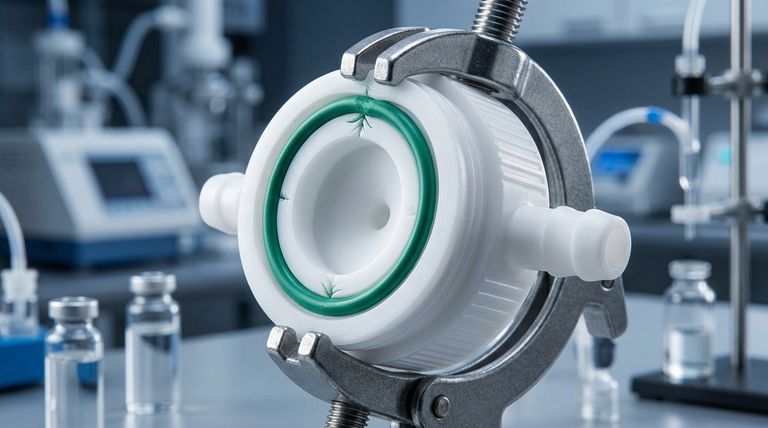
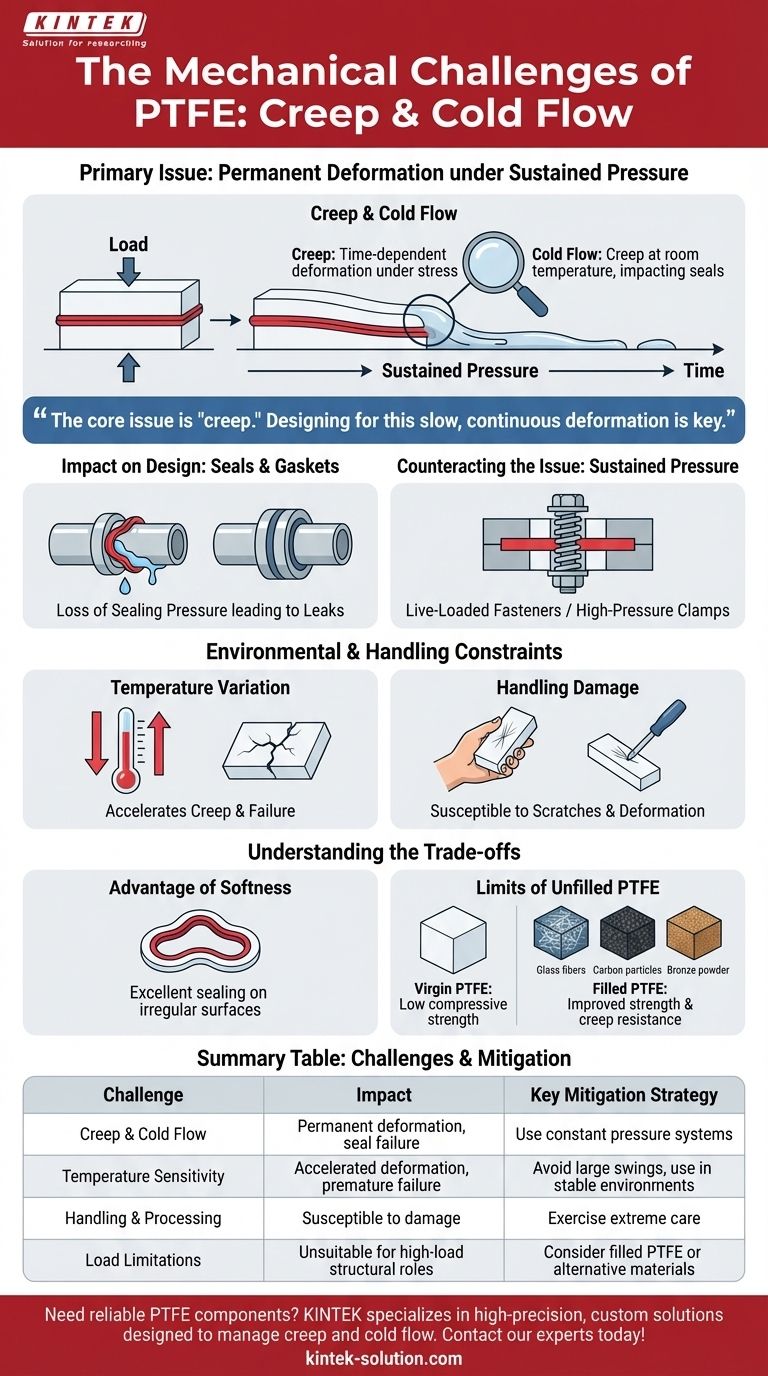
The primary challenges of PTFE's low mechanical strength are its tendencies to creep and cold flow, meaning it deforms permanently under sustained pressure, even at room temperature. This behavior makes it highly sensitive to load and temperature variations, which must be carefully managed in any application.
The core issue with PTFE is not a simple lack of toughness, but a specific material behavior known as "creep." Understanding and designing for this slow, continuous deformation under load is the key to successfully using PTFE in mechanical applications.

The Core Problem: Creep and Cold Flow
PTFE is a polymer, and its molecular structure gives it unique properties. Unlike metals, which deform elastically under normal loads, PTFE can deform permanently over time.
What is Creep?
Creep is the tendency of a solid material to move slowly or deform permanently under the influence of persistent mechanical stress. It is a time-dependent deformation.
For PTFE, this means that a component under a constant load, like a compressed gasket, will continue to slowly compress over weeks, months, or years.
How Cold Flow Impacts Design
Cold flow is essentially creep that occurs at or around room temperature. Because PTFE has a low resistance to this phenomenon, a component can literally "flow" out of its intended shape.
This is a critical consideration for seals and gaskets. If the material flows, the sealing pressure can be lost, leading to leaks.
The Role of Sustained Pressure
To counteract cold flow, PTFE components almost always require constant, managed pressure. This is why it is often used with high-pressure clamps or live-loaded fasteners (using springs).
These systems can follow the material as it deforms, maintaining the necessary force to ensure a proper seal or fit over the component's lifetime.
Application and Environmental Constraints
The inherent weakness of PTFE dictates where and how it can be used effectively. Its performance is directly tied to the stability of its operating environment.
The Challenge of Temperature Variation
PTFE is not recommended for applications with large or frequent temperature swings.
Thermal expansion and contraction, combined with a constant mechanical load, will significantly accelerate creep and material deformation, often leading to premature failure.
Damage During Processing and Handling
The material's low strength means PTFE parts are susceptible to damage. Unfilled PTFE is a soft material.
Care must be taken during machining, installation, and general handling to prevent scratches, gouges, or deformation, all of which can compromise the performance of the final part.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While its low mechanical strength presents challenges, it is also linked to some of its most valuable properties. The key is to leverage its strengths while mitigating its weaknesses.
When Softness is an Advantage
The same properties that lead to creep also make PTFE an excellent sealing material. Its ability to conform to irregular surfaces ensures a tight, void-free seal under the right conditions.
The Limits of Unfilled PTFE
These mechanical limitations are most pronounced in virgin, or unfilled, PTFE. To overcome this, fillers like glass, carbon, or bronze are often added to the polymer.
These filled PTFE grades offer significantly improved compressive strength and resistance to creep, making them suitable for more demanding mechanical roles.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct material requires matching its properties to the demands of the application.
- If your primary focus is a high-load structural component: Unfilled PTFE is almost certainly the wrong choice; consider a filled grade or a different polymer or metal entirely.
- If your primary focus is a gasket or seal in a stable environment: PTFE can be an excellent choice, provided you design for it with appropriate, constant clamping force.
- If your primary focus is an application with significant temperature cycling: Use extreme caution with PTFE and strongly consider materials specifically engineered for thermal stability.
Ultimately, harnessing the benefits of PTFE requires a clear understanding of its inherent mechanical limitations and designing your system accordingly.
Summary Table:
| Challenge | Impact on PTFE Components | Key Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Creep & Cold Flow | Permanent deformation under sustained pressure, leading to seal failure. | Use constant pressure systems (e.g., live-loaded fasteners). |
| Temperature Sensitivity | Accelerated deformation and premature failure with thermal cycling. | Avoid large temperature swings; use in stable environments. |
| Handling & Processing | Susceptible to scratches, gouges, and damage during installation. | Exercise extreme care during machining and handling. |
| Load Limitations | Unsuitable for high-load structural applications in its virgin form. | Consider filled PTFE grades or alternative materials for structural roles. |
Need a PTFE component that performs reliably under pressure?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components—from seals and liners to custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We understand the critical balance between PTFE's superior chemical resistance and its mechanical challenges. Our expertise in custom fabrication ensures your parts are designed and produced to manage creep and cold flow effectively, whether you need prototypes or high-volume orders.
Let us help you design a solution that lasts. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Volumetric Flasks for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Use
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- How does PTFE react to ammonia? Discover Its Superior Chemical Resistance
- What material is the PTFE bottle made from? Discover the Benefits of 100% Virgin PTFE
- What are the chemical resistance properties of PTFE labware? The Ultimate Guide to Inert Labware
- What factors should be considered when choosing between PTFE lined and hard seal butterfly valves? Ensure Optimal Performance and Safety
- What is PTFE (Teflon) and what are its key properties? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance



















