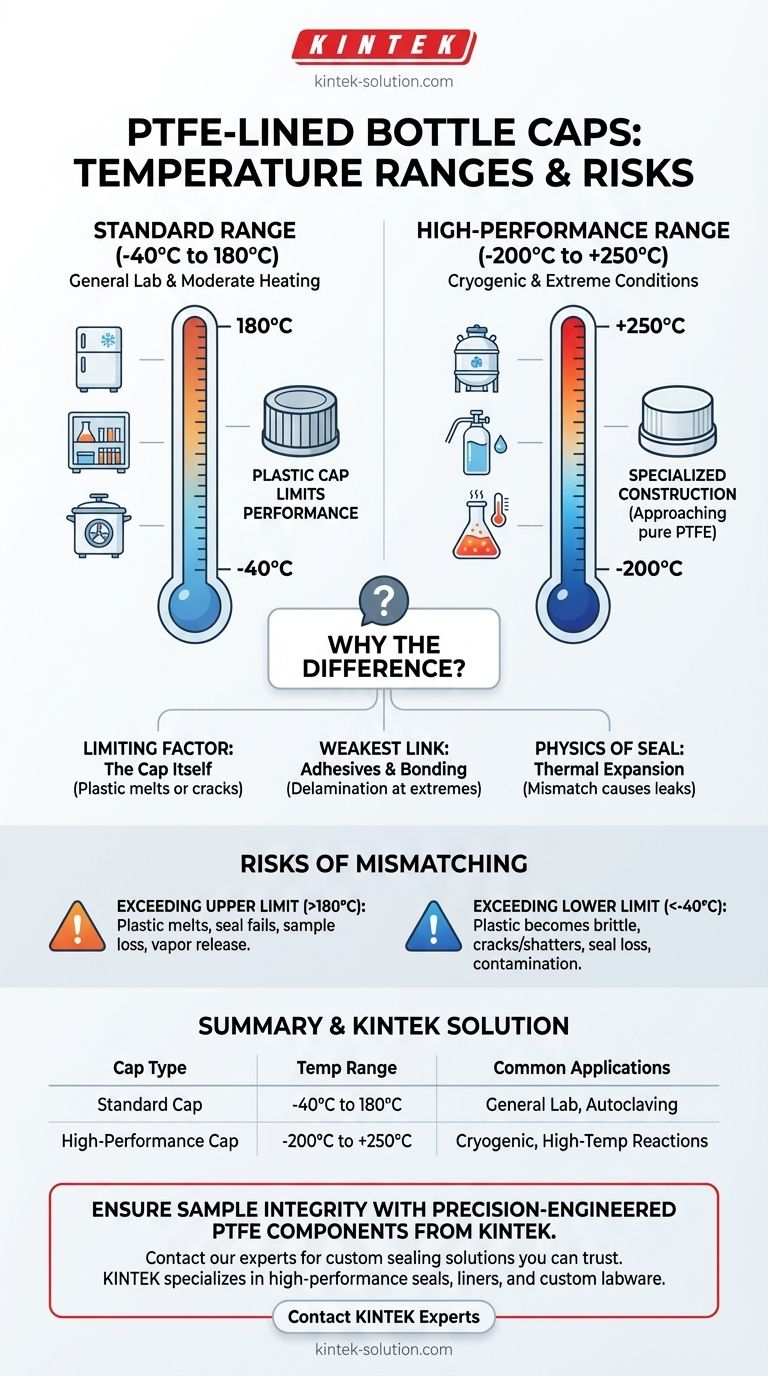
In short, the temperature range depends entirely on the cap's construction. A standard PTFE-lined bottle cap can typically withstand temperatures from -40°C to 180°C. However, high-performance or specialized caps, like those from SSI, extend this range significantly from -200°C to +250°C, approaching the full thermal capability of pure PTFE.
The critical takeaway is that a "PTFE-lined cap" is a multi-component system. While the PTFE liner itself is extremely durable, the cap's overall temperature rating is often limited by its other materials, such as the plastic cap or the bonding adhesive.

Deconstructing the Temperature Ratings
To select the correct cap, you must understand why these different temperature ranges exist. They correspond to different application requirements and cap construction standards.
The Standard Range: -40°C to 180°C
This range is suitable for the vast majority of general laboratory applications.
It safely covers common tasks like refrigeration, freezing, and moderate heating, including most autoclaving cycles (which typically run at 121°C or 134°C).
The High-Performance Range: -200°C to +250°C
This extended range is necessary for more extreme scientific protocols.
These caps are designed for demanding applications such as cryogenic storage in liquid nitrogen or high-temperature reactions and digestions. Their construction ensures all components can withstand these conditions.
Why a Cap's Rating Differs from Pure PTFE
Pure Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a uniquely resilient material with an intrinsic operational temperature range of approximately -200°C to +260°C. The discrepancy between this and a standard cap's rating is due to the other materials in the assembly.
The Limiting Factor: The Cap Itself
Most standard bottle caps are made from plastics like polypropylene, which cannot handle the same temperature extremes as PTFE.
The plastic cap may warp, melt, or become brittle long before the PTFE liner begins to degrade, compromising the seal.
The Weakest Link: Adhesives and Bonding
In some designs, an adhesive is used to bond the PTFE liner to the cap.
This adhesive layer often has a much narrower temperature tolerance than the PTFE and can fail at high or low temperatures, causing the liner to delaminate.
The Physics of the Seal: Thermal Expansion
The plastic cap and the PTFE liner expand and contract at different rates when heated or cooled.
At extreme temperatures, this differential can cause the seal to loosen or fail, leading to leaks or sample contamination. High-performance caps are engineered to account for this effect.
Understanding the Risks of Mismatching
Using a cap outside its specified temperature range is not a matter of performance degradation; it is a matter of catastrophic failure that can compromise your samples and create safety hazards.
Exceeding the Upper Limit
Pushing a standard cap beyond its 180°C limit can cause the plastic to melt, the liner to delaminate, and the seal to fail completely.
This can result in sample loss, atmospheric contamination, or the release of chemical vapors.
Exceeding the Lower Limit
Using a standard cap for cryogenic storage will cause the plastic to become extremely brittle.
The cap is likely to crack or shatter from minor physical stress, leading to a total loss of the seal and potential sample contamination upon thawing.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Always verify the manufacturer's specifications for your specific cap. When in doubt, match the equipment to the demands of your protocol.
- If your primary focus is general lab storage and autoclaving: A standard cap rated for -40°C to 180°C is typically a reliable and cost-effective choice.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature chemistry or analysis: You must source a high-performance cap system specifically rated to handle temperatures up to 250°C.
- If your primary focus is cryogenic storage: Only use caps explicitly designed and rated for cryogenic temperatures (down to -200°C) to prevent physical failure and ensure sample integrity.
Ultimately, choosing the right cap is fundamental to ensuring the stability and safety of your work.
Summary Table:
| Cap Type | Temperature Range | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Standard Cap | -40°C to 180°C | General lab storage, refrigeration, autoclaving |
| High-Performance Cap | -200°C to +250°C | Cryogenic storage, high-temperature reactions, digestions |
Ensure the integrity of your critical samples with precision-engineered PTFE components from KINTEK.
Whether your work involves extreme cryogenic storage, high-temperature reactions, or standard autoclaving, the right sealing solution is paramount. Mismatched components can lead to catastrophic failure, sample loss, and safety hazards.
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We prioritize precision production and offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, ensuring every part meets the exact thermal and chemical demands of your application.
Don't risk your research. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements and secure a sealing solution you can trust.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What is the working temperature range of PTFE? Master Extreme Heat and Cryogenic Applications
- What are some common applications of machined PTFE? Leverage its Unique Properties for Demanding Applications
- What are the base characteristics of PTFE? Unlocking Extreme Performance in Friction, Temperature, and Chemical Resistance
- What are the key benefits of PTFE in custom fabrication? Unlock Performance in Extreme Conditions
- Why is PTFE suitable for cryogenic or high-temperature applications? Unmatched Thermal Stability from -450°F to 500°F



















