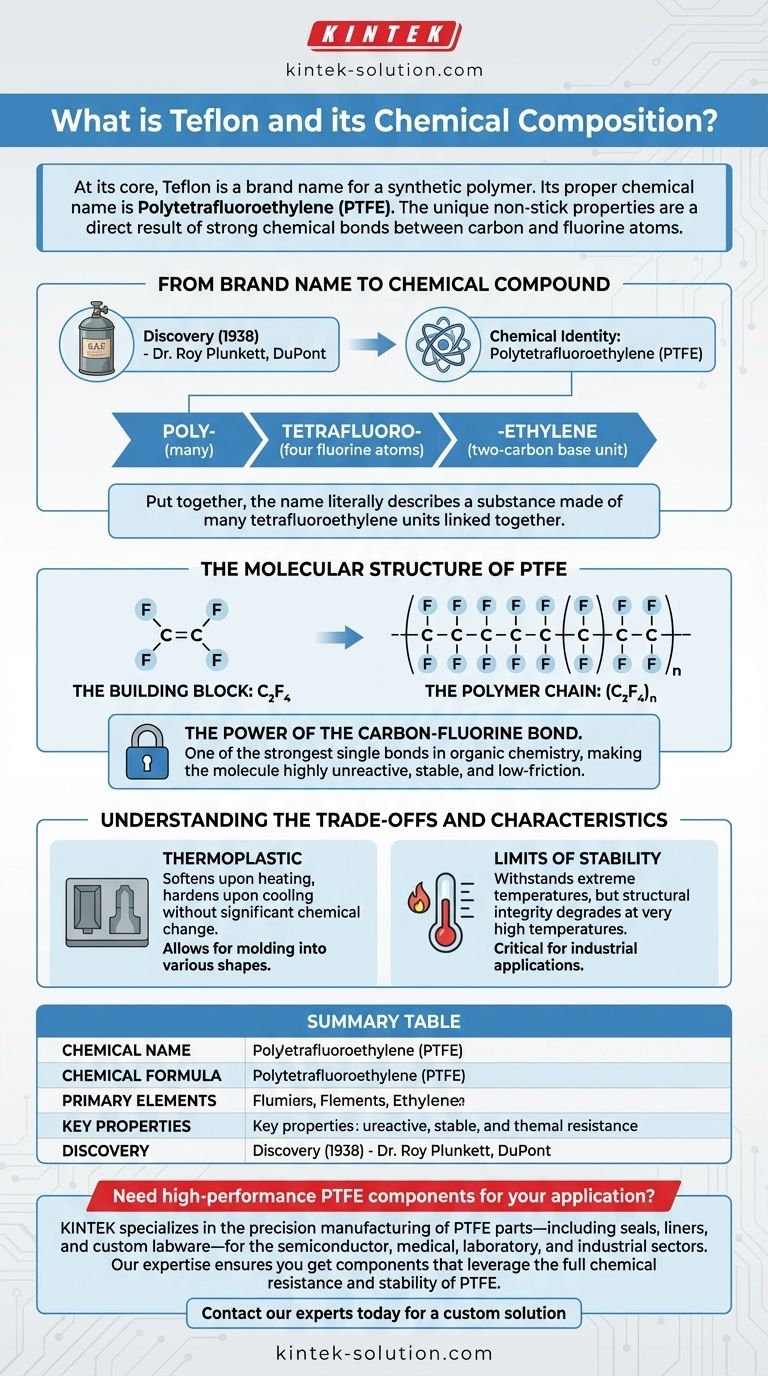
At its core, Teflon is a brand name for a synthetic polymer. Its proper chemical name is Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), a high-molecular-weight compound consisting solely of carbon and fluorine atoms. The chemical formula for this substance is (C₂F₄)n, which signifies a long, repeating chain of the tetrafluoroethylene monomer.
The most critical thing to understand is that "Teflon" is not a chemical substance itself, but a trademark for the polymer Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE). The unique, non-stick properties associated with the name are a direct result of the incredibly strong chemical bonds between the carbon and fluorine atoms in its molecular structure.

From Brand Name to Chemical Compound
To fully grasp what Teflon is, it's essential to distinguish between the commercial product and the underlying chemical. This distinction clarifies much of the common confusion surrounding the material.
A Serendipitous Discovery
Teflon was discovered by accident in 1938 by Dr. Roy Plunkett at DuPont. While attempting to create a new refrigerant, he discovered a gas canister that appeared empty but was still heavy, revealing a waxy, slippery, and remarkably stable substance coating the inside.
The Chemical Identity: PTFE
The substance he discovered is chemically known as Polytetrafluoroethylene, or PTFE. "Teflon" is the trademarked brand name, now owned by the company Chemours, under which this polymer is sold.
Deconstructing the Name
The chemical name itself describes the structure:
- Poly-: Means "many," indicating it is a polymer (a long chain of repeating units).
- tetrafluoro-: Means "four fluorine atoms."
- -ethylene: Refers to the two-carbon base unit (C₂).
Put together, the name literally describes a substance made of many tetrafluoroethylene units linked together.
The Molecular Structure of PTFE
The remarkable properties of PTFE—chemical resistance, temperature stability, and its famous non-stick surface—all originate from its simple and robust molecular structure.
The Building Block: C₂F₄
The fundamental unit, or monomer, is tetrafluoroethylene (C₂F₄). This is essentially an ethylene molecule where all the hydrogen atoms have been replaced by fluorine atoms.
The Polymer Chain: (C₂F₄)n
The "n" in the formula (C₂F₄)n signifies that thousands of these C₂F₄ monomers link together to form an extremely long and stable chain. This process of linking monomers is called polymerization.
The Power of the Carbon-Fluorine Bond
The key to it all is the carbon-fluorine (C-F) bond. This is one of the strongest single bonds in organic chemistry. This immense strength makes the molecule highly unreactive and stable. The fluorine atoms also create a protective, low-friction "sheath" around the carbon backbone, preventing other substances from sticking to it.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Characteristics
While incredibly useful, it's important to understand the fundamental nature of the material to use it correctly.
What Being a Thermoplastic Means
The references identify PTFE as a thermoplastic. This means the material softens upon heating and hardens upon cooling without significant chemical change. This property is what allows it to be molded into various shapes, from coatings on pans to industrial components.
The Limits of Stability
PTFE is famous for its ability to withstand extreme temperatures. However, like all materials, it has its limits. As a thermoplastic, its structural integrity will degrade at very high temperatures, a critical consideration in industrial and engineering applications.
How to Apply This to Your Understanding
Understanding Teflon and PTFE can be broken down based on your specific interest, from simple consumer knowledge to a deeper chemical appreciation.
- If your primary focus is simple identification: Remember that Teflon is the common brand name for the non-stick chemical compound Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE).
- If your primary focus is the chemical composition: The key is the formula (C₂F₄)n, representing a long polymer chain made of repeating carbon and fluorine units.
- If your primary focus is why it's so effective: Its unique non-stick and non-reactive properties come directly from the exceptional strength of the carbon-fluorine bond in its molecular structure.
Ultimately, appreciating the simple yet powerful chemistry of PTFE is the key to understanding why Teflon is so uniquely effective in our daily lives.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Information |
|---|---|
| Chemical Name | Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) |
| Chemical Formula | (C₂F₄)n |
| Primary Elements | Carbon (C) and Fluorine (F) |
| Key Property | Non-stick, chemically inert, high temperature resistance |
| Discovery | 1938 by Dr. Roy Plunkett at DuPont |
Need high-performance PTFE components for your application?
KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of PTFE parts—including seals, liners, and custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise ensures you get components that leverage the full chemical resistance and stability of PTFE, from prototypes to high-volume production.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements and get a custom solution.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs



















