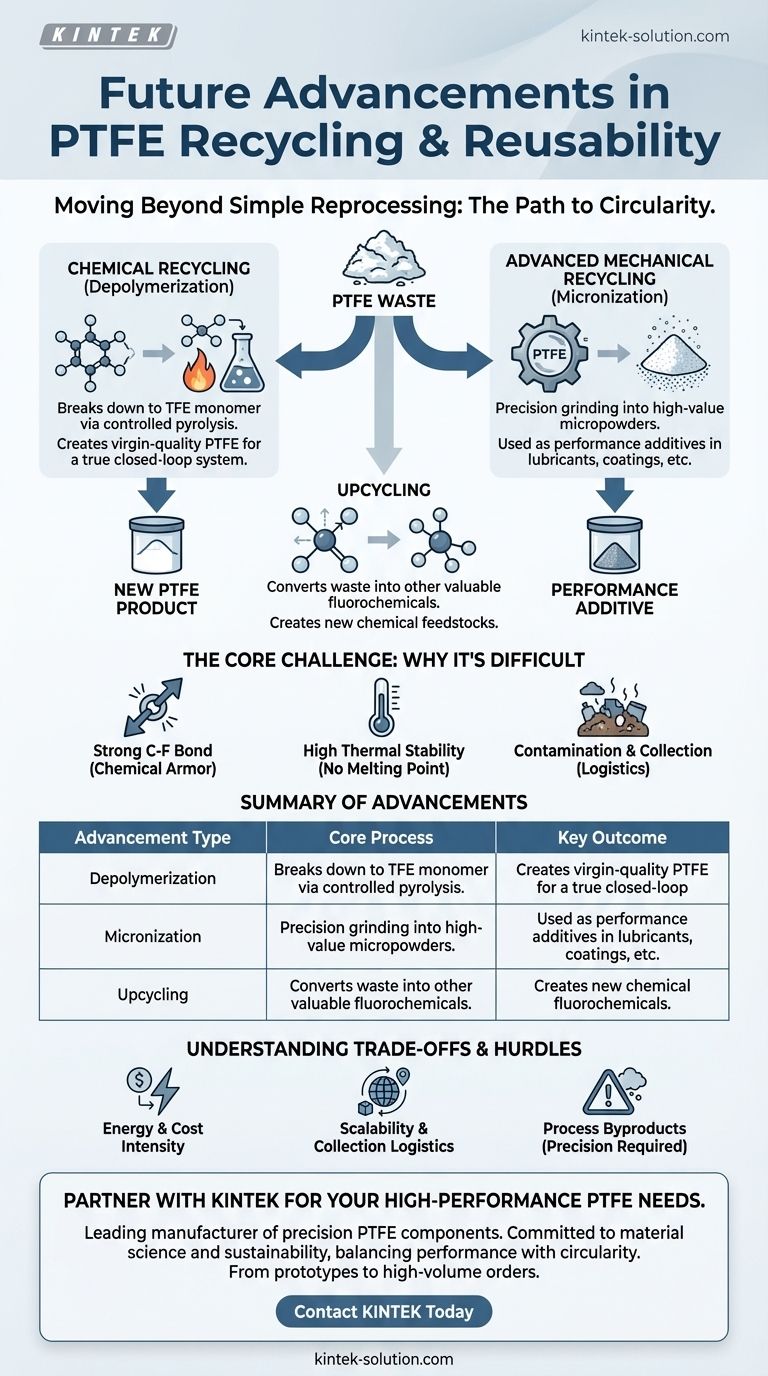
In short, future advancements in PTFE recycling are moving beyond simple reprocessing. The focus is on two primary paths: sophisticated chemical processes that break the material down to its molecular building blocks for reuse, and advanced mechanical methods that create high-value micropowders for use as performance additives.
The core challenge—and opportunity—in PTFE recycling lies in overcoming its legendary chemical stability. Future success will not come from traditional melting and remolding, but from innovative chemical and mechanical technologies that transform waste PTFE into high-purity raw materials.

The Core Challenge: Why PTFE Recycling is So Difficult
To understand the future of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) recycling, we must first appreciate why it is not recycled like common plastics such as PET or Polypropylene. The very properties that make it an indispensable engineering material also make it a formidable recycling challenge.
The Strength of the Carbon-Fluorine Bond
The bond between carbon and fluorine atoms is one of the strongest known in organic chemistry. This bond gives PTFE its incredible chemical inertness and thermal stability.
This chemical armor means PTFE cannot be easily broken down, dissolved, or reprocessed using conventional methods.
High Thermal Stability
Unlike most thermoplastics, PTFE does not have a true melting point where it becomes a liquid that can be easily injection molded. When heated, it becomes a gel-like substance and will decompose before it flows freely.
This behavior makes traditional melt-recycling, the cornerstone of plastic recycling, completely impractical for PTFE.
Contamination and Collection
Industrial and post-consumer PTFE waste is often contaminated with other materials from its application (e.g., fillers in a gasket, metals in a wire coating).
Separating this contamination to achieve a pure PTFE feedstock is a significant logistical and technical hurdle.
Emerging Advancements in PTFE Recycling
Engineers and chemists are developing new methods that work with PTFE's unique chemistry, rather than against it. These advancements represent the future of its circularity.
Chemical Recycling (Depolymerization)
The most promising long-term solution is depolymerization. This process breaks PTFE back down into its original monomer, tetrafluoroethylene (TFE).
Using methods like controlled pyrolysis, waste PTFE is heated in a specific environment to reverse the polymerization process. The resulting TFE gas can then be captured, purified, and used to create new, virgin-quality PTFE with no loss of performance.
This is the key to creating a true closed-loop system for the material.
Advanced Mechanical Recycling (Micronization)
The most common method today, micronization, is also seeing significant advancement. This physical process involves carefully grinding and processing scrap PTFE into extremely fine powders.
Future progress here focuses on tighter control over particle size, shape, and purity. These high-value micropowders are then used as performance additives in other materials, such as industrial lubricants, coatings, inks, and other plastics to impart PTFE's low-friction properties.
Upcycling into New Materials
A more forward-thinking approach involves upcycling PTFE waste. Researchers are exploring ways to use chemical processes to convert waste PTFE not into TFE, but into other valuable fluorochemicals.
This transforms a difficult waste stream into a valuable feedstock for entirely different chemical products, creating new value chains.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Hurdles
While these advancements are promising, it's critical to acknowledge the practical barriers that must be overcome for them to become widespread.
Energy and Cost Intensity
Chemical recycling methods, particularly depolymerization, are currently very energy-intensive. The cost of the energy and specialized equipment required can make the resulting recycled monomer more expensive than virgin material.
Scalability and Collection Logistics
Building a robust supply chain to collect, sort, and process enough pure PTFE waste to feed a large-scale recycling plant remains a major logistical challenge. Without a consistent and clean feedstock, these processes cannot be economically viable.
Process Byproducts
Breaking the powerful C-F bond must be done with extreme precision. Poorly controlled processes could potentially create harmful fluorine-containing byproducts. A significant portion of ongoing research is dedicated to ensuring these new recycling methods are both efficient and environmentally safe.
How to Evaluate PTFE's Sustainability for Your Project
The decision to use PTFE should be based on a clear understanding of its current and future state of recyclability.
- If your primary focus is immediate circularity: You may need to consider materials like PET or PP, which already have established, large-scale recycling infrastructures.
- If your primary focus is unmatched performance: PTFE remains the superior choice for harsh chemical and thermal environments. The best sustainable practice today is to source from manufacturers who incorporate high-quality, reprocessed micronized PTFE into their products.
- If your primary focus is long-term sustainable design: Keep a close watch on the maturation of chemical recycling technologies, as this is the pathway that will eventually allow high-performance PTFE to become a truly circular material.
Ultimately, the journey to make PTFE fully recyclable is a direct consequence of its exceptional chemical resilience, but progress is steady and scientifically promising.
Summary Table:
| Advancement Type | Core Process | Key Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Recycling (Depolymerization) | Breaking PTFE down to its monomer (TFE) via controlled pyrolysis | Creates virgin-quality PTFE for a closed-loop system |
| Advanced Mechanical Recycling (Micronization) | Grinding scrap PTFE into fine, controlled powders | Produces high-value micropowders for use as performance additives |
| Upcycling | Converting waste PTFE into other valuable fluorochemicals | Transforms waste into feedstock for new chemical products |
Partner with KINTEK for Your High-Performance PTFE Needs
As a leading manufacturer of precision PTFE components (seals, liners, labware, and more) for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors, KINTEK is committed to sustainability and innovation. We understand the critical balance between PTFE's unmatched performance and the evolving landscape of its recyclability.
By choosing KINTEK, you gain a partner who prioritizes material science and efficient production, from custom prototypes to high-volume orders. Let us help you navigate the future of PTFE with components designed for durability and performance, while supporting the industry's progress toward a circular economy.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific requirements and discover how our expertise can enhance your projects.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Customizable PTFE Scrapers and Shovels for Demanding Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech



















