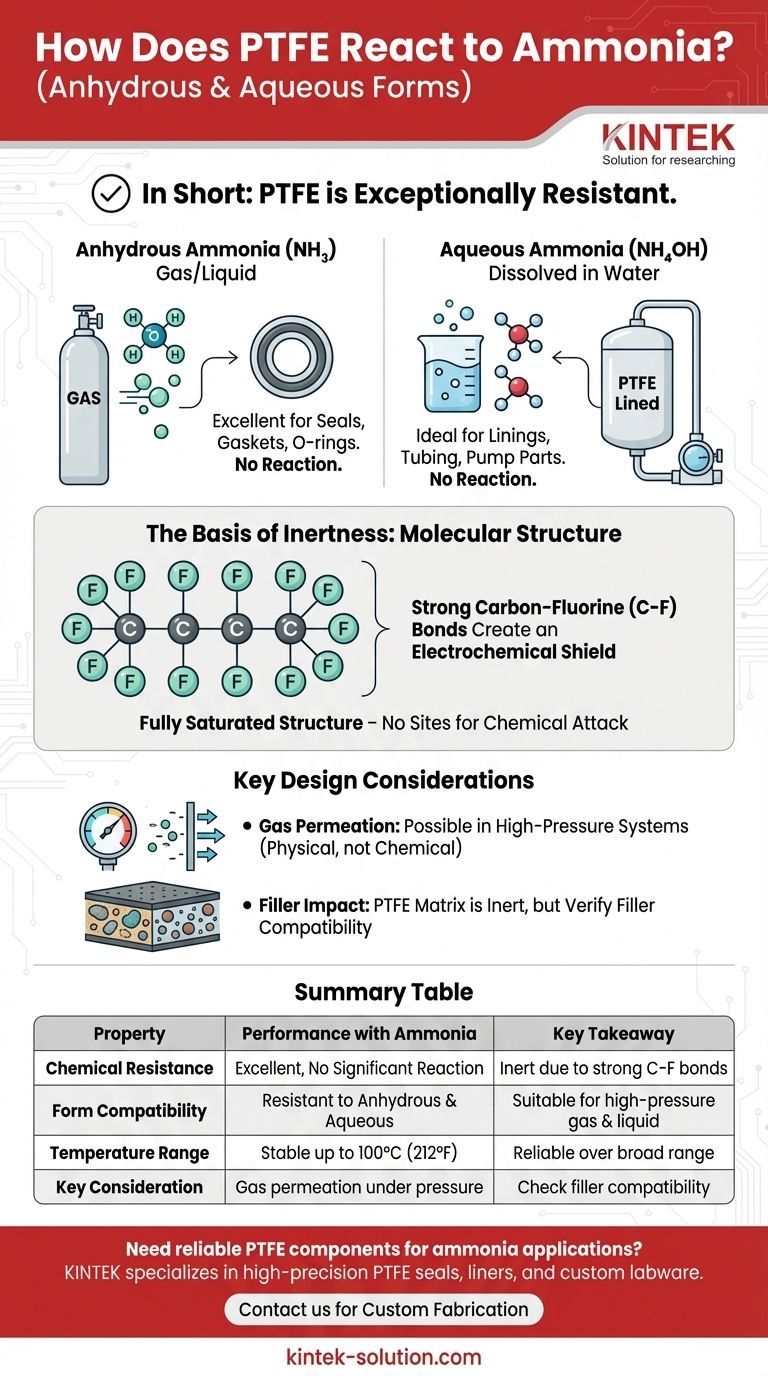
In short, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is exceptionally resistant to ammonia. It demonstrates no significant chemical reaction or degradation when exposed to ammonia in either its anhydrous (pure liquid or gas) or aqueous (dissolved in water) forms. This high level of resistance is maintained across a broad range of temperatures, including up to 100°C (212°F).
The fundamental reason for PTFE's compatibility with ammonia lies in its molecular structure. The incredibly strong carbon-fluorine bonds that define PTFE create a chemically inert and non-reactive surface, making it a premier material choice for demanding ammonia service applications.

The Basis of PTFE's Chemical Inertness
To understand why PTFE is so reliable in this context, we need to look at its fundamental chemistry. Its performance is not an accident but a direct result of its molecular architecture.
The Strength of the Carbon-Fluorine Bond
PTFE is composed of long chains of carbon atoms, where each carbon is completely surrounded and protected by fluorine atoms. The bond between carbon and fluorine is one of the strongest known single bonds in organic chemistry.
This powerful bond creates an electrochemical "shield" around the carbon backbone of the polymer. This shield is extremely difficult for other chemicals, including the polar molecules of ammonia, to penetrate or break.
A Saturated, Non-Reactive Structure
The molecule is also fully saturated, meaning there are no double or triple bonds that could serve as potential sites for chemical attack. This simple, repeating, and well-shielded structure leaves no pathway for ammonia to initiate a chemical reaction.
Performance with Different Forms of Ammonia
While PTFE's core resistance is consistent, it's useful to consider the two primary forms of ammonia used in industrial and commercial applications.
Exposure to Anhydrous Ammonia
Anhydrous ammonia (NH₃) is pure ammonia in its gaseous or pressurized liquid state. It is widely used in industrial refrigeration and chemical manufacturing.
PTFE is completely resistant to anhydrous ammonia. This makes it an ideal material for critical components like valve seats, gaskets, O-rings, and seals in high-pressure ammonia systems where material failure is not an option.
Exposure to Aqueous Ammonia
Aqueous ammonia, also known as ammonium hydroxide (NH₄OH), is ammonia dissolved in water. This solution is a weak base and is common in cleaning products and chemical processing.
PTFE is equally unaffected by aqueous ammonia. Its non-polar nature and chemical stability prevent any reaction with the basic solution, making it a superior choice for pump components, tank linings, and tubing.
Key Considerations for System Design
While chemically inert, a successful implementation of PTFE requires an understanding of its physical properties and how they interact with system demands.
Physical Properties Remain Unchanged
Exposure to ammonia does not compromise the key physical characteristics that make PTFE valuable. Its low coefficient of friction, excellent dielectric strength, and mechanical integrity remain stable, ensuring predictable performance over the long term.
Gas Permeation in High-Pressure Systems
All polymers are permeable to gases to some extent, and PTFE is no exception. While it will not react with ammonia, highly pressurized ammonia gas can slowly permeate through the material.
For applications involving thin-walled PTFE components like tubing or linings under high pressure, the rate of permeation must be a design consideration to prevent unacceptable losses or gas migration. This is a matter of physical transport, not chemical degradation.
The Impact of Fillers
Many applications use "filled" grades of PTFE, where materials like glass, carbon, or graphite are added to enhance properties like compressive strength or wear resistance.
While the PTFE matrix itself is inert to ammonia, the filler material may not be. It is critical to verify that the specific filler in a composite PTFE material is also compatible with your operating environment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
PTFE is an excellent material for ammonia service, but proper selection is based on the specific application.
- If your primary focus is sealing high-pressure anhydrous ammonia: Pure PTFE is an outstanding choice for gaskets and seals, but for thin components, ensure your design accounts for the physical reality of gas permeation.
- If your primary focus is handling aqueous ammonia solutions: PTFE is a top-tier material for wetted components like linings, tubing, and pump parts, offering virtually zero risk of corrosion or material breakdown.
- If you are evaluating a filled grade of PTFE: Always confirm the chemical compatibility of the specific filler material with ammonia to ensure the integrity of the entire composite.
Ultimately, the inherent chemical stability of PTFE makes it one of the most reliable and trusted materials for safe and effective ammonia handling.
Summary Table:
| Property | Performance with Ammonia | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent, no significant reaction or degradation. | PTFE remains inert due to strong carbon-fluorine bonds. |
| Form Compatibility | Resistant to both anhydrous (NH₃) and aqueous (NH₄OH) forms. | Suitable for high-pressure gas systems and liquid solutions. |
| Temperature Range | Stable up to 100°C (212°F). | Reliable performance across a broad operational range. |
| Key Consideration | Gas permeation can occur under high pressure; filler materials may not be compatible. | Design for permeation and verify filler compatibility. |
Need reliable PTFE components for your ammonia applications?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, O-rings, and custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise ensures your systems benefit from PTFE's superior chemical resistance and long-term durability.
Contact us today to discuss your custom fabrication needs, from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Volumetric Flasks for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Use
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- Why is PTFE suitable for cryogenic or high-temperature applications? Unmatched Thermal Stability from -450°F to 500°F
- What are some common applications of machined PTFE? Leverage its Unique Properties for Demanding Applications
- What are the key benefits of PTFE in custom fabrication? Unlock Performance in Extreme Conditions
- What is the working temperature range of PTFE? Master Extreme Heat and Cryogenic Applications
- What is PTFE commonly known as and what are its unique properties? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance



















