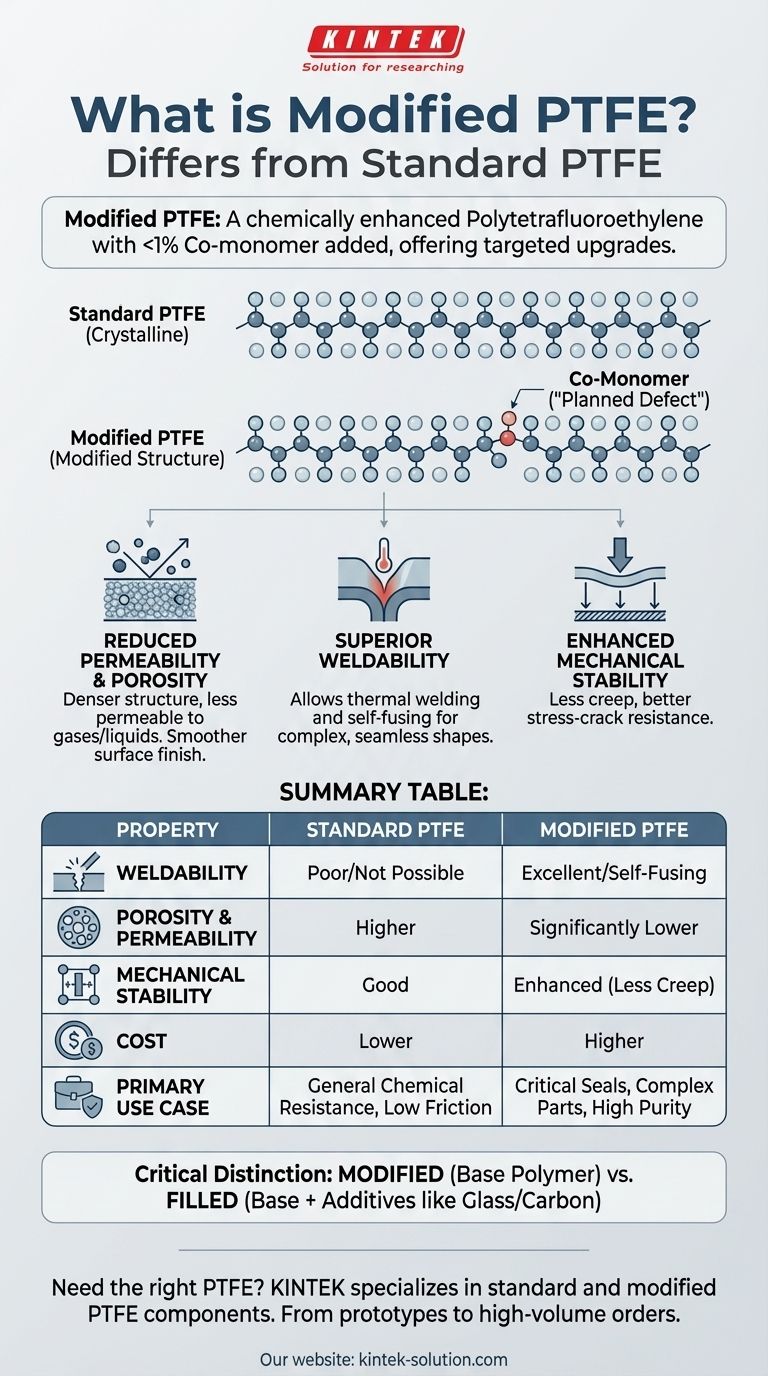
To be precise, modified PTFE is a chemically enhanced version of standard Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE). It is created by introducing a very small amount—typically less than 1%—of a co-monomer during the polymerization process. This subtle change to the polymer's molecular structure results in significant improvements to key physical properties that standard PTFE lacks.
The essential difference is not a complete reinvention but a targeted upgrade. While standard PTFE sets the benchmark for chemical inertness and low friction, modified PTFE enhances weldability, reduces porosity, and improves mechanical stability for more demanding applications.

How Modification Changes the Polymer Structure
Standard PTFE's incredible properties stem from its highly stable, crystalline molecular structure. However, this same structure is responsible for its limitations, such as its tendency to creep under load and its inability to be melt-processed.
The Role of the Co-Monomer
A co-monomer (a type of perfluorinated modifier) is introduced during polymerization.
This modifier acts as a planned "defect" in the otherwise uniform polymer chain. This slight disruption in the crystalline structure is the source of its enhanced properties.
The Impact on Physical Properties
This molecular-level change creates a denser, less porous material.
The modified structure lowers the melt viscosity, which makes self-fusing or welding possible—a capability that is nearly impossible with standard PTFE.
Key Performance Enhancements of Modified PTFE
The decision to use modified PTFE over its standard counterpart is driven by specific engineering requirements that go beyond the basic benefits of PTFE.
Reduced Permeability and Porosity
Modified PTFE has a significantly denser polymer structure. This makes it far less permeable to gases and liquids, which is critical for high-purity or critical sealing applications.
This density also results in a smoother machined surface finish, an important factor for sealing faces and high-performance components.
Superior Weldability
The ability to be thermally welded is perhaps the most significant advantage.
This allows for the fabrication of complex shapes, tank liners, and encapsulated components that are not feasible with standard PTFE, which must be joined mechanically or with adhesives.
Enhanced Mechanical Stability
While not as creep-resistant as filled grades, modified PTFE exhibits less deformation under load and better stress-crack resistance than standard PTFE.
This makes it a more reliable choice for components that experience mechanical stress in addition to chemical exposure.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between standard and modified PTFE is not about which is universally "better," but which is appropriate for the task. The enhancements of modified PTFE come with clear trade-offs.
The Critical "Filled" vs. "Modified" Distinction
It is crucial to distinguish between modified PTFE and filled PTFE.
Modified PTFE refers to the base polymer resin that has been chemically altered.
Filled PTFE involves adding materials like glass, carbon, or silica to either standard or modified PTFE resin. These fillers dramatically improve properties like wear resistance and creep resistance but can sometimes compromise overall chemical resistance.
When Standard PTFE is Sufficient
For applications where the primary needs are excellent chemical resistance and low friction—and where properties like permeability or weldability are not critical—standard PTFE remains an effective and more economical choice.
The Cost Factor
Due to the more complex manufacturing process, modified PTFE resin is inherently more expensive than standard grades. This cost must be justified by a genuine need for its enhanced performance characteristics.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct material requires a clear understanding of your primary engineering goal.
- If your primary focus is sealing critical gases or high-purity chemicals: Choose modified PTFE for its significantly lower permeability and porosity.
- If your primary focus is fabricating complex, seamless parts: Choose modified PTFE for its unique ability to be thermally welded.
- If your primary focus is high mechanical loads or wear resistance: A filled PTFE (using either a standard or modified base resin) is the correct choice.
- If your primary focus is general chemical compatibility on a budget: Standard PTFE offers nearly identical chemical resistance and is the most cost-effective solution.
Ultimately, understanding these material distinctions empowers you to select the precise polymer that meets your application's demands without over-engineering or unnecessary cost.
Summary Table:
| Property | Standard PTFE | Modified PTFE |
|---|---|---|
| Weldability | Poor / Not possible | Excellent / Self-fusing |
| Porosity & Permeability | Higher | Significantly lower |
| Mechanical Stability | Good | Enhanced (less creep) |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Primary Use Case | General chemical resistance, low friction | Critical seals, complex parts, high purity |
Need the right PTFE for your specific application?
KINTEK specializes in precision manufacturing of both standard and modified PTFE components—from custom seals and liners to complex labware. Whether you require the superior weldability and low permeability of modified PTFE or the cost-effective chemical resistance of standard PTFE, our experts can help you select and fabricate the ideal solution, from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your project requirements and get a quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the key benefits of PTFE in custom fabrication? Unlock Performance in Extreme Conditions
- What is the working temperature range of PTFE? Master Extreme Heat and Cryogenic Applications
- What are the base characteristics of PTFE? Unlocking Extreme Performance in Friction, Temperature, and Chemical Resistance
- What is PTFE commonly known as and what are its unique properties? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What are some common applications of machined PTFE? Leverage its Unique Properties for Demanding Applications



















