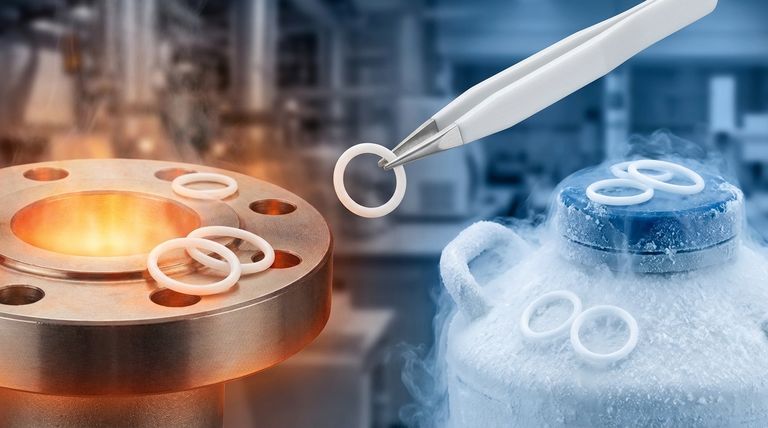
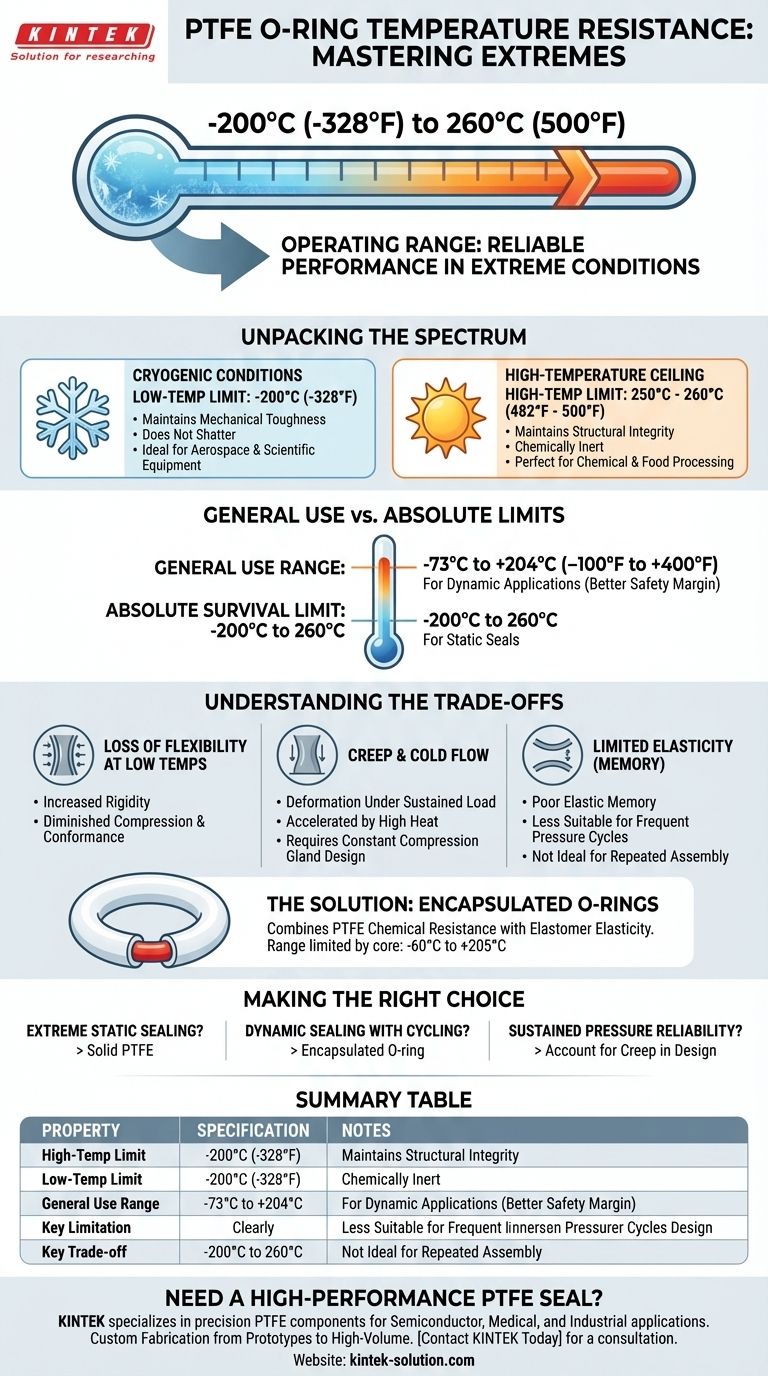
In short, PTFE O-rings operate reliably within a broad temperature range, typically from -200°C (-328°F) to 260°C (500°F). This remarkable thermal stability allows them to function in extreme conditions where most standard elastomer and rubber compounds would quickly fail, making them a specialized solution for demanding applications.
While specific ratings can vary slightly based on the application, the fundamental value of PTFE is its consistent structural integrity and chemical inertness in both cryogenic and high-heat environments.

Unpacking the Full Temperature Spectrum
The wide operating range of PTFE is its defining characteristic. However, it's important to understand the material's behavior at both ends of this spectrum to use it effectively.
The High-Temperature Ceiling
PTFE O-rings perform exceptionally well at high temperatures, with a consistent upper limit of 250°C to 260°C (482°F to 500°F).
Unlike many plastics that melt, PTFE maintains its solid form and chemical structure at these temperatures. This makes it ideal for industries like chemical processing, food production, and automotive systems where high heat is a constant.
Resilience in Cryogenic Conditions
At the other extreme, PTFE maintains its mechanical toughness in deep cold, with a standard low-temperature rating of -200°C (-328°F).
While most materials become extremely brittle and fracture at such low temperatures, PTFE retains its structural integrity. This property is critical for applications in aerospace, space exploration, and scientific equipment.
"General Use" vs. Absolute Limits
You will often see more conservative "general use" temperature ranges, such as -73°C to +204°C.
These ratings provide a wider safety margin and are intended for dynamic applications where the O-ring must remain somewhat flexible to maintain a seal under changing conditions. The broader -200°C to 260°C range represents the material's absolute survival limits, typically for static seals.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While its thermal range is impressive, PTFE is not a universal solution. Its unique mechanical properties introduce critical trade-offs that every engineer must consider.
Loss of Flexibility at Low Temperatures
As PTFE approaches its lower temperature limit, it becomes increasingly rigid. While it does not shatter, its ability to compress and conform to surfaces diminishes significantly.
This stiffness can compromise sealing performance in dynamic applications or where flange surfaces are not perfectly smooth.
Creep and Cold Flow
One of the most significant properties of PTFE is its tendency to "creep" or cold flow. Under sustained compressive load, the material will slowly deform over time.
High temperatures can accelerate this process, potentially leading to a loss of sealing pressure. This must be accounted for in the design of the gland or housing.
Limited Elasticity (Memory)
PTFE is a plastic, not a true elastomer like rubber. It has poor "elastic memory," meaning it does not spring back to its original shape effectively after being compressed.
This makes it less suitable for applications involving frequent pressure cycles or where repeated assembly and disassembly are required.
Encapsulated vs. Solid PTFE
To overcome the lack of elasticity, encapsulated O-rings were developed. These feature a flexible core (like silicone or FKM) inside a thin PTFE shell.
This design combines the chemical resistance of PTFE with the elasticity of an elastomer. However, the temperature range is then limited by the core material, which is often narrower, such as -60°C to +205°C.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct seal requires matching the material's properties to the operational demands.
- If your primary focus is extreme high-heat or cryogenic static sealing: Solid PTFE is an excellent choice, offering unmatched thermal stability where flexibility is not a key requirement.
- If your primary focus is dynamic sealing with temperature cycling: An encapsulated O-ring is likely a better solution, as the elastomeric core provides the necessary resilience that solid PTFE lacks.
- If your primary focus is reliability under sustained pressure: You must account for PTFE's tendency to creep in your design, ensuring the gland provides constant and even compression.
Ultimately, understanding that PTFE's strength lies in its thermal stability, not its elasticity, is the key to deploying it effectively in your design.
Summary Table:
| Property | Specification | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| High-Temperature Limit | 250°C to 260°C (482°F to 500°F) | Maintains structural integrity; ideal for static seals in high-heat environments. |
| Low-Temperature Limit | -200°C (-328°F) | Remains tough and does not shatter; excellent for cryogenic applications. |
| General Use Range | -73°C to +204°C (-100°F to +400°F) | Conservative rating for dynamic applications requiring more flexibility. |
| Key Limitation | Creep (Cold Flow) | Deforms under sustained load; design must account for this property. |
| Key Trade-off | Limited Elasticity | Poor 'memory'; not ideal for frequent pressure cycles without special design (e.g., encapsulated). |
Need a High-Performance PTFE Seal for Extreme Temperatures?
Selecting the right seal is critical for the reliability of your equipment in harsh environments. KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE components, including O-rings, seals, liners, and custom labware.
We provide solutions for:
- Semiconductor manufacturing processes requiring ultra-clean, high-temperature stability.
- Medical and laboratory equipment demanding chemical inertness and reliability from cryogenics to autoclave temperatures.
- Industrial applications where extreme heat or cold would cause standard elastomers to fail.
Our expertise includes custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, ensuring you get a seal perfectly matched to your application's thermal and mechanical demands.
Let our engineers help you solve your toughest sealing challenges. Contact KINTEK today for a consultation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs



















