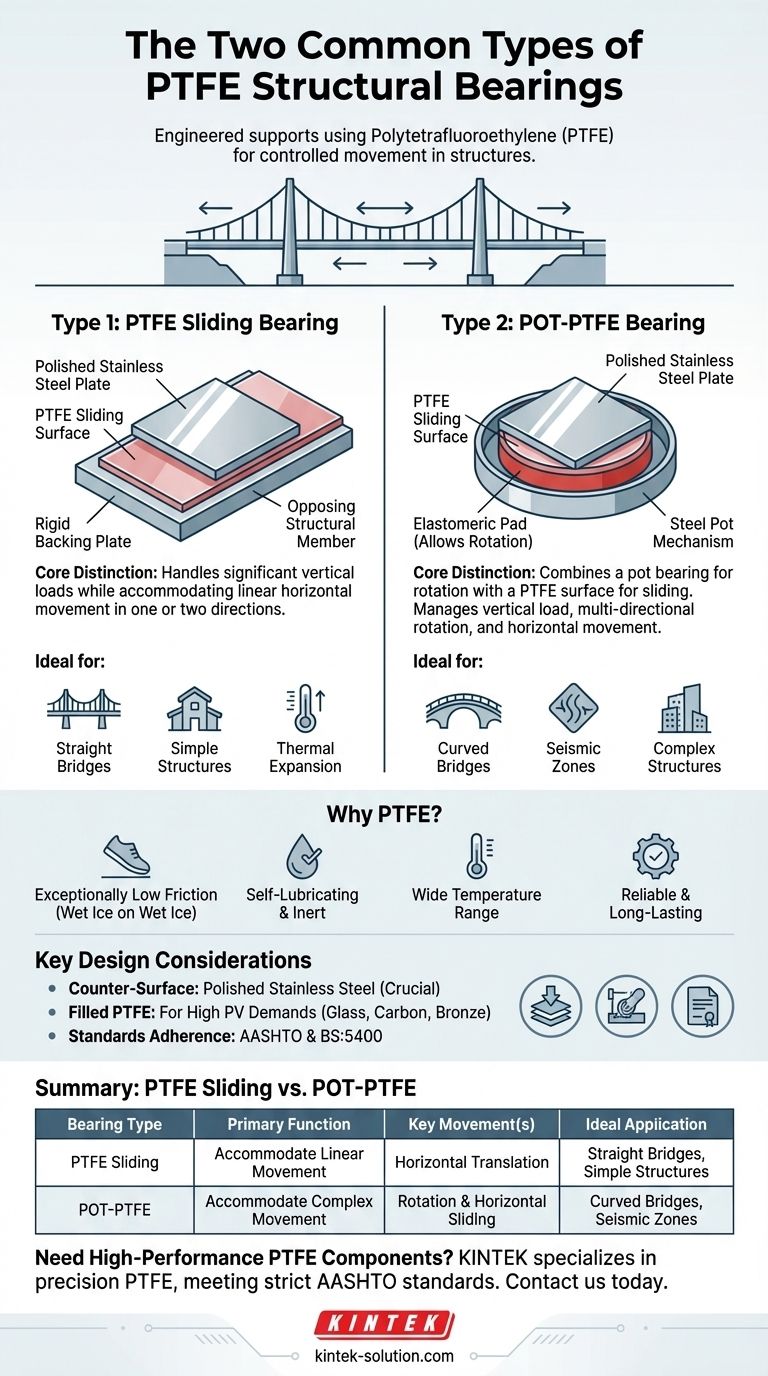
When it comes to engineered structural supports, the two most common types of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) bearings are PTFE sliding bearings and POT-PTFE bearings. Both leverage the exceptionally low friction of PTFE to allow for controlled movement between structural elements, but they are designed to accommodate different types of forces and rotations.
The core distinction lies in their capacity for rotation. A simple sliding bearing only permits linear movement, while a POT-PTFE bearing is engineered to handle both linear sliding and rotational forces, making it essential for more complex structures.

The Fundamental Principle: Why PTFE?
Before comparing the two types, it's critical to understand why PTFE is the material of choice for these high-stakes applications. Its properties make it uniquely suited for managing the immense forces and subtle movements inherent in large structures like bridges and buildings.
The Unique Properties of PTFE
PTFE has an exceptionally low coefficient of friction, often compared to wet ice on wet ice. This allows massive structural components to slide against each other with minimal resistance.
It is also self-lubricating, chemically inert, and capable of performing across a wide range of temperatures. This ensures reliability and longevity without the need for external lubrication or maintenance.
The Role in Structural Engineering
Large structures are not static; they must accommodate movements from thermal expansion and contraction, wind loads, traffic vibration, and even seismic activity.
Structural bearings are the critical interface that allows this movement to occur safely, preventing the buildup of destructive stress within the structure itself.
Differentiating the Two Bearing Types
While both bearings use a PTFE surface to facilitate movement, their internal construction dictates their function and application.
Type 1: The PTFE Sliding Bearing
This is the most straightforward design. It consists of a sheet of PTFE bonded to a rigid backing plate.
A polished stainless steel plate rests on the PTFE surface and is attached to the opposing structural member. As the structure moves, the steel plate glides smoothly over the PTFE.
This bearing is designed to handle significant vertical loads while accommodating horizontal, or translational, movement in one or two directions.
Type 2: The POT-PTFE Bearing
This is a more complex, multi-component system. It combines the features of a "pot" bearing with a PTFE sliding surface.
The "pot" is a shallow steel cylinder containing a confined elastomeric pad. This pad is what allows for rotation or tilting in any direction, much like a ball-and-socket joint.
A PTFE layer is then incorporated on top of the pot mechanism to provide the same horizontal sliding capability as a simple sliding bearing. The result is a bearing that manages vertical load, multi-directional rotation, and horizontal movement.
Understanding Key Design Considerations
The performance of these bearings is not just about the PTFE itself. The entire system, including its materials and adherence to standards, is critical for safety and performance.
The Importance of the Counter-Surface
The effectiveness of the bearing depends on the interaction between the PTFE and the plate sliding against it.
This is why a highly polished stainless steel plate is almost always used as the mating surface. Its smoothness and corrosion resistance are essential for maintaining the system's low-friction properties over decades.
The Role of Filled PTFE
For applications with exceptionally high pressure and velocity (PV) demands, standard PTFE may not be sufficient.
In these cases, filled PTFE—which includes additives like glass fiber, carbon, or bronze—is used. These fillers enhance the material's compressive strength and wear resistance, allowing it to handle more extreme loads without deforming.
Adherence to Engineering Standards
The design and specification of structural bearings are governed by rigorous engineering codes.
Standards like AASHTO (American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials) and BS:5400 (British Standard) ensure that these critical components meet strict requirements for load capacity, movement, and durability.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct bearing type is a foundational decision in structural design, directly impacting the structure's behavior and longevity.
- If your primary focus is accommodating linear thermal expansion in a straight bridge or simple structure: A standard PTFE sliding bearing provides a direct, reliable, and cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is accommodating complex movements, including rotation and deflection (e.g., in a curved bridge or seismic zone): A POT-PTFE bearing is the necessary choice to handle these multi-directional forces safely.
Choosing the right bearing ensures the structure can move as designed, preventing stress concentrations and guaranteeing its long-term integrity.
Summary Table:
| Bearing Type | Primary Function | Key Movement(s) | Ideal Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| PTFE Sliding Bearing | Accommodate linear movement | Horizontal translation | Straight bridges, simple structures with thermal expansion |
| POT-PTFE Bearing | Accommodate complex movement | Rotation & horizontal sliding | Curved bridges, seismic zones, complex structures |
Need High-Performance PTFE Components for Your Structural Project?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE components, including the critical materials used in structural bearings. Our expertise in custom fabrication ensures you get parts that meet the exacting standards of AASHTO and other engineering codes, from prototypes to high-volume orders.
We serve:
- Semiconductor and Industrial equipment manufacturers
- Medical and Laboratory device makers
- Specialized industries requiring durable, low-friction solutions
Let us provide the reliable PTFE that your critical applications demand. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your project requirements and receive a quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments



















