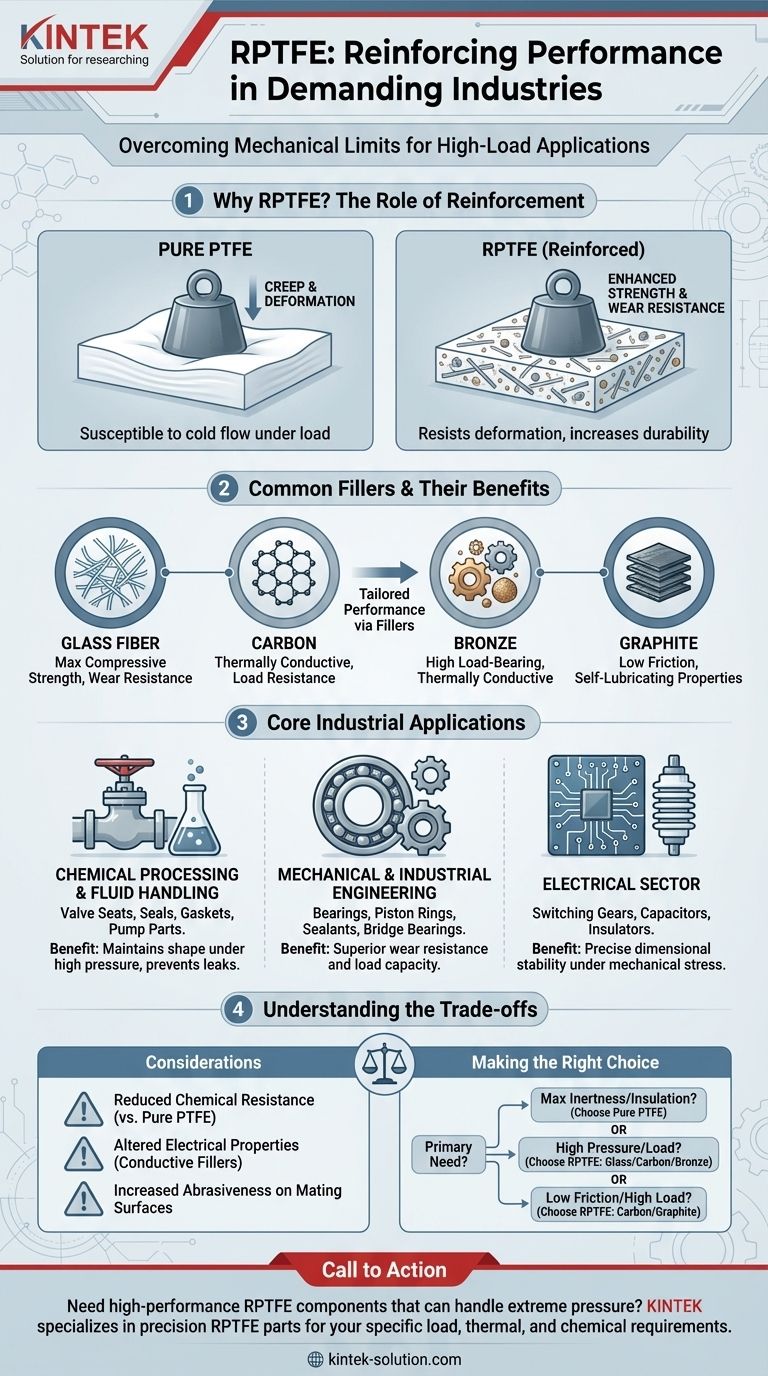
In short, Reinforced PTFE (RPTFE) is used in industries where standard PTFE fails due to mechanical stress. It is primarily found in chemical processing, fluid handling, and mechanical engineering for high-load applications like valve seats, heavy-duty seals, and bearings that require enhanced strength and wear resistance.
The decision to use RPTFE over standard PTFE is driven by a single need: overcoming the mechanical limitations of pure PTFE. By adding fillers like glass fiber, carbon, or bronze, RPTFE gains the strength and resistance to deformation required for high-pressure, high-load, and abrasive environments.

The Role of Reinforcement: Why Not Just Use PTFE?
To understand where RPTFE is used, we must first understand why it exists. Pure Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is famous for its chemical inertness and low friction, but it has significant mechanical weaknesses.
The Limits of Pure PTFE
Pure PTFE is a relatively soft material. Under high pressure or a sustained load, it is susceptible to creep, or cold flow, where the material slowly deforms over time. This makes it unsuitable for applications like high-pressure valve seats or heavy-duty bearings.
How Fillers Elevate Performance
RPTFE is a composite material that combines a PTFE base with a reinforcing filler. Each type of filler imparts specific properties to address the weaknesses of pure PTFE.
Glass Fiber: This is the most common filler. It dramatically increases compressive strength and wear resistance, making the material more durable and resistant to creep.
Carbon: Adding carbon also improves compressive strength and load resistance. Crucially, it enhances thermal conductivity, helping to dissipate heat in high-friction applications like bearings.
Bronze: Bronze provides the best improvements in strength and load-bearing capacity. It also has excellent thermal conductivity but compromises some of the chemical resistance of the base PTFE.
Graphite: Often used in combination with other fillers, graphite reduces the coefficient of friction and improves wear properties, particularly in self-lubricating components.
Core Industrial Applications of RPTFE
The enhanced mechanical properties of RPTFE make it the material of choice for demanding components within several key industries.
Fluid Handling and Chemical Processing
This is the most common arena for RPTFE. It is used for components that must maintain their shape under high fluid pressure and potential abrasion.
Key applications include valve seats, seals, gaskets, and pump parts. A pure PTFE valve seat would deform under high pressure, causing a leak, whereas an RPTFE seat holds its shape, ensuring a reliable seal.
Mechanical and Industrial Engineering
In applications with significant mechanical loads and friction, RPTFE provides the necessary durability.
Components like bearings, piston rings, and sealants benefit from RPTFE's superior wear resistance and load capacity. A notable example is its use in bridge bearings, where massive structural loads must be accommodated.
Electrical Sector
While pure PTFE is an exceptional electrical insulator, some applications require greater dimensional stability than it can offer.
RPTFE is used for mechanically stressed insulators or components in switching gears and capacitors where maintaining precise dimensions under load is critical.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Reinforcing PTFE is not a universal upgrade; it involves clear trade-offs that are critical to understand.
Compromised Chemical Resistance
The fillers are not as chemically inert as pure PTFE. For example, glass fiber can be attacked by strong alkalis or hydrofluoric acid. This means the specific chemical environment must be carefully considered when selecting an RPTFE grade.
Altered Electrical Properties
Adding conductive fillers like carbon or bronze fundamentally changes the material's electrical properties. While pure PTFE is an excellent insulator, a bronze-filled RPTFE will be conductive, making it completely unsuitable for insulation purposes.
Increased Abrasiveness on Mating Surfaces
Fillers, particularly glass fiber, can make the RPTFE material more abrasive than pure PTFE. This can cause increased wear on softer mating surfaces, such as stainless steel shafts, a factor that must be accounted for in system design.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct material requires a clear understanding of your primary operational demand.
- If your primary focus is maximum chemical inertness or electrical insulation: Pure PTFE is almost always the superior choice, provided mechanical loads are low.
- If your primary focus is handling high pressure or mechanical loads: RPTFE is the necessary upgrade. Choose a glass-filled grade for general-purpose strength or a carbon/bronze-filled grade for high thermal conductivity.
- If your primary focus is reducing friction in a high-load bearing: An RPTFE with carbon or graphite filler provides enhanced strength with self-lubricating properties.
Ultimately, choosing RPTFE is a deliberate engineering decision to enhance mechanical performance where it matters most.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Primary Applications | Key Benefits of RPTFE |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Processing & Fluid Handling | Valve seats, seals, gaskets, pump parts | High compressive strength, resistance to creep and abrasion under pressure |
| Mechanical & Industrial Engineering | Bearings, piston rings, bridge bearings | Enhanced load capacity, improved wear resistance, dimensional stability |
| Electrical Sector | Insulators in switching gears, capacitors | Greater mechanical strength while maintaining insulation properties (with specific fillers) |
Need high-performance PTFE components that can handle extreme pressure and mechanical stress? At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision RPTFE parts—including custom seals, liners, and labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise in custom fabrication ensures you get components tailored to your specific load, thermal, and chemical requirements, from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Enhance your application's durability and performance—contact our experts today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
People Also Ask
- What chemical processing applications involve PTFE-machined parts? Essential Components for Corrosive & High-Purity Systems
- What fabrication services are available for PTFE? Shearing, Stamping, Laser Cutting, Molding & Machining
- What are the main applications of PTFE type Teflon? Unlock Its Versatility for Your Industry
- What industrial benefits do PTFE-machined parts offer? Achieve Peak Performance in Demanding Applications
- What challenges arise when machining PTFE (Teflon)? Overcome Softness, Heat, and Instability



















