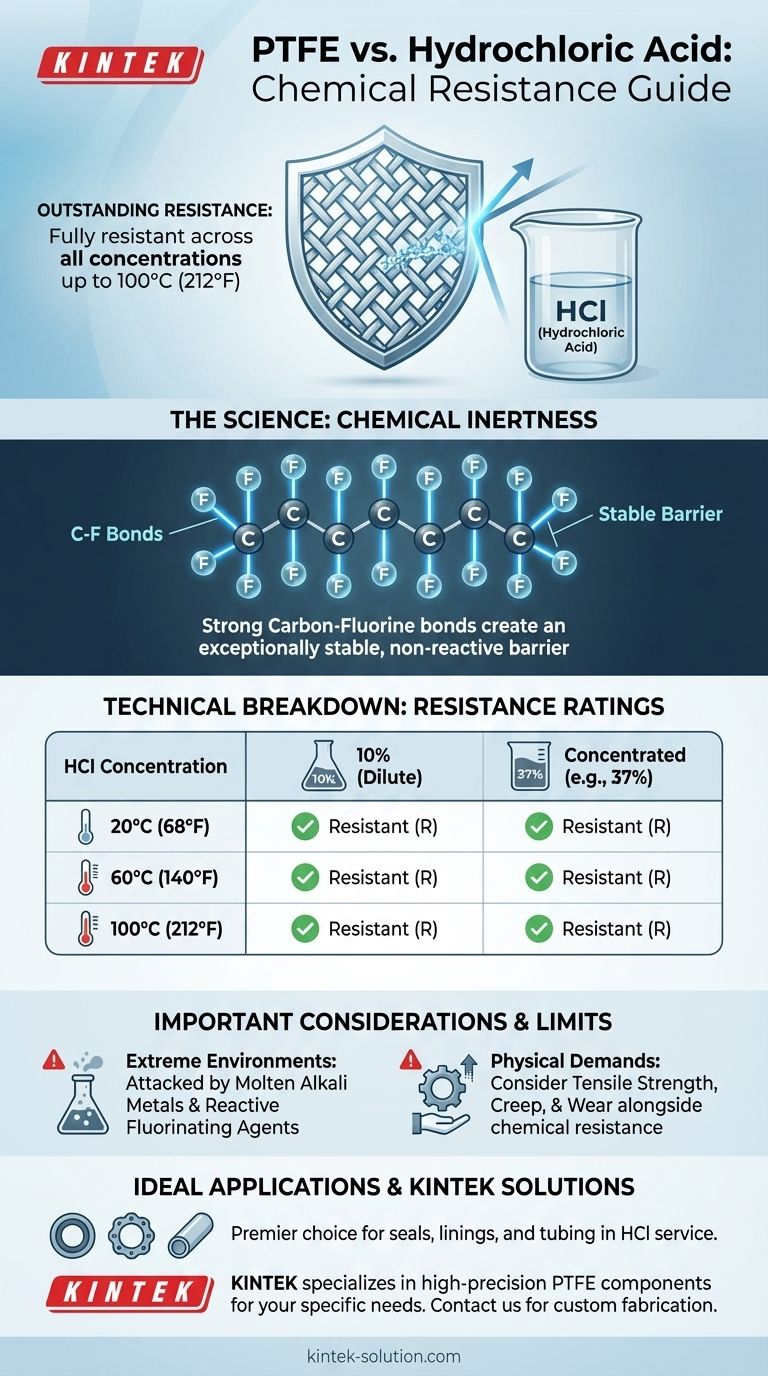
In short, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) has outstanding chemical resistance to hydrochloric acid (HCl). It is considered fully resistant across all concentrations, from dilute 10% solutions to concentrated forms, at temperatures up to at least 100°C (212°F). This makes it a premier material choice for applications involving this aggressive acid.
The core reason for PTFE's exceptional performance is its chemical inertness. The powerful carbon-fluorine bonds that make up its molecular structure are extremely stable and non-reactive, creating a reliable barrier against chemical attack from substances like hydrochloric acid.

The Technical Breakdown of PTFE's Resistance
The data confirms that PTFE's performance is consistent and reliable when exposed to hydrochloric acid under a variety of common industrial conditions. This predictability is critical for designing safe and long-lasting systems.
Resistance at Dilute Concentrations
PTFE is rated as fully resistant (R) to 10% hydrochloric acid solutions. This rating holds true across a functional temperature range, including 20°C (68°F), 60°C (140°F), and 100°C (212°F).
Resistance at High Concentrations
The material's performance does not degrade with more aggressive media. It is also fully resistant (R) to concentrated hydrochloric acid at the same tested temperatures of 20°C (68°F), 60°C (140°F), and 100°C (212°F).
The Decisive Role of Molecular Structure
The source of this remarkable resistance lies in PTFE's molecular makeup. It is a fluoropolymer, composed of a long chain of carbon atoms completely shielded by fluorine atoms.
The carbon-fluorine (C-F) bond is one of the strongest single bonds in organic chemistry. This inherent stability makes the polymer chain exceptionally difficult for chemicals to break down or react with, rendering the material inert.
Understanding the Limits and Considerations
While PTFE is exceptionally resistant to HCl, no material is without its absolute limits. Understanding its broader profile ensures it is used correctly and safely.
Extreme Chemical Environments
The true limits of PTFE are found in conditions far more aggressive than hydrochloric acid. It can be attacked by substances like molten alkali metals and certain highly reactive fluorinating agents (such as fluorine gas), particularly at elevated temperatures.
This context is important: the fact that it takes such exotic and aggressive chemicals to affect PTFE underscores its durability in nearly all other applications, including HCl.
Physical vs. Chemical Properties
It is crucial to remember that chemical resistance is only one aspect of material selection. You must also consider the physical demands of the application.
Properties like tensile strength, resistance to creep (deformation under load), and wear resistance may be the limiting factors in a design, even when the material is chemically compatible.
Is PTFE the Right Choice for Your HCl Application?
Based on its chemical profile, PTFE is a highly reliable option for handling hydrochloric acid. Your final decision should be guided by the specific operational demands of your project.
- If your primary focus is containing HCl at any concentration below 100°C (212°F): PTFE is one of the safest and most reliable material choices available for components like seals, gaskets, linings, and tubing.
- If your application involves physical stress like high pressure or abrasive flow: You should evaluate filled grades of PTFE or other materials to ensure the physical properties are as robust as the chemical resistance.
Ultimately, PTFE's inherent chemical inertness makes it a default, top-tier candidate for service in hydrochloric acid.
Summary Table:
| Hydrochloric Acid (HCl) Concentration | Temperature | PTFE Resistance Rating |
|---|---|---|
| 10% (Dilute) | 20°C, 60°C, 100°C | Resistant (R) |
| Concentrated (e.g., 37%) | 20°C, 60°C, 100°C | Resistant (R) |
Need reliable components for handling aggressive chemicals like hydrochloric acid?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, and labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our custom fabrication services, from prototypes to high-volume orders, ensure you get chemically inert parts that meet your exact specifications.
Contact us today to discuss how our PTFE solutions can enhance the safety and longevity of your chemical processing systems!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
People Also Ask
- What material is the PTFE bottle made from? Discover the Benefits of 100% Virgin PTFE
- What are the characteristics of narrow mouth PTFE laboratory bottles? Superior Chemical Resistance & Purity
- What makes the PTFE bottle durable? Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Stability for Demanding Applications
- How does the PTFE bottle perform in terms of chemical resistance? Unmatched Protection for Harsh Chemicals
- What are the key applications of the PTFE bottle? Ensure Chemical Safety and Sample Purity



















