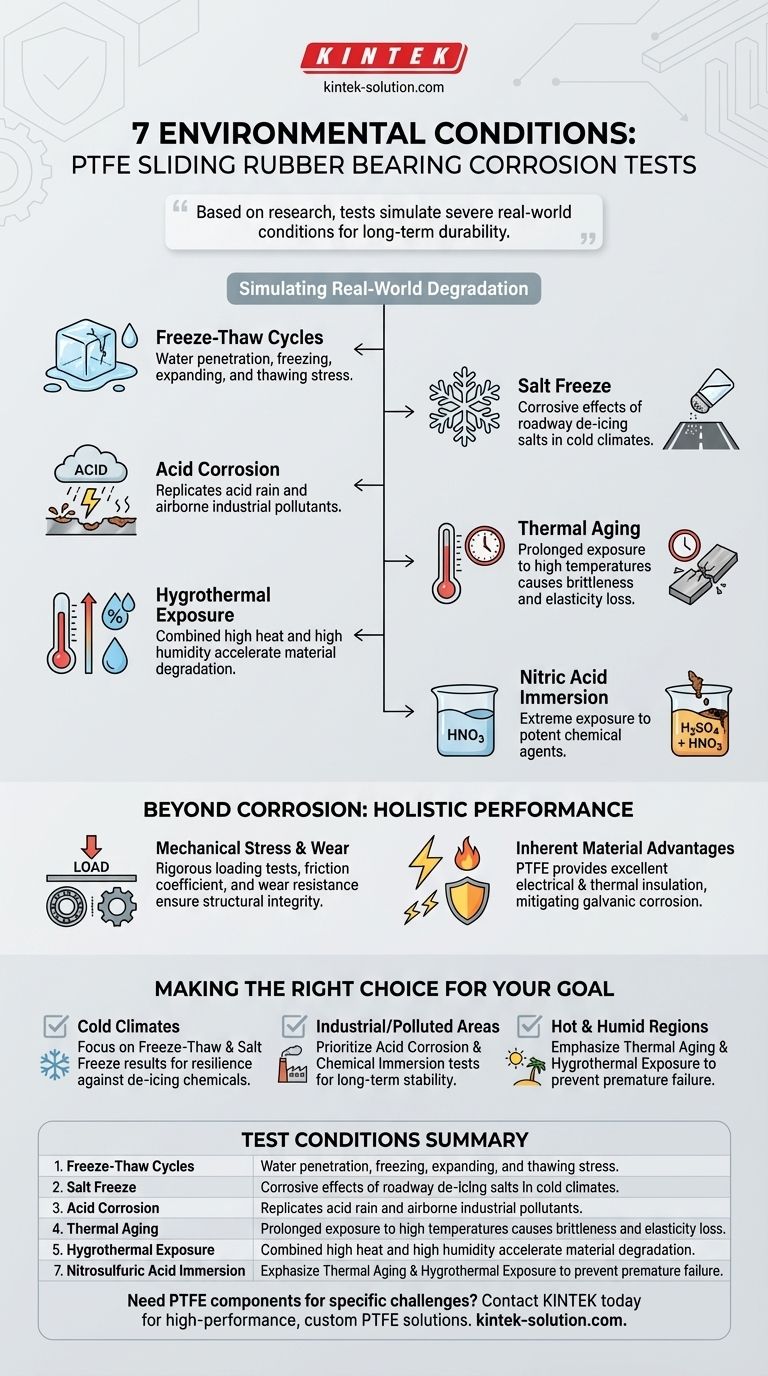
Based on the research, seven specific environmental conditions were studied to evaluate the corrosion and degradation of PTFE sliding rubber bearings. These include freeze-thaw cycles, salt freeze, acid corrosion, thermal aging, hygrothermal exposure, nitric acid immersion, and nitrosulfuric acid immersion.
The core purpose of this rigorous testing is to simulate the most severe real-world conditions a bridge bearing will face. This ensures the component's long-term durability and performance by assessing its resistance to environmental degradation, not just mechanical stress.

Simulating Real-World Degradation
To ensure reliability, PTFE sliding rubber bearings are subjected to a battery of tests that mimic decades of harsh environmental exposure. Each test targets a specific, common cause of material failure in civil infrastructure.
Freeze-Thaw and Salt Freeze Cycles
Freeze-thaw cycles simulate the physical stress caused by water penetrating the material, freezing, expanding, and then thawing.
The salt freeze test is even more aggressive, representing the highly corrosive effect of de-icing salts used on roadways in cold climates.
Chemical and Acid Corrosion
Acid corrosion tests are designed to replicate the effects of acid rain and airborne industrial pollutants, which can chemically attack both the rubber and metal components of the bearing over time.
To accelerate this, bearings are also subjected to nitric acid immersion and nitrosulfuric acid immersion, representing extreme exposure to potent chemical agents.
Heat and Humidity Exposure
Thermal aging evaluates how the bearing's materials withstand prolonged exposure to high temperatures, which can cause rubber to become brittle and lose its elasticity.
Hygrothermal exposure combines high heat with high humidity. This is a critical test as the simultaneous presence of heat and moisture can significantly accelerate material degradation.
Beyond Corrosion: A Holistic View of Performance
While environmental resistance is critical, it is only one aspect of a bearing's performance. A comprehensive evaluation of a PTFE sliding bearing also includes assessing its fundamental mechanical properties.
Mechanical Stress and Wear
In addition to environmental tests, these bearings undergo rigorous loading tests to confirm their vertical and shear capacity.
Friction coefficient and wear resistance tests are also performed specifically on the PTFE plate. These ensure the low-friction sliding surface remains effective and durable throughout the structure's service life.
Inherent Material Advantages
It is also important to recognize the inherent benefits of using PTFE. The material provides excellent electrical and thermal insulation.
This property helps mitigate issues like galvanic corrosion between dissimilar metals and reduces unwanted heat transfer through the structural connection.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding these test conditions allows you to specify the right product for your project's specific environmental challenges.
- If your primary focus is performance in cold climates: Scrutinize the data from freeze-thaw and salt freeze cycle tests to ensure resilience against de-icing chemicals.
- If your primary focus is durability in industrial or polluted areas: The results from acid corrosion and chemical immersion tests are the most critical indicators of long-term stability.
- If your primary focus is reliability in hot and humid regions: Prioritize the findings from thermal aging and hygrothermal exposure tests to prevent premature material failure.
Ultimately, this comprehensive testing provides the necessary confidence that the bearing will maintain its structural integrity for the entire lifespan of the bridge.
Summary Table:
| Environmental Condition Tested | Simulates Real-World Exposure |
|---|---|
| Freeze-Thaw Cycles | Water penetration, freezing, and thawing stress |
| Salt Freeze | Corrosive effects of roadway de-icing salts |
| Acid Corrosion | Acid rain and industrial pollutants |
| Thermal Aging | Prolonged high-temperature exposure |
| Hygrothermal Exposure | Combined high heat and high humidity |
| Nitric Acid Immersion | Extreme chemical agent exposure |
| Nitrosulfuric Acid Immersion | Extreme chemical agent exposure |
Need PTFE components that can withstand your project's specific environmental challenges?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-performance, custom PTFE components—including seals, liners, and labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our precision production and rigorous testing ensure your components deliver unmatched durability and reliability, whether you need prototypes or high-volume orders.
Contact us today to discuss how our PTFE solutions can enhance the longevity and performance of your critical applications.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers



















