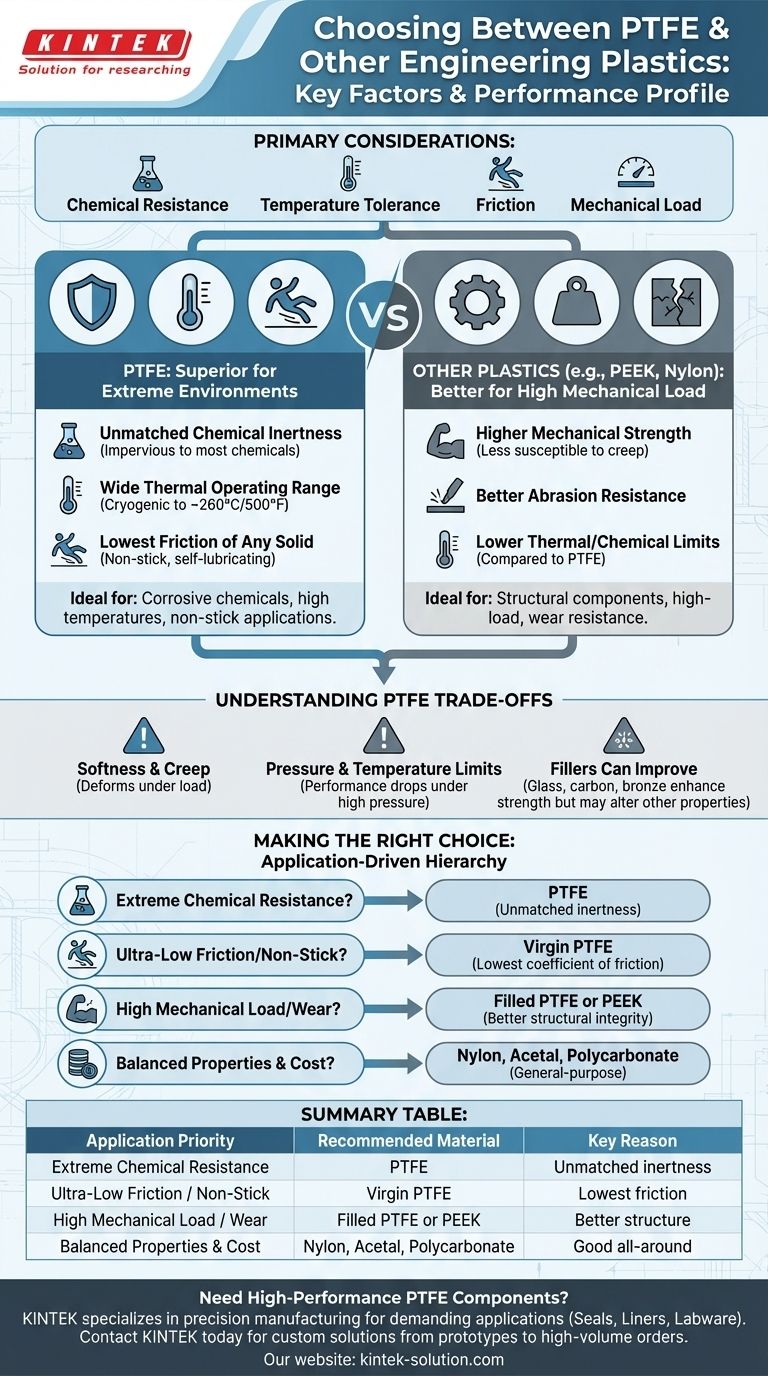
When choosing an engineering plastic, the primary factors to consider are chemical resistance, temperature tolerance, friction requirements, and mechanical load. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is the superior choice for extreme environments characterized by corrosive chemicals, high temperatures, and the need for a non-stick, low-friction surface. However, its relative softness and lower mechanical strength compared to other plastics make it unsuitable for high-load structural applications without modification.
The decision to use PTFE is not a simple comparison of material properties; it is a strategic choice for applications where other plastics fundamentally fail. You choose PTFE when its unique combination of extreme chemical, thermal, and low-friction performance is the only viable solution to a demanding engineering problem.

The Core Performance Pillars of PTFE
To select the right material, you must understand where PTFE provides a distinct, non-negotiable advantage over other engineering plastics like PEEK, Nylon, or Polycarbonate.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
PTFE is virtually impervious to almost all industrial chemicals, solvents, and corrosive agents. This level of chemical resistance is its most significant differentiator.
While materials like PEEK offer good chemical resistance, PTFE provides reliable performance across a much broader spectrum of aggressive media, making it essential for seals, gaskets, and linings in chemical processing.
Wide Thermal Operating Range
PTFE maintains its properties across a vast range of temperatures, from cryogenic levels up to approximately 260°C (500°F).
This thermal stability far exceeds that of many common plastics, ensuring reliability in high-temperature applications where others would degrade or melt.
The Lowest Friction of Any Solid
PTFE has an exceptionally low coefficient of friction, making it one of the most slippery materials known. This property is inherent and does not require external lubrication.
This makes it the ideal choice for non-stick coatings, sliding bearings, and seals where minimizing friction and preventing stick-slip phenomena are critical design requirements. Plastics like Acetal and Nylon cannot match this performance.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting PTFE requires a clear-eyed view of its limitations. Its elite performance in some areas comes at the cost of others, which is a critical consideration for any engineer.
Mechanical Strength and Creep
A primary weakness of virgin PTFE is its relative softness and susceptibility to creep—the tendency to deform permanently under a sustained load.
For applications requiring high structural integrity or abrasion resistance, other plastics like PEEK or even Nylon may be a better choice. PTFE is not a material for high-load structural components.
The Pressure and Temperature (Pr) Limit
While excellent at high temperatures, PTFE's performance can be limited when high pressure is also applied. Most gaskets and seals have a specific pressure-rating value that must be respected.
This is a crucial point: the material's limits are defined by the combination of operational stressors, not just one.
Customization with Fillers
The mechanical weaknesses of PTFE can be mitigated by adding fillers like glass fiber, carbon, or bronze.
These additives significantly improve hardness, wear resistance, and resistance to creep. However, they can slightly alter other properties, such as the coefficient of friction or chemical compatibility, creating another layer of trade-offs to consider.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision should be guided by a clear hierarchy of your application's non-negotiable requirements.
- If your primary focus is extreme chemical resistance: PTFE is almost always the correct choice, especially when dealing with a wide variety of aggressive media.
- If your primary focus is an ultra-low friction or non-stick surface: Virgin PTFE is the unmatched industry standard for applications like self-lubricating bearings or non-stick coatings.
- If your primary focus is high mechanical load or wear resistance: You should consider filled PTFE for moderate loads or look to other engineering plastics like PEEK, Torlon, or metal components for structural applications.
- If your primary focus is a balance of good all-around properties and lower cost: Materials like Nylon, Acetal, or Polycarbonate are often more suitable for general-purpose components that do not face extreme conditions.
Ultimately, choosing the right material is about precisely matching the unique performance profile of the plastic to the specific challenges of your operating environment.
Summary Table:
| Application Priority | Recommended Material | Key Reason |
|---|---|---|
| Extreme Chemical Resistance | PTFE | Unmatched inertness against corrosive agents |
| Ultra-Low Friction / Non-Stick | Virgin PTFE | Lowest coefficient of friction of any solid |
| High Mechanical Load / Wear | Filled PTFE or PEEK | Better structural integrity and creep resistance |
| Balanced Properties & Cost | Nylon, Acetal, Polycarbonate | Good all-around performance for non-extreme conditions |
Need a High-Performance PTFE Component for a Demanding Application?
KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—for industries where failure is not an option. Whether your priority is unmatched chemical resistance in semiconductor processing, reliable thermal stability in medical devices, or low-friction performance in specialized industrial equipment, we deliver.
We offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, ensuring your components are perfectly matched to your operational environment.
Contact KINTEL today to discuss your project requirements and get a quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech



















