |
| High-Temperature Effect | Resistance can diminish near melting point (327°C / 621°F). | Assess compatibility at operating temperature. |
| Virgin vs. Filled PTFE | Maximum chemical inertness. | Filled grades have resistance limited by the filler material. |
Need a chemically inert component that won't fail?
At KINTEK, we specialize in precision-manufactured Virgin PTFE components (seals, liners, labware, and more) for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise ensures your components deliver maximum chemical resistance and reliability, even in the most aggressive environments.
We offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, prioritizing precision to meet your exact specifications.
Contact our experts today to discuss your application and receive a custom solution quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support



















