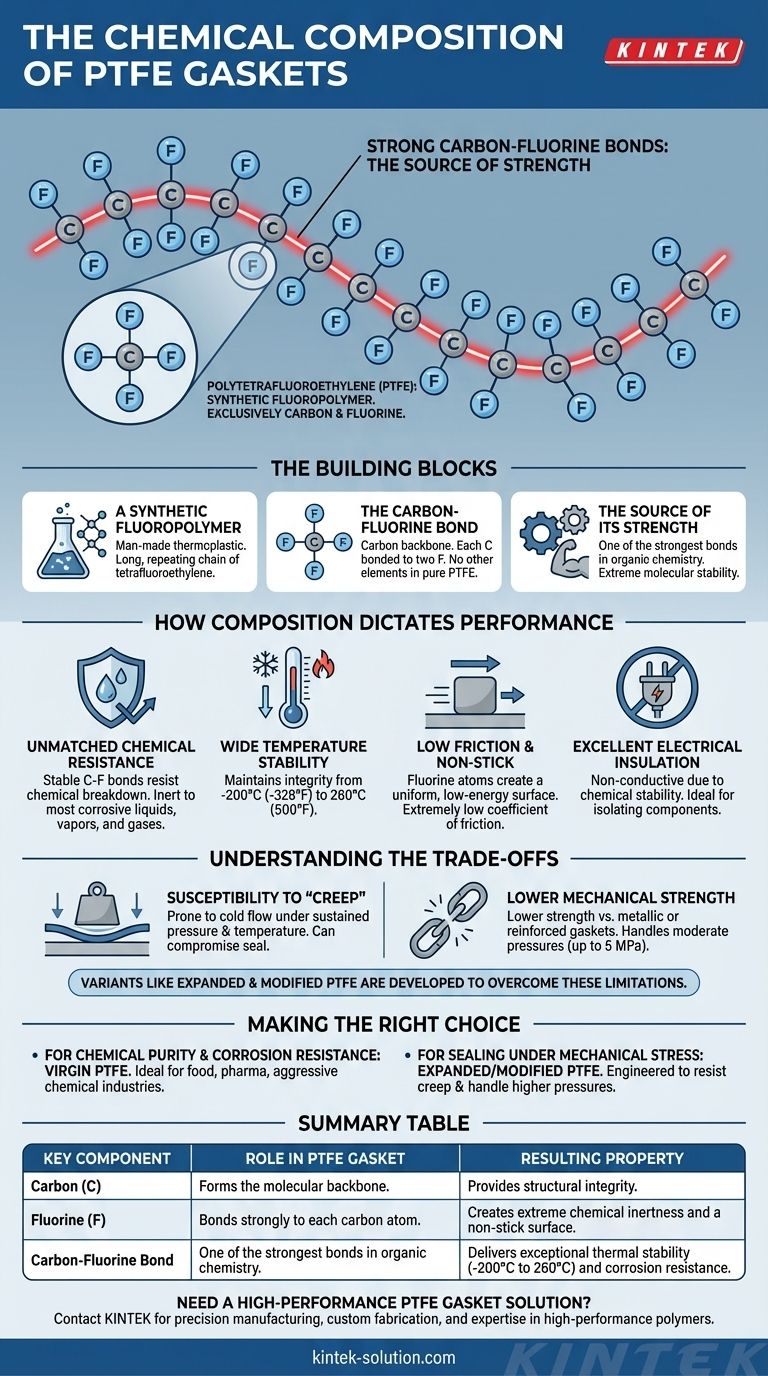
At its core, a PTFE gasket is a synthetic fluoropolymer composed exclusively of carbon and fluorine atoms. This material, scientifically known as polytetrafluoroethylene, is a high-molecular-weight compound, meaning it consists of very long molecular chains made up solely of these two elements.
The simple, incredibly strong bond between carbon and fluorine atoms is the source of a PTFE gasket's remarkable properties. This fundamental chemical structure is what gives it exceptional resistance to chemicals, temperature extremes, and surface adhesion.

The Building Blocks of a PTFE Gasket
To understand why PTFE performs the way it does, we must look at its fundamental chemical makeup. It is not a complex alloy or blend, but a remarkably simple and robust polymer.
A Synthetic Fluoropolymer
PTFE, or polytetrafluoroethylene, is a man-made thermoplastic polymer. Its structure is a long, repeating chain of tetrafluoroethylene molecules.
The Carbon-Fluorine Bond
The molecule consists of a "backbone" of carbon atoms, with each carbon atom bonded to two fluorine atoms. There are no other elements present in pure, or "virgin," PTFE.
The Source of Its Strength
The bond between a carbon atom and a fluorine atom is one of the strongest known in organic chemistry. This extreme molecular stability is the direct cause of the material's signature performance characteristics.
How Composition Dictates Performance
A material's properties are a direct reflection of its chemical structure. For PTFE, the powerful carbon-fluorine bond translates into a unique combination of high-performance traits ideal for demanding sealing applications.
Unmatched Chemical Resistance
Because the carbon-fluorine bonds are so stable and strong, it is extremely difficult for other chemicals to break them. This makes PTFE gaskets inert and resistant to nearly all corrosive liquids, vapors, and gases.
Wide Temperature Stability
The molecular structure maintains its integrity across an exceptionally broad temperature range. PTFE gaskets can function effectively in conditions from as low as -200°C (-328°F) up to 260°C (500°F).
Low Friction and Non-Stick Surface
The fluorine atoms create a very uniform, low-energy surface at the molecular level. This results in an extremely low coefficient of friction and the non-adhesive, non-stick properties for which the material is famous.
Excellent Electrical Insulation
The same chemical stability that provides corrosion resistance also makes PTFE an excellent electrical insulator. It is a non-conductive material suitable for isolating components.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While its chemical composition provides many benefits, it also creates inherent limitations. No single material is perfect for every application.
Susceptibility to "Creep"
Standard, or virgin, PTFE can be prone to "creep" or cold flow. Under sustained pressure and temperature, the material can deform over time, potentially compromising the seal. This is a direct result of its thermoplastic nature.
Lower Mechanical Strength
Compared to metallic or reinforced gasket materials, pure PTFE has lower mechanical strength and can only handle moderate pressures, typically up to 5 MPa.
Performance Variations
To overcome these limitations, variants like expanded PTFE and modified PTFE have been developed. These versions alter the physical structure or include fillers to improve creep resistance and mechanical durability while retaining the core chemical resistance of the original polymer.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the fundamental carbon-fluorine chemistry allows you to select the right material for your specific sealing challenge.
- If your primary focus is chemical purity and corrosion resistance: Virgin PTFE is the ideal choice for applications in the food, pharmaceutical, or aggressive chemical industries where contamination is not an option.
- If your primary focus is sealing performance under mechanical stress: Consider expanded or modified PTFE, which are engineered to resist creep and handle higher pressures while maintaining excellent chemical stability.
By recognizing that PTFE's performance stems directly from its simple two-element composition, you can confidently specify it for the most demanding environments.
Summary Table:
| Key Component | Role in PTFE Gasket | Resulting Property |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon (C) | Forms the molecular backbone of the polymer chain. | Provides structural integrity. |
| Fluorine (F) | Bonds strongly to each carbon atom in the chain. | Creates extreme chemical inertness and a non-stick surface. |
| Carbon-Fluorine Bond | One of the strongest bonds in organic chemistry. | Delivers exceptional thermal stability (-200°C to 260°C) and corrosion resistance. |
Need a High-Performance PTFE Gasket Solution?
Understanding the chemistry is the first step. Applying it to your specific application is the next. KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of PTFE components, including gaskets, seals, and custom labware.
Whether you require the ultimate purity of virgin PTFE for chemical processing or an engineered variant like expanded PTFE for improved creep resistance, we provide the right material solution. We serve the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors with custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Let us put our expertise in high-performance polymers to work for you. Contact our team today to discuss your project requirements and receive a quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support



















