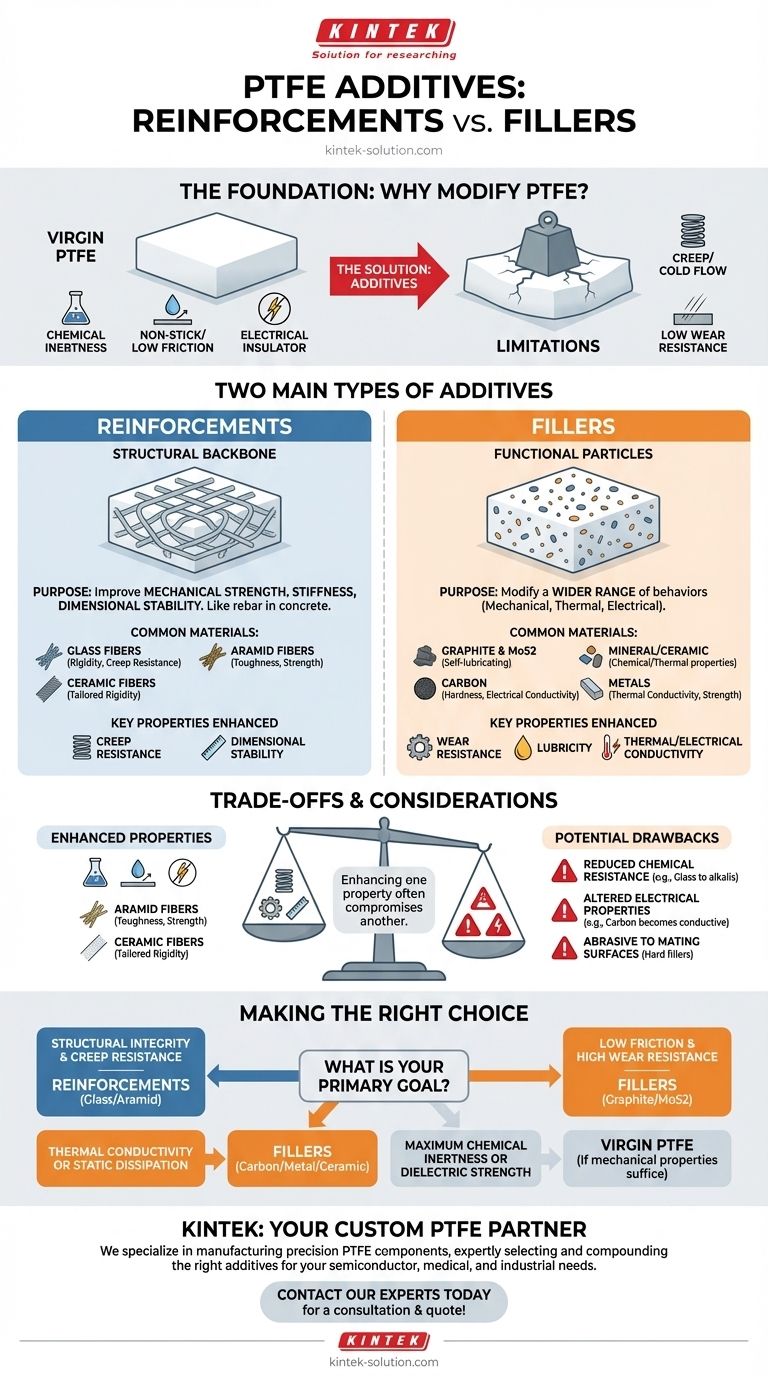
At its core, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is modified using two primary classes of additives: reinforcements and fillers. Reinforcements are added almost exclusively to improve mechanical properties like strength and stiffness. Fillers are more versatile and are used to modify a wider range of characteristics, including mechanical, thermal, and electrical behaviors.
The fundamental distinction is one of purpose. Reinforcements act as a structural backbone to bolster PTFE's mechanical integrity, while fillers are functional particles blended in to fine-tune a broader spectrum of performance properties.

The Foundation: Why Modify PTFE?
The Promise of Virgin PTFE
Pure, or virgin PTFE, is a remarkable material. It is valued for its exceptional chemical inertness, extremely low coefficient of friction (its non-stick quality), and excellent performance as an electrical insulator.
The Inherent Limitations
However, virgin PTFE has significant mechanical weaknesses. It is susceptible to creep (cold flow, or deformation under sustained load) and has relatively low resistance to wear and abrasion. Additives are used to overcome these limitations.
A Closer Look at Reinforcements
The Goal: Enhancing Mechanical Strength
Reinforcements are primarily fibrous materials integrated into the PTFE matrix. Their function is analogous to rebar in concrete—they provide a rigid skeleton that dramatically increases the material's strength, stiffness, and dimensional stability.
Common Reinforcement Materials
The most common reinforcements are fibers that provide structural support.
- Glass Fibers: Often woven into a fabric, they provide excellent rigidity and creep resistance.
- Aramid Fibers: Known for their toughness and strength, they improve the overall durability of the composite.
- Ceramic Fibers: These can be used to enhance rigidity while tailoring other specific properties of the material.
Exploring the Versatility of Fillers
The Goal: Modifying a Spectrum of Properties
Fillers are typically particulate materials mixed into the PTFE resin before it is processed. Unlike reinforcements, their purpose is not just structural. They are used to precisely alter a wide range of behaviors.
Common Filler Materials
Fillers can be chosen to achieve very specific outcomes.
- Graphite & Molybdenum Disulfide (MoS2): These are self-lubricating fillers that further reduce the coefficient of friction and improve wear resistance, making them ideal for bearings and seals.
- Carbon: Often added in powder or fiber form, carbon increases hardness and wear resistance while also improving thermal conductivity and making the PTFE electrically conductive (anti-static).
- Mineral & Ceramic Particles: Fillers like barium sulfate can enhance chemical resistance, while other ceramic particles improve thermal properties.
- Metals: Powdered metals like bronze or stainless steel can be added to significantly increase thermal conductivity and compressive strength.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Cost of Enhancement
Adding any substance to pure PTFE inevitably alters its original profile. Enhancing one property often comes at the expense of another, creating critical trade-offs that must be considered.
Impact on Chemical Resistance
While PTFE is famous for its chemical inertness, some additives can compromise it. For example, glass-filled PTFE has poor resistance to strong alkalis and hydrofluoric acid, which would not affect virgin PTFE.
Altered Electrical Properties
PTFE is an excellent electrical insulator. The addition of conductive fillers like carbon or metal powders will completely change this, transforming the material into a conductor or a static-dissipative material.
Effect on Mating Surfaces
Some harder fillers, while improving the wear resistance of the PTFE component itself, can be more abrasive to the surfaces they run against. This is a critical factor in the design of dynamic seals and bearings.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing the correct additive is entirely dependent on the primary problem you need to solve.
- If your primary focus is structural integrity and creep resistance: Specify a PTFE variant with a reinforcement like glass or aramid fiber.
- If your primary focus is low friction and high wear resistance: Look for PTFE with self-lubricating fillers like graphite or MoS2.
- If your primary focus is thermal conductivity or static dissipation: Your solution will involve a filler like carbon, ceramic, or bronze powder.
- If your primary focus is maximum chemical inertness or dielectric strength: Virgin (unfilled) PTFE is the superior choice, provided its mechanical properties are sufficient.
By understanding the distinct roles of reinforcements and fillers, you can precisely specify a PTFE material that meets your exact engineering requirements.
Summary Table:
| Additive Type | Primary Goal | Common Materials | Key Properties Enhanced |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reinforcements | Improve Mechanical Strength & Stiffness | Glass, Aramid, Ceramic Fibers | Creep Resistance, Dimensional Stability |
| Fillers | Modify a Spectrum of Properties | Graphite, Carbon, Bronze, Ceramics | Wear Resistance, Lubricity, Thermal/Electrical Conductivity |
Need a Custom PTFE Solution for Your Project?
Understanding the difference between reinforcements and fillers is the first step. KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE components—from custom seals and liners to complex labware—by expertly selecting and compounding the right additives for your specific requirements.
We serve the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors, offering custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume production. Let us help you overcome the limitations of virgin PTFE and achieve the perfect balance of properties for your application.
Contact our experts today for a consultation and quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials



















