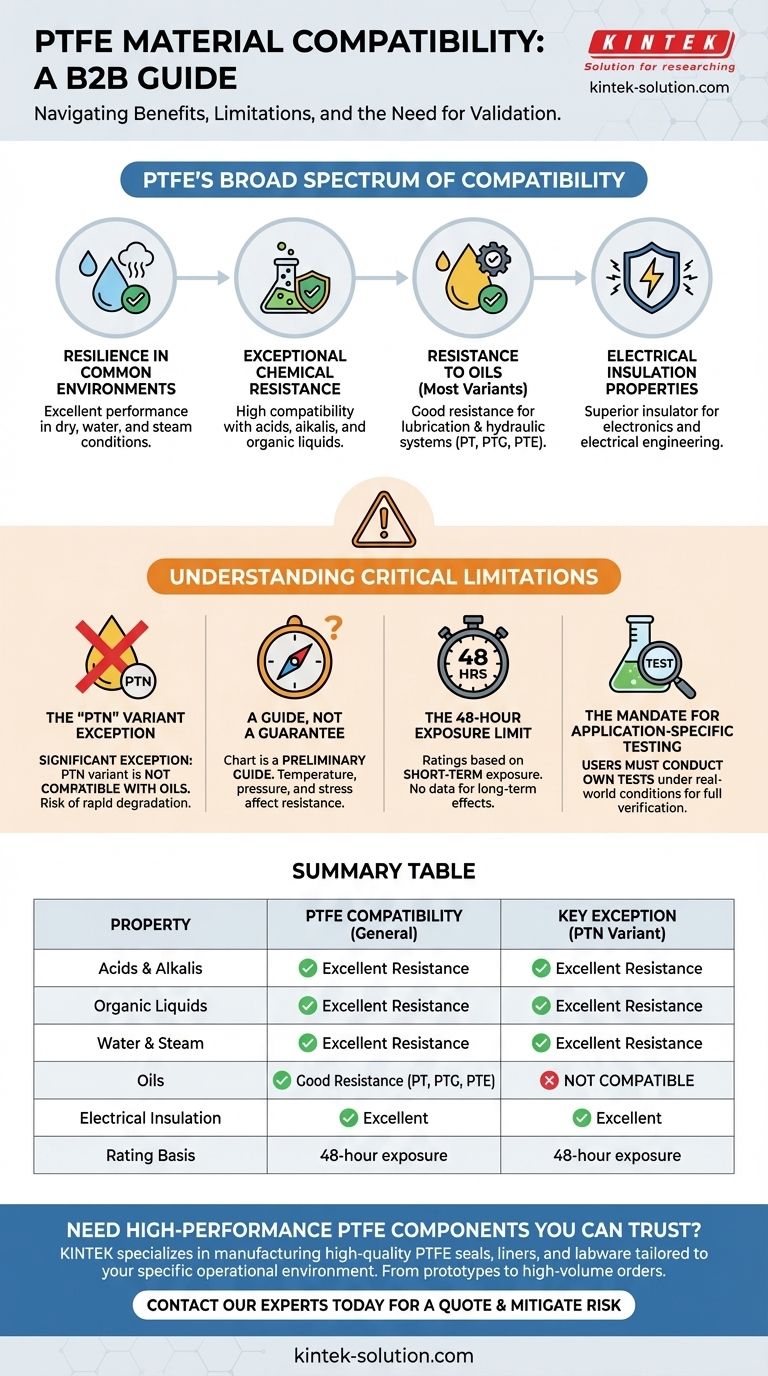
Based on the provided chart, PTFE is a highly versatile material demonstrating excellent compatibility with a wide range of substances. It is generally resistant to water, steam, acids, alkaline solutions, and organic liquids, and also serves as a superior electrical insulator. However, it is critical to note that one specific variant, PTN, is not compatible with oils.
The core takeaway is that while PTFE offers exceptionally broad chemical resistance, compatibility data is a preliminary guide, not a final guarantee. For any critical application, users must conduct their own tests under real-world conditions to confirm suitability.
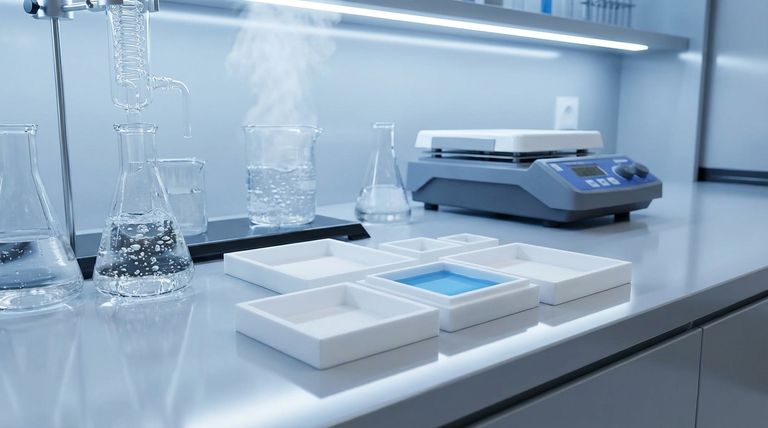

PTFE's Broad Spectrum of Compatibility
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is recognized for its inertness, making it a default choice for many demanding environments. The compatibility chart highlights its reliability across several key areas.
Resilience in Common Environments
PTFE performs exceptionally well in a variety of common conditions. This includes dry environments as well as exposure to water and steam.
Exceptional Chemical Resistance
The material shows high compatibility with aggressive chemical agents. This encompasses strong acids, alkaline solutions, and a wide array of organic liquids.
Resistance to Oils
Most variants of PTFE (specifically codes PT, PTG, and PTE) have good resistance to oils. This makes them suitable for many lubrication and hydraulic systems.
Electrical Insulation Properties
Beyond its chemical resistance, PTFE is listed as an excellent electrical insulator. This property is crucial for applications in electronics and electrical engineering.
Understanding the Critical Limitations
This data must be used with caution. A failure to understand the context and limitations of a compatibility chart can lead to material failure, safety hazards, and costly damage.
The "PTN" Variant Exception
The most significant exception noted is for the PTN variant of PTFE. Unlike other grades, this specific type is not compatible with oils. Misapplying this variant in an oil-based system would likely lead to rapid degradation.
A Guide, Not a Guarantee
The chart must be treated only as a guide. Many factors beyond the chemical itself can affect material resistance, including temperature, pressure, concentration, and mechanical stress.
The 48-Hour Exposure Limit
The provided ratings are based on a 48-hour exposure period. There is no data available on the effects of long-term exposure, which is a critical consideration for permanent installations.
The Mandate for Application-Specific Testing
Because of these variables, the provider of the chart explicitly states that users should conduct their own tests. Only testing under your specific operational conditions can ensure full and lasting compatibility.
Making an Informed Decision with PTFE
Use this data to create a shortlist of materials, not to make a final selection. Your specific goals will determine the necessary level of verification.
- If your primary focus is general chemical handling: PTFE is an excellent candidate, but you must confirm the specific variant you are using and test it against your exact chemical concentrations.
- If your application involves oils: You must explicitly avoid the PTN variant and verify the performance of other PTFE grades for your specific type of oil.
- If your application is for a long-term or critical system: The chart data is insufficient as a standalone resource; you must conduct your own long-term exposure tests that simulate the system's operational environment.
Ultimately, using this compatibility data wisely means treating it as the first step in a thorough validation process.
Summary Table:
| Property | PTFE Compatibility (General) | Key Exception (PTN Variant) |
|---|---|---|
| Acids & Alkalis | Excellent Resistance | Excellent Resistance |
| Organic Liquids | Excellent Resistance | Excellent Resistance |
| Water & Steam | Excellent Resistance | Excellent Resistance |
| Oils | Good Resistance (PT, PTG, PTE) | Not Compatible |
| Electrical Insulation | Excellent | Excellent |
| Rating Basis | 48-hour exposure | 48-hour exposure |
Need High-Performance PTFE Components You Can Trust?
Navigating material compatibility charts is just the first step. For critical applications in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors, you need components fabricated with precision and a deep understanding of material science.
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-quality PTFE components—including seals, liners, and labware—tailored to your specific operational environment. We offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, ensuring your parts meet exact performance requirements.
Let us help you mitigate risk and ensure reliability. Contact our experts today to discuss your project and receive a quote for PTFE solutions you can depend on.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
People Also Ask
- What is PTFE and what class of plastics does it belong to? A Guide to High-Performance Fluoropolymers
- How does PTFE react to common solvents? Discover Its Near-Total Chemical Immunity
- How was PTFE discovered and developed? From Lab Accident to Essential High-Performance Polymer
- What is PTFE commonly known as and what type of material is it? A Guide to High-Performance PTFE Properties
- What is Teflon and what are its alternative names? Understanding PTFE, the Material Behind the Brand



















