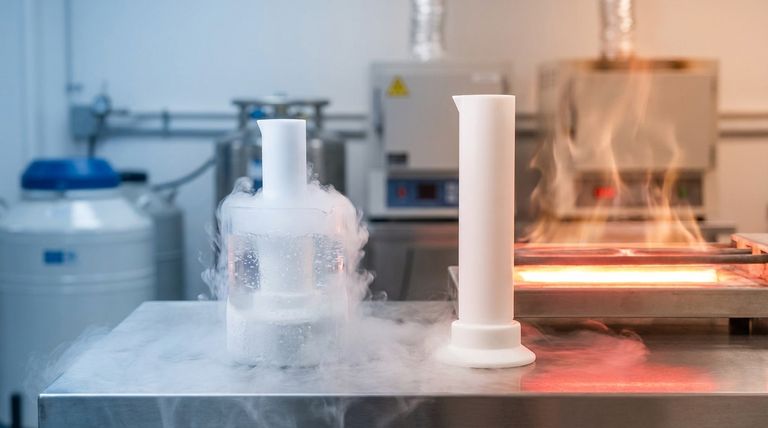
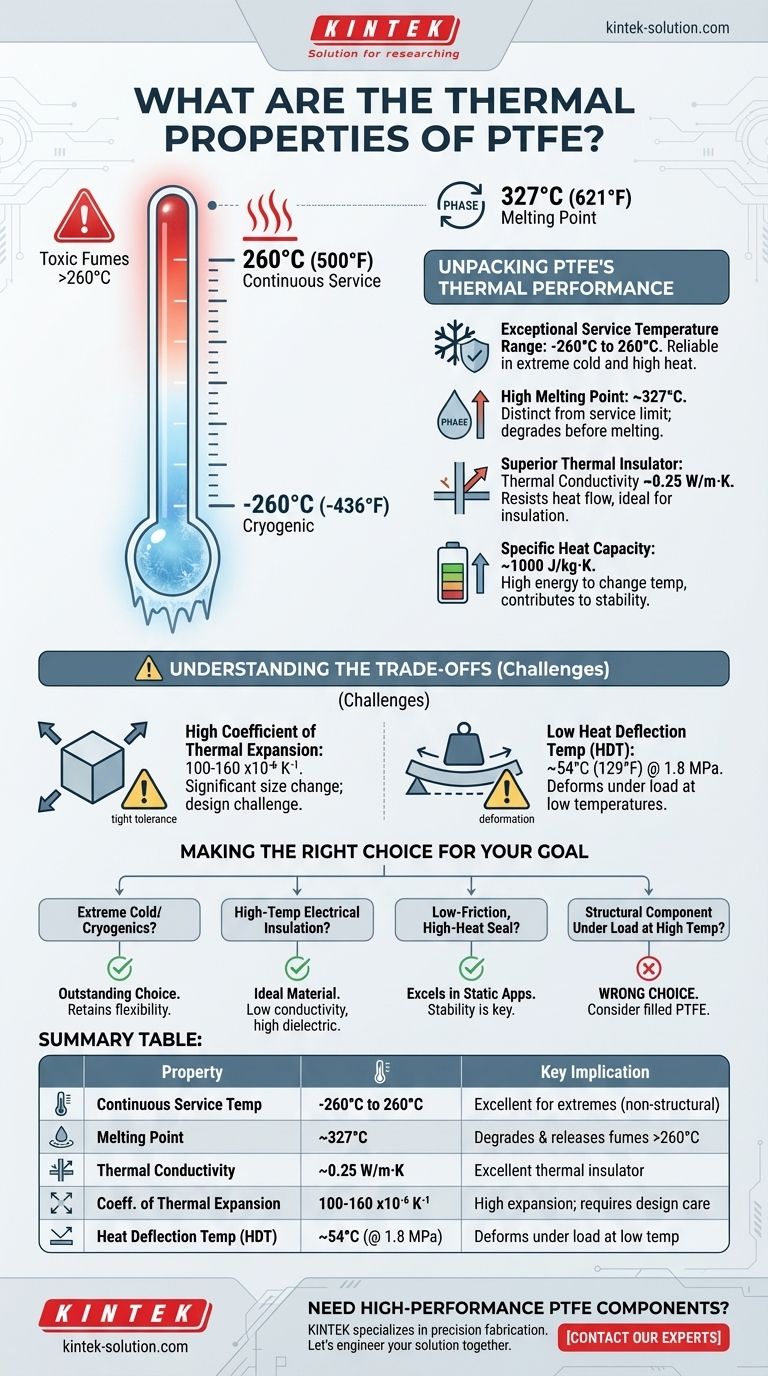
To be direct, PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) possesses exceptional thermal stability, making it one of the most versatile high-performance polymers. It maintains its critical properties across an extremely wide temperature range, from cryogenic conditions at -260°C (-436°F) up to a continuous service temperature of 260°C (500°F). Its high melting point of approximately 327°C (621°F) further underscores its resilience to heat.
The core takeaway is that while PTFE offers a uniquely broad operating temperature range and is an excellent thermal insulator, its practical application is often limited by two critical factors: a high rate of thermal expansion and a low heat deflection temperature, which causes it to deform under load at temperatures far below its maximum service limit.

Unpacking PTFE's Thermal Performance
Understanding PTFE's thermal behavior requires looking beyond its impressive service temperature. Several key properties define its performance, each with distinct implications for engineering and design.
Exceptional Service Temperature Range
PTFE is renowned for its ability to function reliably across a vast temperature spectrum. Its lower working temperature can reach as low as -260°C, making it suitable for many cryogenic applications where other materials would become brittle.
Its upper continuous service temperature is 260°C. Above this point, while the material won't melt, it begins to degrade, releasing potentially harmful fumes—a critical safety consideration.
High Melting Point
The crystalline melting point of PTFE is approximately 327°C. It's important to distinguish this from the service temperature. The melting point is the temperature at which the material undergoes a phase change, whereas the service temperature is the maximum temperature for safe, continuous use without significant degradation of its properties.
A Superior Thermal Insulator
PTFE is an excellent thermal insulator, not a conductor. Its thermal conductivity is very low, around 0.25 W/m·K. This means it resists the flow of heat, making it ideal for applications requiring thermal insulation, such as in high-frequency electronic components where heat management is crucial.
Specific Heat Capacity
The specific heat of PTFE is approximately 1000 J/kg·K. This value indicates that it requires a relatively high amount of energy to raise its temperature. This property contributes to its overall thermal stability, as it does not heat up or cool down instantaneously.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While its stability is a primary advantage, PTFE has thermal characteristics that present significant design challenges. Ignoring these trade-offs is a common source of application failure.
High Coefficient of Thermal Expansion
PTFE has a very high coefficient of thermal expansion, roughly 100-160 x10⁻⁶ K⁻¹. In practical terms, this means a component made from PTFE will change in size significantly more than a metal part would for the same change in temperature.
This must be accounted for in designs with tight tolerances. Mating PTFE parts with metal components requires careful engineering to prevent failure due to expansion or contraction.
Low Heat Deflection Temperature (HDT)
This is arguably PTFE's most critical thermal limitation. The HDT is the temperature at which a material deforms under a specified load. For PTFE, this can be as low as 54°C (129°F) under a load of 1.8 MPa.
This means that even at moderately warm temperatures, PTFE can lose its shape and structural integrity if it is also under mechanical stress. This is why pure PTFE is rarely used for high-temperature structural applications.
Flammability and Safety
PTFE has an excellent flammability rating of V0, meaning it is self-extinguishing and will not propagate a flame. However, when heated above its service temperature of 260°C, and especially above 350°C, it will degrade and release toxic fluorocarbon fumes, which can cause a condition known as polymer fume fever.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting PTFE depends entirely on matching its unique thermal profile to the specific demands of your application.
- If your primary focus is extreme cold or cryogenics: PTFE is an outstanding choice, as it retains its flexibility and properties at temperatures where many materials fail.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature electrical insulation: PTFE's low thermal conductivity and high dielectric strength make it an ideal material for insulating wires and connectors.
- If your primary focus is a low-friction, high-heat seal or gasket: PTFE excels in static applications like these, where its stability up to 260°C is a key advantage and mechanical load is minimal.
- If your primary focus is a structural component under load at high temperatures: Pure PTFE is likely the wrong choice; you must consider its low HDT and high thermal expansion or specify a filled grade of PTFE (e.g., glass- or carbon-filled) to improve its mechanical performance.
Ultimately, harnessing PTFE's remarkable thermal properties requires a clear understanding of both its exceptional stability and its critical mechanical limitations under heat.
Summary Table:
| Property | Value | Key Implication |
|---|---|---|
| Continuous Service Temperature | -260°C to 260°C | Excellent for extreme cold and high heat (non-structural) |
| Melting Point | ~327°C | Degrades before melting; releases fumes above 260°C |
| Thermal Conductivity | ~0.25 W/m·K | Excellent thermal insulator |
| Coefficient of Thermal Expansion | 100-160 x10⁻⁶ K⁻¹ | High expansion/contraction; requires design consideration |
| Heat Deflection Temperature (HDT) | ~54°C (at 1.8 MPa) | Deforms under load at relatively low temperatures |
Need High-Performance PTFE Components That Master Heat and Cold?
PTFE's unique thermal properties make it ideal for demanding applications in semiconductors, medical devices, laboratories, and specialized industrial equipment. However, successfully designing with it requires deep expertise to navigate its trade-offs, like high thermal expansion and low heat deflection.
KINTEK specializes in precision PTFE fabrication. We don't just supply parts; we provide engineering solutions. From custom prototypes to high-volume production of seals, liners, labware, and complex components, we ensure your PTFE parts perform reliably within their thermal limits.
Let's engineer your solution together. Contact our experts today to discuss your project requirements.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
People Also Ask
- Why are PTFE vials considered environmentally friendly? Reduce Lab Waste with Durable Reusables
- What are the primary applications of Teflon? Leverage Its Unique Properties for Your Industry
- What are the primary applications of PTFE? Unlocking High-Performance Solutions
- What makes the PTFE bottle durable? Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Stability for Demanding Applications
- What material is the PTFE bottle made from? Discover the Benefits of 100% Virgin PTFE



















