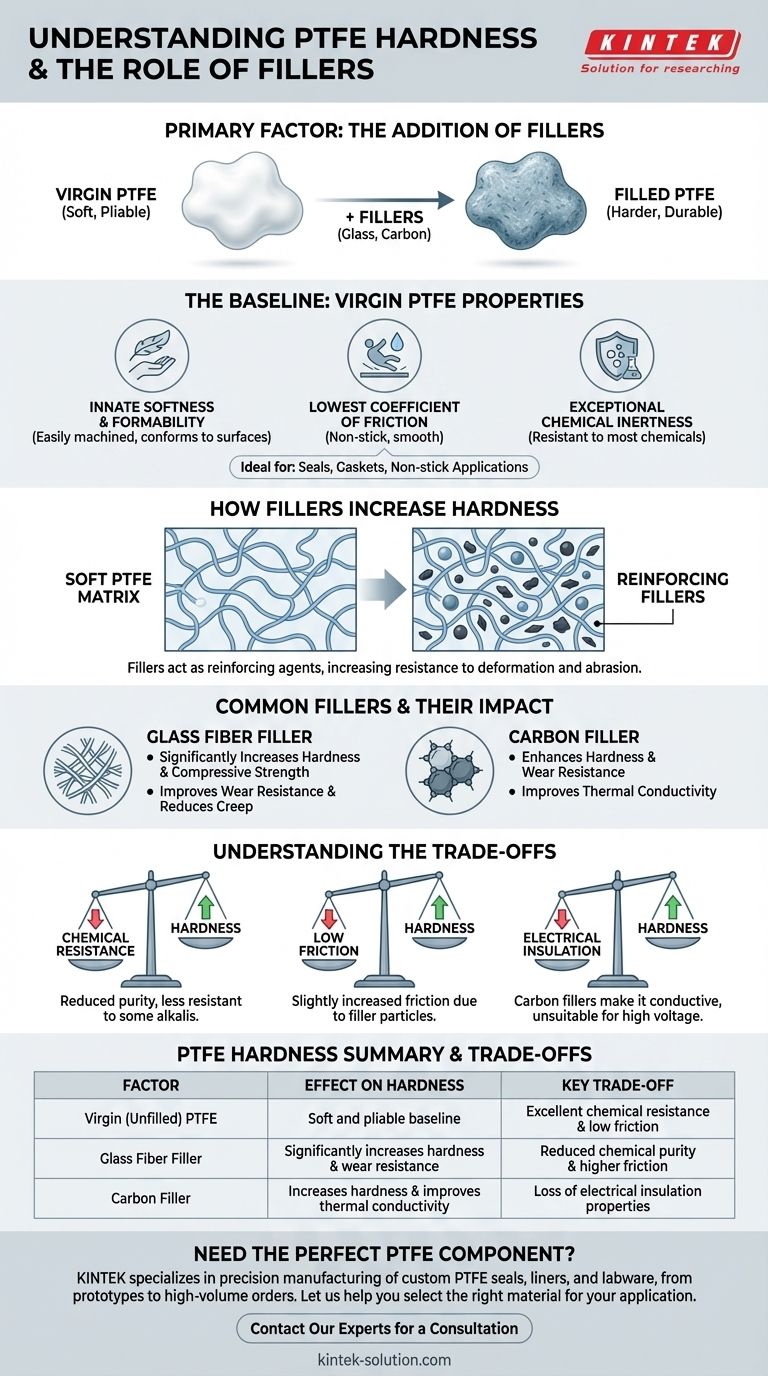
The hardness of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is primarily influenced by one key factor: the addition of fillers. While virgin PTFE is famously soft and pliable, incorporating reinforcing materials like glass fiber or carbon fundamentally alters its mechanical properties. These additives integrate into the PTFE matrix, increasing its overall hardness, stiffness, and durability for more demanding applications.
While virgin PTFE is known for its inherent softness and extremely low friction, its hardness is intentionally modified through the use of additives. The core principle is that incorporating fillers transforms the material from a soft, pliable polymer into a more robust composite, trading some of its natural characteristics for enhanced mechanical strength and wear resistance.

The Baseline: Understanding Virgin PTFE
Before modifying its hardness, it's essential to understand the inherent properties of pure, unfilled PTFE. These characteristics define its performance in its natural state and highlight the reasons why modification is sometimes necessary.
Innate Softness and Formability
Virgin PTFE is a relatively soft polymer. This softness allows it to be easily formed and machined, and it enables the material to conform to irregular surfaces, making it an excellent choice for seals and gaskets.
The Lowest Coefficient of Friction
Often cited as the most slippery solid material known, pure PTFE has an exceptionally low coefficient of friction. This property is critical for applications requiring smooth, non-stick surfaces, such as in low-friction bearings or non-stick coatings.
Exceptional Chemical Inertness
PTFE is resistant to nearly all industrial chemicals, acids, and solvents. This chemical stability, combined with its non-toxic nature, makes it a default choice for use in corrosive environments and food-grade applications.
How Fillers Increase Hardness
To overcome the mechanical limitations of virgin PTFE, fillers are compounded into the raw material. This creates a composite material with significantly different properties.
The Role of Reinforcing Additives
Fillers act as a reinforcing agent within the soft PTFE matrix. These microscopic particles are much harder than the surrounding polymer, effectively increasing the material's resistance to deformation and abrasion.
Common Filler: Glass Fiber
Glass fibers are a common additive used to significantly increase the hardness and compressive strength of PTFE. This makes the material more rigid and substantially improves its resistance to wear and creep under load.
Common Filler: Carbon
Adding carbon as a filler also enhances hardness and wear resistance. Furthermore, carbon can improve the thermal conductivity of the composite, allowing heat to dissipate more effectively in high-speed bearing applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Modifying PTFE with fillers is not a simple upgrade; it is an engineering trade-off. Enhancing one property, like hardness, often comes at the expense of another.
Sacrificing Purity and Chemical Resistance
Fillers are not as chemically inert as pure PTFE. The addition of glass or other materials can reduce the composite's overall resistance to certain aggressive chemicals, particularly strong alkalis.
Increasing the Coefficient of Friction
While still very low, the coefficient of friction for filled PTFE is higher than that of virgin PTFE. The hard filler particles disrupt the uniquely slippery surface, introducing more frictional resistance.
Impact on Electrical Properties
Virgin PTFE is an outstanding electrical insulator. However, additives like carbon are electrically conductive. Adding carbon will drastically reduce the material's dielectric strength, making it unsuitable for high-voltage insulation applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your choice between virgin and filled PTFE depends entirely on the primary demands of your application. There is no universally "better" option, only the one best suited for the task.
- If your primary focus is maximum slipperiness, chemical purity, or electrical insulation: Virgin (unfilled) PTFE is the superior choice for its unmatched lubricity and inertness.
- If your primary focus is wear resistance, stiffness, or load-bearing capability: A filled PTFE, such as one with glass or carbon, will provide the necessary mechanical performance that virgin PTFE lacks.
Ultimately, understanding the role of fillers empowers you to select the precise grade of PTFE that meets your engineering requirements.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Effect on PTFE Hardness | Key Trade-off |
|---|---|---|
| Virgin (Unfilled) PTFE | Soft and pliable baseline | Excellent chemical resistance & low friction |
| Glass Fiber Filler | Significantly increases hardness & wear resistance | Reduced chemical purity & higher friction |
| Carbon Filler | Increases hardness & improves thermal conductivity | Loss of electrical insulation properties |
Need the Perfect PTFE Component for Your Application?
Choosing between virgin and filled PTFE is critical for performance. KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, and labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We prioritize precision production and offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders to ensure your parts meet exact hardness, chemical resistance, and wear requirements.
Let us help you select the right material and fabricate a solution that optimizes your design.
Contact our experts today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Volumetric Flasks for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Use
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability



















