The choice is not between PTFE and Teflon, but rather which specific fluoropolymer is right for your application. Teflon™ is a brand name owned by Chemours that most famously applies to the polymer Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), but it also covers other related fluoropolymers like FEP and PFA. Therefore, when you specify a Teflon™ gasket, you might be getting PTFE or a different material entirely.
The critical task is to move beyond the brand name and evaluate the specific polymer properties. Your decision should be based on matching the distinct characteristics of a fluoropolymer—like PTFE, PFA, or FEP—to the precise operational demands of your gasket, including temperature, chemical exposure, and mechanical stress.

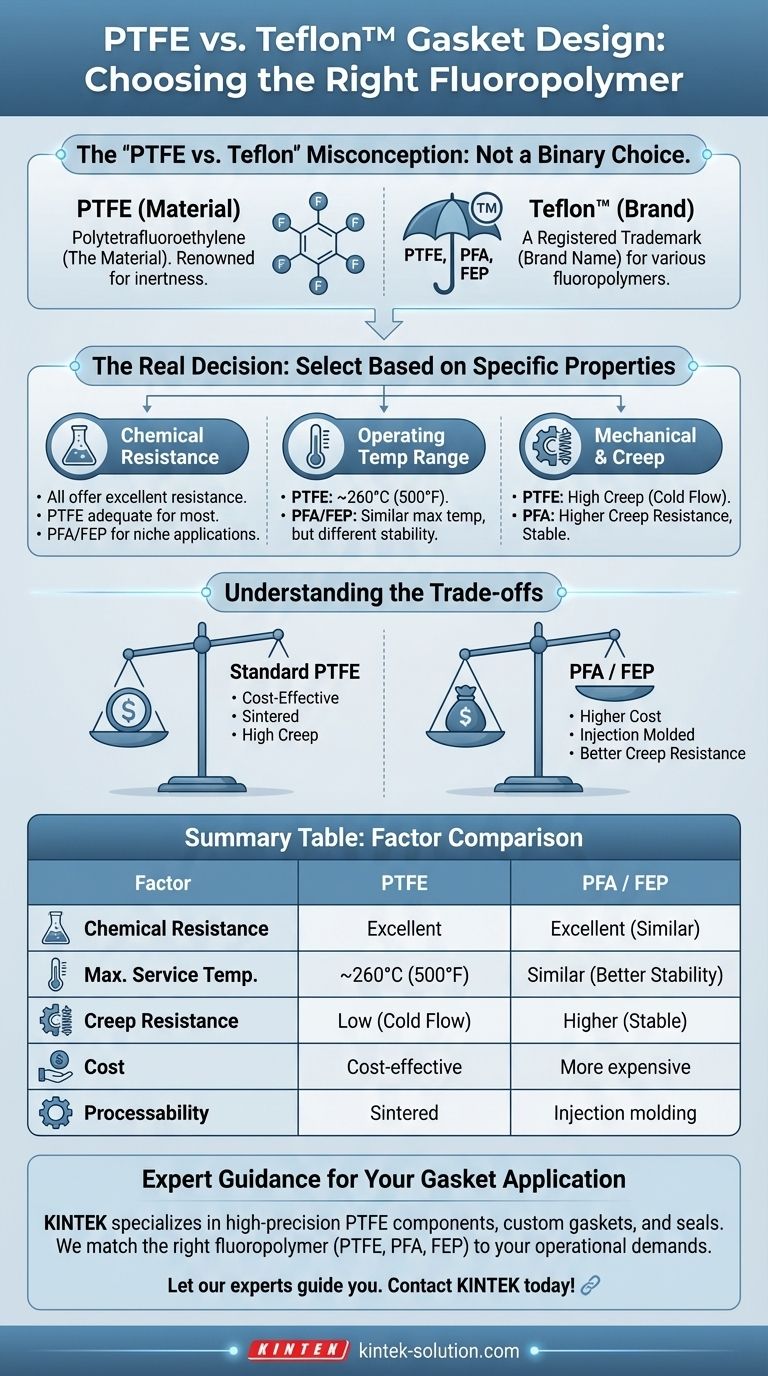
Deconstructing the "PTFE vs. Teflon" Misconception
To make an informed decision, we must first clarify the terminology. The confusion between these two terms is the most common source of error in material selection.
What is PTFE?
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is the specific chemical name for a particular fluoropolymer. It is a synthetic material renowned for its exceptional chemical inertness and low coefficient offriction. When engineers refer to the raw material's properties, they are talking about PTFE.
What is Teflon™?
Teflon™ is a registered trademark, not a material. While it is most famously associated with PTFE, the Teflon™ brand is also applied to other fluoropolymers, such as Perfluoroalkoxy alkanes (PFA) and Fluorinated ethylene propylene (FEP).
Think of it like this: all adhesive bandages are not Band-Aids, but Band-Aid is a well-known brand of adhesive bandage. Similarly, not all PTFE is Teflon™, but Teflon™ is the most famous brand of PTFE.
The Real Decision: Choosing the Right Fluoropolymer Gasket
Once you understand that the choice is about the specific polymer, you can focus on the factors that truly matter for gasket performance.
Chemical Resistance
All fluoropolymers offer outstanding resistance to a wide range of chemicals. For most applications, standard PTFE provides more than enough protection. However, for extreme or unusual chemical services, consulting compatibility charts for specific grades is always prudent.
Operating Temperature Range
This is a key differentiator between fluoropolymers. Standard PTFE has a continuous service temperature of around 260°C (500°F).
Other fluoropolymers sold under the Teflon™ brand, like PFA, offer similar temperature resistance but have different mechanical properties at those high temperatures.
Mechanical Properties and Creep
A critical factor for gasket design is creep, or "cold flow." This is the tendency of a material to deform over time under a constant load, which can lead to a loss of sealing pressure.
Standard PTFE is susceptible to creep. For applications requiring high-integrity seals over long periods, filled PTFE grades or other fluoropolymers like PFA may offer superior performance.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a material is always a balancing act. Choosing the right fluoropolymer requires weighing performance benefits against their associated costs and limitations.
The Cost Factor
Standard, virgin PTFE is generally the most cost-effective fluoropolymer option for gaskets.
Specialty polymers like PFA and FEP are more expensive. This cost is driven by their enhanced properties (like better creep resistance or easier processing) and more complex manufacturing processes. Always justify the higher cost with a genuine performance requirement.
The Challenge of "Creep" in PTFE
The primary drawback of standard PTFE in sealing applications is its tendency to cold flow. Over-tightening a PTFE gasket can actually worsen the seal over time by accelerating this process. This must be a central consideration in your design and installation procedures.
Processing and Formability
Standard PTFE is not melt-processable; it is compressed and sintered into shape. In contrast, FEP and PFA are true thermoplastics that can be injection molded. This makes them better suited for highly complex or intricate gasket geometries where sintering PTFE would be impractical.
Making the Right Choice for Your Gasket Design
Your application's primary goal should dictate your material selection. Use this framework as your guide.
- If your primary focus is general chemical service at the lowest cost: Standard PTFE is almost always the correct and most economical choice.
- If your primary focus is minimizing gasket creep and maintaining bolt load: Investigate filled-PTFE options or consider PFA for its superior mechanical stability at temperature.
- If your primary focus is a complex gasket geometry that requires injection molding: Your best option will be a melt-processable fluoropolymer like FEP or PFA.
By focusing on the specific polymer properties instead of the brand name, you ensure your gasket design is optimized for performance and reliability.
Summary Table:
| Factor | PTFE | PFA / FEP |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent for most chemicals | Excellent, similar to PTFE |
| Max. Service Temp. | ~260°C (500°F) | Similar to PTFE, with better high-temp stability |
| Creep Resistance | Low (susceptible to cold flow) | Higher (better for long-term sealing) |
| Cost | Most cost-effective | More expensive |
| Processability | Sintered (not melt-processable) | Injection molding (complex shapes) |
Struggling to select the perfect fluoropolymer for your gasket application? At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components, including custom gaskets, seals, and liners for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise in material science ensures you get the right fluoropolymer—whether it's standard PTFE for cost-effective chemical resistance or advanced PFA for superior creep resistance—perfectly matched to your operational demands. We handle everything from prototypes to high-volume orders with a focus on precision and reliability.
Let our experts guide you to the optimal solution. Contact KINTEK today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications



















