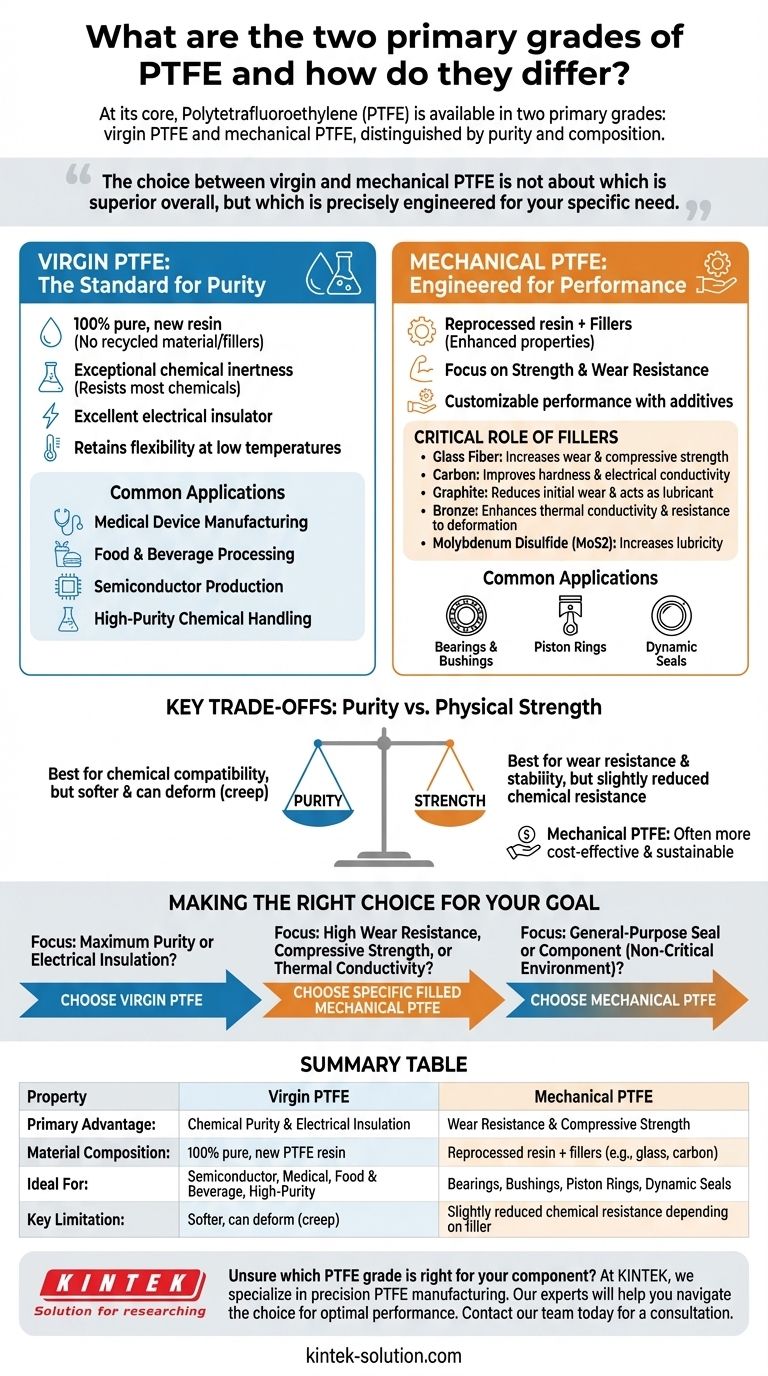
At its core, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is available in two primary grades: virgin PTFE and mechanical PTFE. Virgin PTFE is made from 100% pure, new resin, prized for its exceptional chemical purity and electrical insulation. Mechanical PTFE, by contrast, utilizes reprocessed resin and is often enhanced with fillers to improve specific physical properties like wear resistance and strength.
The choice between virgin and mechanical PTFE is not about which is superior overall, but which is precisely engineered for your specific need. Virgin PTFE offers unmatched purity, while mechanical PTFE provides tailored physical performance for demanding applications.
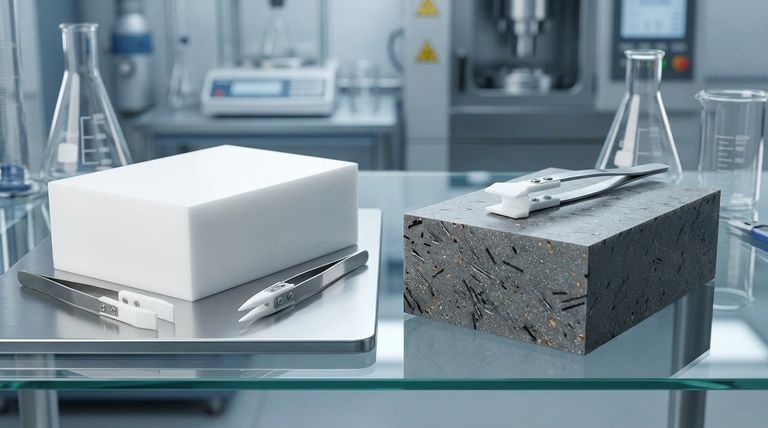

Understanding Virgin PTFE: The Standard for Purity
Virgin PTFE represents the polymer in its purest form. It is manufactured directly from new, unused PTFE resin without the inclusion of any recycled material or reinforcing fillers.
The Foundation of Purity
Because it is made from 100% raw material, virgin PTFE guarantees there are no impurities from previous processing. This makes it the default choice for sensitive applications where contamination is not an option.
Key Characteristics
The defining properties of virgin PTFE are its exceptional chemical inertness, making it resistant to nearly all industrial chemicals, and its excellent performance as an electrical insulator. It also retains its flexibility even at very low temperatures.
Common Applications
Due to these traits, virgin PTFE is indispensable in industries like food and beverage processing, medical device manufacturing, and semiconductor production. It is also a top material for high-purity chemical handling and electrical components.
Understanding Mechanical PTFE: Engineered for Performance
Mechanical PTFE, often called reprocessed or filled PTFE, is designed to overcome some of the natural physical limitations of the pure polymer, such as its softness and tendency to deform under load.
A Focus on Strength
This grade starts with reprocessed PTFE resin, which is then blended with various fillers. These additives are not impurities; they are intentionally included to enhance specific physical characteristics of the final material.
The Critical Role of Fillers
Fillers fundamentally change the material's behavior. The type of additive determines the specific performance boost, allowing for a high degree of customization.
Common fillers and their effects include:
- Glass Fiber: Increases wear resistance and compressive strength.
- Carbon: Improves hardness, compressive strength, and electrical conductivity.
- Graphite: Reduces initial wear and acts as a lubricant.
- Bronze: Enhances thermal conductivity and resistance to deformation.
- Molybdenum Disulfide (MoS2): Increases lubricity for a lower coefficient of friction.
Common Applications
Mechanical PTFE excels in demanding physical environments. It is commonly used for bearings, bushings, piston rings, and dynamic seals where high wear resistance and compressive strength are critical.
Key Trade-offs: Purity vs. Physical Strength
Choosing the correct grade requires a clear understanding of the compromises you are making. Each material is optimized for a different set of challenges.
Purity and Chemical Compatibility
Virgin PTFE is the only choice for applications demanding absolute purity and the broadest range of chemical resistance. While filled PTFE is still highly resistant, certain fillers may react to extremely aggressive chemicals, slightly narrowing their application window.
Wear and Deformation Resistance
Pure PTFE is relatively soft and can deform under sustained pressure (a phenomenon known as "creep"). Mechanical (filled) PTFE is explicitly designed to solve this, offering significantly better wear resistance and dimensional stability under load.
Cost and Environmental Impact
Because it uses reprocessed material, mechanical PTFE can often be a more cost-effective and sustainable option for applications where its enhanced physical properties are a good fit and absolute purity is not required.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the appropriate grade, you must first define your primary engineering objective.
- If your primary focus is maximum chemical purity or electrical insulation: Virgin PTFE is the correct and only choice.
- If your primary focus is high wear resistance, compressive strength, or thermal conductivity: A specific blend of filled mechanical PTFE is required.
- If your primary focus is a general-purpose seal or component in a non-critical environment: Mechanical PTFE often provides the best balance of performance and cost.
Ultimately, selecting the right grade of PTFE is a matter of matching the material's inherent properties to the specific demands of your application.
Summary Table:
| Property | Virgin PTFE | Mechanical PTFE |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Advantage | Chemical Purity & Electrical Insulation | Wear Resistance & Compressive Strength |
| Material Composition | 100% pure, new PTFE resin | Reprocessed resin + fillers (e.g., glass, carbon, bronze) |
| Ideal For | Semiconductor, Medical, Food & Beverage, High-Purity Chemical Handling | Bearings, Bushings, Piston Rings, Dynamic Seals |
| Key Limitation | Softer, can deform under sustained pressure (creep) | Slightly reduced chemical resistance depending on filler |
Unsure which PTFE grade is right for your component?
At KINTEK, we specialize in precision PTFE manufacturing for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our experts will help you navigate the choice between virgin and mechanical PTFE to ensure optimal performance, purity, and cost-effectiveness for your specific application.
We offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, ensuring you get the exact PTFE seals, liners, or labware you need.
Contact our team today for a consultation and let us engineer the perfect PTFE solution for you.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support



















