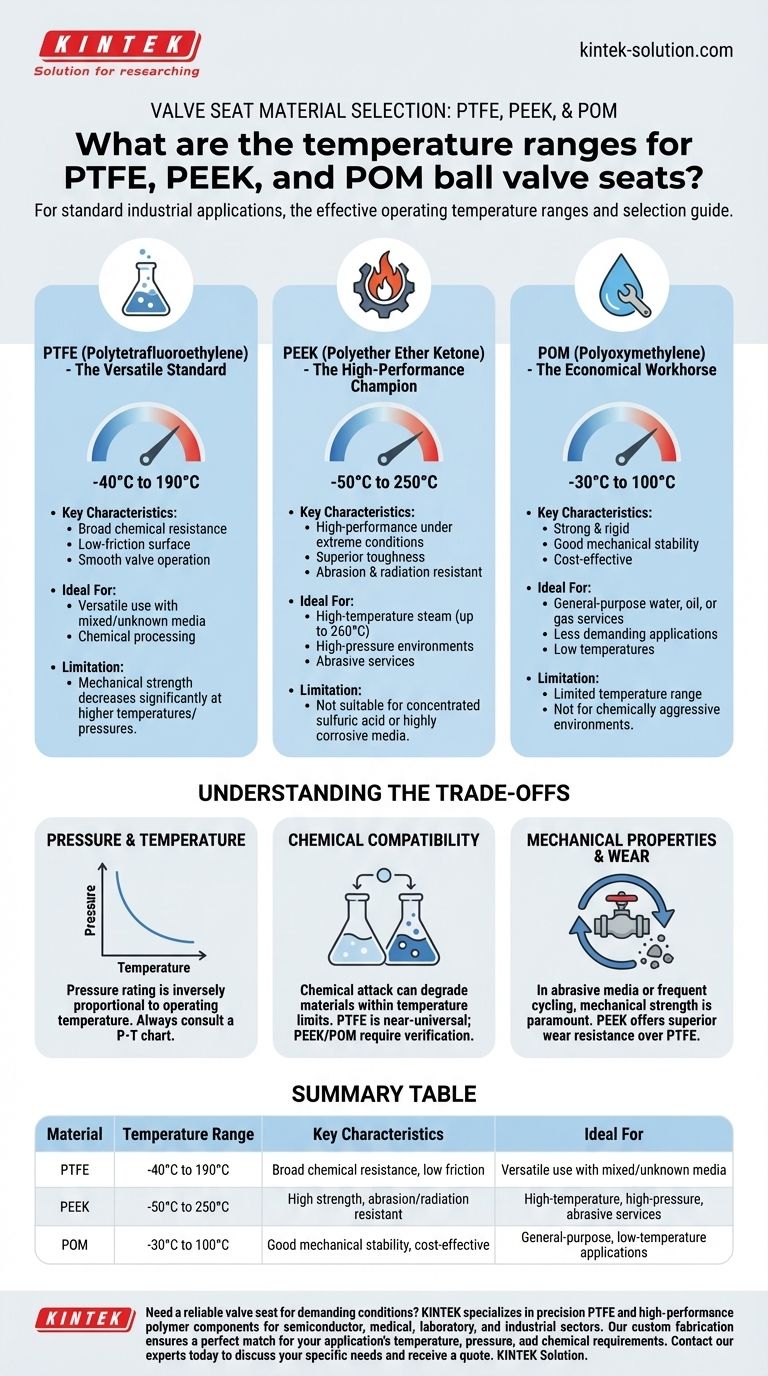
For standard industrial applications, the effective operating temperature ranges for these common ball valve seats are approximately -30°C to 100°C for POM, -40°C to 190°C for PTFE, and -50°C to 250°C for PEEK. These safety-adjusted ranges account for real-world conditions and provide a reliable baseline for material selection.
Selecting the correct valve seat material requires looking beyond a single temperature value. The optimal choice always depends on a careful balance of operating temperature, system pressure, and chemical compatibility.

A Closer Look at Each Material
Understanding the unique profile of each polymer is the first step toward making a sound engineering decision. Each material occupies a distinct niche based on its performance characteristics.
PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene): The Versatile Standard
PTFE is often the default choice due to its exceptionally broad chemical resistance and low-friction surface, which ensures smooth valve operation. It provides an excellent seal in a wide variety of services.
Its primary limitation is its mechanical strength, especially at higher temperatures. As temperatures rise, its ability to withstand pressure decreases significantly.
For example, while PTFE can handle pressures up to 350 bar in smaller valves at ambient temperatures, this rating drops to around 150 bar for larger valve sizes.
PEEK (Polyether Ether Ketone): The High-Performance Champion
PEEK is a high-performance polymer engineered for the most demanding applications. It excels where PTFE fails, particularly in high-temperature and high-pressure environments.
This material is significantly tougher and more resistant to abrasion and radiation than PTFE. It is an excellent choice for services like high-temperature steam (up to 260°C).
However, its chemical resistance is not as universal as PTFE's. PEEK is notably unsuitable for use with concentrated sulfuric acid and other highly corrosive media.
POM (Polyoxymethylene): The Economical Workhorse
POM, often known by trade names like Delrin®, is a strong, rigid polymer valued for its mechanical stability in less demanding applications.
It offers good performance at a lower cost but has a much more limited temperature range, topping out at around 100°C. It is best suited for general-purpose water, oil, or gas services where temperatures and chemical aggression are low.
Understanding the Trade-offs
A material's datasheet provides a starting point, but its real-world performance is dictated by the interplay of multiple factors. Ignoring these trade-offs is a common cause of premature valve failure.
The Pressure and Temperature Relationship
A valve seat's pressure rating is inversely proportional to its operating temperature. As the process fluid gets hotter, the polymer seat softens and loses its ability to resist pressure.
Always consult a pressure-temperature (P-T) chart specific to the valve and material. A seat rated for 200 bar at room temperature might be unsuitable for service above 50 bar at 150°C.
Chemical Compatibility
While temperature is critical, chemical attack can degrade a seat material even within its acceptable temperature range.
PTFE's near-universal compatibility makes it a safe choice for mixed or unknown media. PEEK and POM require more careful verification to ensure they will not be compromised by the process fluid.
Mechanical Properties and Wear
In applications with abrasive media (like slurries) or frequent cycling, mechanical strength is paramount.
PEEK’s superior toughness and abrasion resistance give it a much longer service life in these conditions compared to the softer PTFE.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Use your specific operational needs to guide your selection.
- If your primary focus is broad chemical compatibility and moderate conditions: PTFE is the most reliable and versatile choice.
- If your primary focus is high temperature, high pressure, or abrasive media: PEEK is the clear engineering solution, provided the media is compatible.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose, low-temperature service on a budget: POM offers excellent mechanical performance for less demanding applications.
Choosing the right seat material ensures your valve operates safely and reliably throughout its intended service life.
Summary Table:
| Material | Temperature Range | Key Characteristics | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|
| PTFE | -40°C to 190°C | Broad chemical resistance, low friction | Versatile use with mixed/unknown media |
| PEEK | -50°C to 250°C | High strength, abrasion/radiation resistant | High-temperature, high-pressure, abrasive services |
| POM | -30°C to 100°C | Good mechanical stability, cost-effective | General-purpose, low-temperature applications |
Need a reliable valve seat for demanding conditions? KINTEK specializes in precision PTFE and high-performance polymer components for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our custom fabrication services—from prototypes to high-volume orders—ensure you get a component perfectly matched to your application's temperature, pressure, and chemical requirements. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific needs and receive a quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE and Nitrile Diaphragm Pump Components for Demanding Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments



















