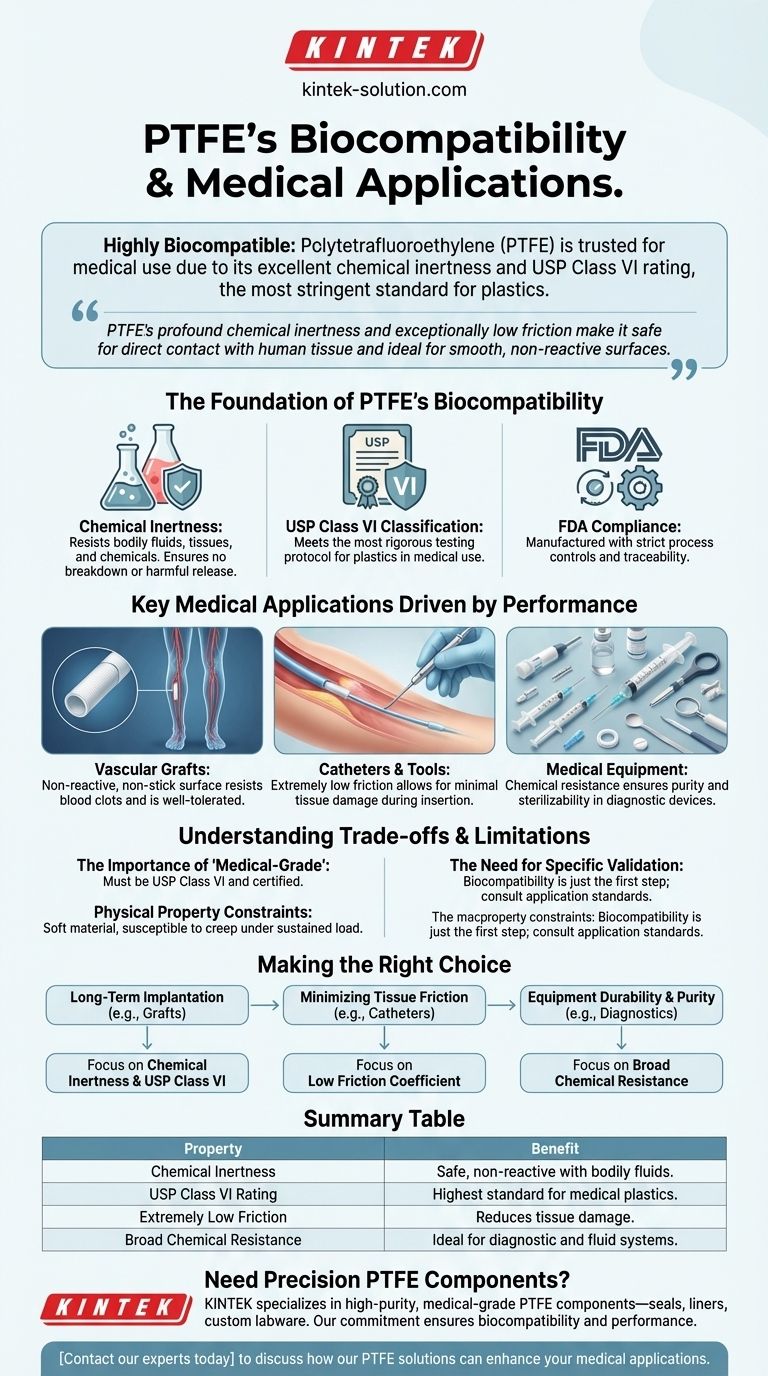
In short, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is considered highly biocompatible and is a trusted material for medical applications. Its excellent chemical inertness prevents it from reacting with bodily fluids or tissues, which is why it achieves a USP Class VI rating—the most stringent standard for plastics in medical use. This biocompatibility, combined with its unique physical properties, makes it suitable for devices like vascular grafts, catheters, and other implants.
PTFE's value in medicine stems from its profound chemical inertness and exceptionally low friction. These two properties make it safe for direct contact with human tissue and ideal for applications requiring smooth, non-reactive surfaces.

The Foundation of PTFE's Biocompatibility
To understand why PTFE is trusted for medical use, we need to look at its core chemical properties and the regulatory standards it meets.
Chemical Inertness
PTFE is one of the most chemically resistant polymers known. It does not react with bodily fluids, tissues, or common chemicals. This inertness ensures that the material will not break down inside the body or release harmful substances, making it fundamentally safe for implantation.
USP Class VI Classification
Materials intended for medical devices are often tested against United States Pharmacopeia (USP) standards. A USP Class VI classification is the most rigorous testing protocol for plastics, involving multiple tests to assess toxicity and biological reactivity. PTFE that meets this standard has been proven safe for direct human tissue contact.
FDA Compliance
In addition to USP standards, medical-grade PTFE complies with Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulations. This ensures that the material is manufactured with strict process controls and traceability, which are critical for medical devices.
Key Medical Applications Driven by Performance
PTFE's physical properties directly enable its most common medical uses. Its biocompatibility is the ticket to entry, but its performance characteristics determine its role.
Vascular Grafts and Implants
PTFE's non-reactive and non-stick surface is ideal for creating artificial blood vessels (vascular grafts). The material's surface resists the formation of blood clots and is well-tolerated by the body, reducing the risk of implant rejection.
Catheters and Surgical Tools
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material, giving it an extreme "slipperiness." This property is invaluable for catheters, which must be inserted into the body with minimal friction and tissue damage. It's also used to coat surgical instruments for the same reason.
Components in Medical Equipment
Beyond implants, PTFE is used in a variety of medical and scientific equipment. Its chemical resistance is essential for components in testing devices, syringes, and fluid handling systems, ensuring that samples are not contaminated and that the equipment can be reliably sterilized.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While highly effective, PTFE is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is critical for proper application.
The Importance of "Medical-Grade"
Industrial-grade PTFE is not the same as medical-grade PTFE. Only materials that have undergone rigorous testing, are certified as USP Class VI, and have a clear manufacturing history are suitable for medical devices. Sourcing from a reputable supplier is non-negotiable.
Physical Property Constraints
PTFE is a relatively soft material and can be susceptible to "creep," or deformation under a sustained load. This means it may not be suitable for high-load-bearing structural implants without reinforcement.
The Need for Specific Validation
Biocompatibility is just the first step. Every medical device and application has unique requirements. There are often restrictions on material use, and engineers must consult specific application standards to ensure PTFE is the correct and safe choice for a given device.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When evaluating PTFE, align its strengths with the primary demand of your application.
- If your primary focus is long-term implantation: PTFE's proven chemical inertness and USP Class VI rating make it a primary candidate for devices like grafts.
- If your primary focus is minimizing tissue friction: PTFE's exceptionally low friction coefficient is its most significant advantage for devices like catheters and guidewires.
- If your primary focus is equipment durability and purity: PTFE's broad chemical resistance makes it ideal for components in diagnostic and fluid-handling systems.
Ultimately, understanding these core properties empowers you to select materials that ensure both patient safety and device performance.
Summary Table:
| Property | Benefit for Medical Use |
|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | Does not react with bodily fluids or tissues, ensuring safety. |
| USP Class VI Rating | Meets the highest standard for plastics in medical applications. |
| Extremely Low Friction | Reduces tissue damage in catheters and surgical tools. |
| Broad Chemical Resistance | Ideal for diagnostic equipment and fluid handling systems. |
Need precision PTFE components for your medical device?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-purity, medical-grade PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, and laboratory industries. Our commitment to precision production and rigorous quality control ensures your devices meet the demanding standards for biocompatibility and performance.
We offer custom fabrication from initial prototypes to high-volume production runs. Contact our experts today to discuss how our PTFE solutions can enhance the safety and efficacy of your medical applications.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers



















