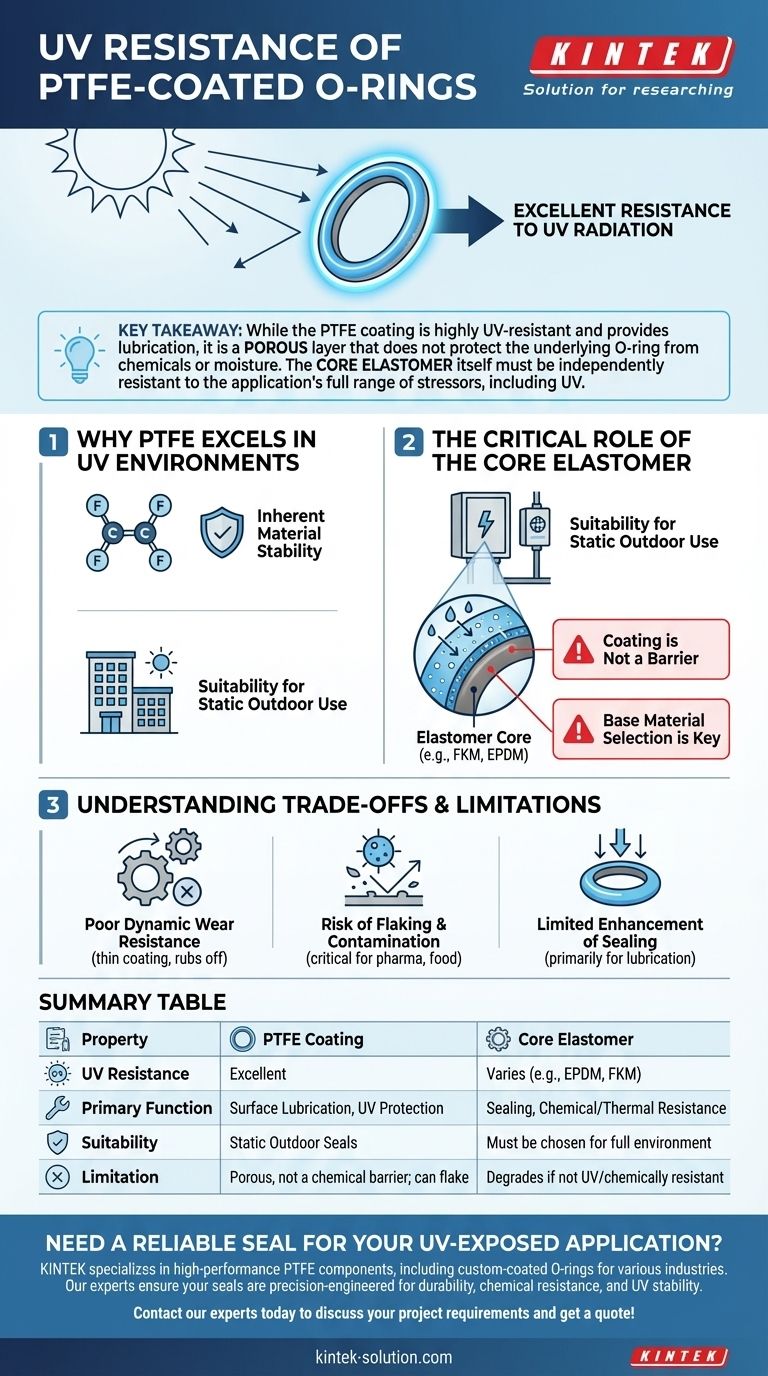
To be clear, PTFE-coated O-rings possess excellent resistance to UV radiation. The inherent chemical stability of polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) makes it highly resilient to degradation from sunlight and other UV sources. This property makes them a frequent consideration for outdoor applications in industries like construction and marine environments.
The central takeaway is that while the PTFE coating provides exceptional UV resistance and surface lubrication, it is a porous layer that does not protect the underlying O-ring. The core elastomer itself must be independently resistant to the application's full range of environmental stressors, including UV, chemicals, and temperature.

Why PTFE Excels in UV-Exposed Environments
The value of a PTFE coating in an outdoor or high-UV setting comes from the fundamental properties of the material itself. It provides a stable outer surface that resists the primary mode of solar degradation.
Inherent Material Stability
The carbon-fluorine bonds that make up PTFE are extremely strong and stable. This molecular structure is not easily broken down by the energy from UV radiation, preventing the material from becoming brittle, discolored, or cracked over time.
Suitability for Static Outdoor Use
Because of this UV stability, PTFE-coated O-rings are well-suited for static sealing applications where they will be constantly exposed to sunlight. This includes sealing electrical enclosures, outdoor equipment, and architectural fixtures.
The Critical Role of the Core Elastomer
Understanding the limitation of the coating is essential for proper seal design. The PTFE layer is a microscopic surface treatment, not an impermeable shield.
The Coating is Not a Barrier
The PTFE coating is porous. It does not provide an additional chemical or environmental barrier for the O-ring itself. Aggressive chemicals or moisture can still permeate the coating and reach the core material.
Base Material Selection is Key
The underlying elastomer (such as FKM, EPDM, or Silicone) must be chosen for its own inherent resistance to the application's environment. If the core material is not UV-stable, it will degrade and fail, regardless of the coating's presence.
Matching All Properties
The core elastomer must be fully compatible with the application's temperature range and chemical media. The PTFE coating primarily adds UV resistance at the surface and reduces friction; it does not enhance the core material's fundamental chemical or thermal properties.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While excellent for UV resistance and low friction, PTFE-coated O-rings have specific drawbacks that make them unsuitable for certain applications. Acknowledging these limitations is critical to preventing seal failure.
Poor Dynamic Wear Resistance
The PTFE coating is thin and can be easily rubbed off in dynamic applications involving sliding or rotation. It functions best as a one-time lubricant to ease installation, not as a durable coating for moving parts.
Risk of Flaking and Contamination
In some applications, the coating can flake off. These microscopic PTFE particles can contaminate the system, which is a critical failure point in industries like pharmaceuticals, food processing, or semiconductors.
Limited Enhancement of Sealing
The primary benefits of the coating are as an inexpensive dry-film lubricant and for color identification. It does not meaningfully improve the O-ring's ability to seal against pressure.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Your decision should be based on the specific demands of your application, weighing the benefits of the coating against its physical limitations.
- If your primary focus is a static seal with high UV exposure: A PTFE-coated O-ring with a UV-stable core like EPDM or FKM is an excellent and cost-effective choice.
- If your application involves dynamic movement or abrasion: Avoid a PTFE coating, as it will wear away quickly. Consider an internally lubricated elastomer or a solid PTFE O-ring instead.
- If system cleanliness is critical: Do not use PTFE-coated O-rings due to the significant risk of particle flaking and contamination.
By correctly identifying the role of both the coating and the core material, you can effectively determine if a PTFE-coated O-ring is the right solution for your design.
Summary Table:
| Property | PTFE Coating | Core Elastomer |
|---|---|---|
| UV Resistance | Excellent | Varies (e.g., EPDM, FKM) |
| Primary Function | Surface lubrication, UV protection | Sealing, chemical/thermal resistance |
| Suitability | Static outdoor seals | Must be chosen for full environment |
| Limitation | Porous, not a chemical barrier; can flake | Degrades if not UV/chemically resistant |
Need a reliable seal for your UV-exposed application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components, including custom-coated O-rings for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise ensures your seals are precision-engineered with the right combination of PTFE coating and core elastomer to withstand harsh environmental conditions.
We provide custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, guaranteeing a solution tailored to your specific needs for durability, chemical resistance, and UV stability.
Contact our experts today to discuss your project requirements and get a quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What design considerations are important for custom PTFE parts? Design for Performance & Reliability
- What challenges arise when machining PTFE (Teflon)? Overcome Softness, Heat, and Instability
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Demanding Applications
- What fabrication services are available for PTFE? Shearing, Stamping, Laser Cutting, Molding & Machining
- What finishing techniques are effective for machined Teflon parts? Achieve Functional Performance and Dimensional Stability



















