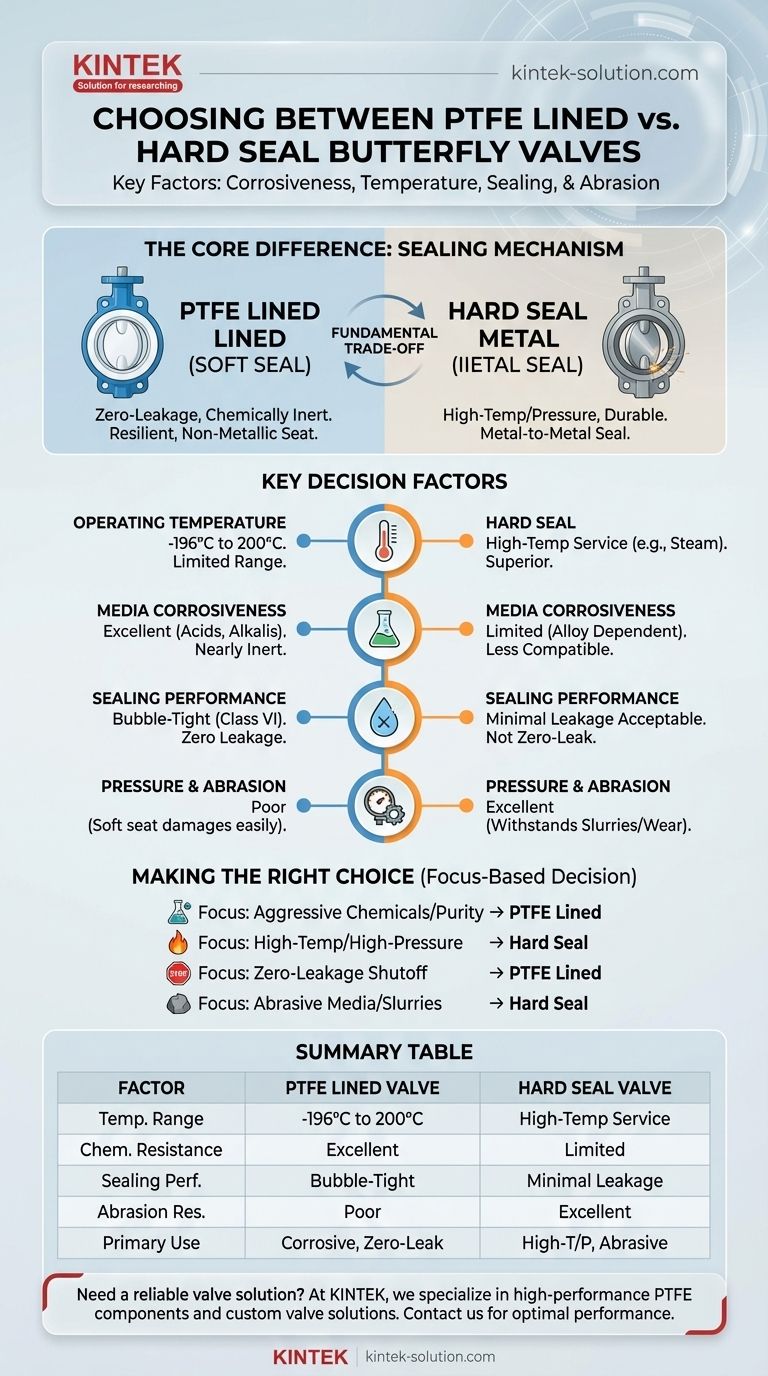
Choosing the right butterfly valve is a critical engineering decision that hinges on four primary factors: the corrosiveness of your media, the operating temperature and pressure, your required sealing performance, and the presence of abrasive particles. PTFE lined valves are the standard for highly corrosive applications requiring a bubble-tight seal, while hard seal valves are built for durability in high-temperature, high-pressure, and abrasive environments.
The decision between a PTFE lined and a hard seal butterfly valve is a fundamental trade-off. You are choosing between the superior chemical resistance and zero-leakage sealing of a soft seal (PTFE) versus the high-temperature and abrasion resistance of a metal-to-metal seal (hard seal).
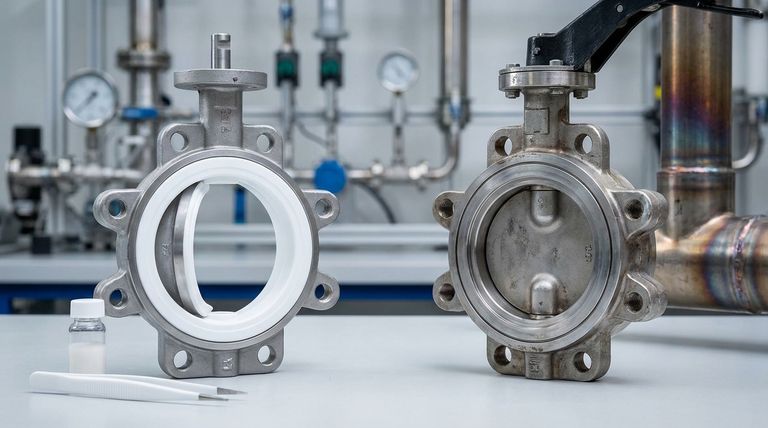

The Core Difference: Sealing Mechanism and Material
The fundamental distinction between these two valve types lies in how they create a seal. This single difference dictates their ideal applications.
PTFE Lined (Soft Seal) Valves
A PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene) lined valve is a type of soft-seated valve. The seal is formed when the valve disc presses against a resilient, non-metallic seat.
The PTFE lining covers all wetted parts of the valve, isolating the valve body from the process media. This creates a tight, zero-leakage (often Class VI) shutoff and provides exceptional protection against chemical attack.
Hard Seal (Metal Seal) Valves
A hard seal valve, as the name implies, uses precisely machined metal sealing surfaces on both the disc and the body. These are often made from stainless steel or other durable alloys.
This metal-to-metal contact is designed for durability under extreme conditions, not for a perfect seal. An acceptable, minimal leakage rate is an expected characteristic of this design.
Key Decision Factors Explained
Your specific operating conditions will point you directly to the correct valve choice. Evaluate each of these factors carefully.
Operating Temperature
This is often the most straightforward deciding factor. PTFE has a distinct operating temperature range, typically from -196°C to 200°C (-320°F to 392°F).
Hard seal valves are engineered for service well above this limit, making them the only viable option for high-temperature applications like steam or thermal fluids.
Media Corrosiveness
If you are handling strong acids, alkalis, or other aggressive chemicals, a PTFE lined valve is almost always the correct choice. PTFE is a nearly inert polymer, providing outstanding protection.
While some metal alloys used in hard seal valves offer corrosion resistance, they cannot match the comprehensive chemical compatibility of PTFE.
Sealing Performance (Leakage Requirements)
The critical distinction is your need for shutoff. If your application demands bubble-tight or zero-leakage shutoff, a PTFE lined valve is necessary.
If a small, specified amount of leakage is acceptable in exchange for durability, a hard seal valve is a suitable choice. They are not designed to be zero-leak valves.
Pressure and Abrasive Media
Hard seal valves are inherently more robust and better suited for high-pressure service.
Furthermore, if your media contains abrasive particles or is a slurry, the metal surfaces of a hard seal valve can withstand the wear and erosion. The soft seat of a PTFE valve would be quickly damaged in such an application.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Every engineering choice involves compromises. Understanding the limitations of each valve type is key to avoiding costly failures.
The Limitation of PTFE: Temperature and Wear
The primary weakness of PTFE is its relatively low temperature limit. It will fail catastrophically if exposed to temperatures beyond its design range. It is also susceptible to damage from abrasive particles, which can tear the liner and compromise the seal.
The Compromise of Hard Seals: Imperfect Sealing
The core trade-off for a hard seal valve is its sealing capability. It is not a zero-leak solution. Specifying a hard seal valve for an application that requires bubble-tight shutoff (like isolating hazardous chemicals) is a common and dangerous mistake.
Lifespan and Maintenance
In a highly corrosive environment, a PTFE lined valve will have a significantly longer lifespan and lower maintenance cost than a metal valve that is slowly degrading. Conversely, a hard seal valve is the only option that will survive long-term in a high-temperature, abrasive process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Use your primary operational goal to make a clear decision.
- If your primary focus is handling aggressive chemicals or ensuring purity: A PTFE lined valve is the correct choice due to its inertness and non-stick surface.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature or high-pressure service: A hard seal valve is mandatory to ensure structural integrity and operational safety.
- If your primary focus is achieving zero-leakage shutoff: A PTFE lined soft-seated valve is the only design that can reliably meet this requirement.
- If your primary focus is managing abrasive media like slurries: A hard seal valve provides the necessary durability to resist wear and erosion.
By aligning the valve's fundamental design with your most critical operational demand, you ensure long-term system reliability and safety.
Summary Table:
| Factor | PTFE Lined Valve | Hard Seal Valve |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range | -196°C to 200°C | High-temperature service (e.g., steam) |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent (ideal for acids, alkalis) | Limited (depends on metal alloy) |
| Sealing Performance | Bubble-tight (Class VI) | Minimal leakage acceptable |
| Abrasion Resistance | Poor (soft seat damages easily) | Excellent (withstands slurries) |
| Primary Use Case | Corrosive media, zero-leakage shutoff | High-temperature, high-pressure, abrasive environments |
Need a reliable valve solution tailored to your specific conditions? At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components, including custom seals, liners, and labware for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you require PTFE lined valves for corrosive applications or need durable solutions for extreme environments, our precision production and custom fabrication—from prototypes to high-volume orders—ensure optimal performance and longevity. Contact us today to discuss your project and let our experts help you achieve superior system reliability!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What makes PTFE suitable for custom industrial parts? Discover the Ideal Material for Harsh Environments
- How does temperature range affect the selection of PTFE packing? Choose the Right Material for Your Application
- What modifications exist for PTFE O-ring temperature performance? Enhance High-Temp Stability with Fillers
- What are the chemical resistance properties of expanded PTFE gaskets? A Guide to Universal Sealing Performance
- What are the key steps for properly installing PTFE seals? Ensure a Leak-Free, Long-Lasting Seal
- What are the primary applications of PTFE fasteners and custom parts? Critical Solutions for Extreme Environments
- What role does temperature stability play in PTFE coated fasteners? Ensuring Reliability in Extreme Environments
- What are PTFE rotary shaft seals and what are they designed for? Solve Extreme Sealing Challenges



















