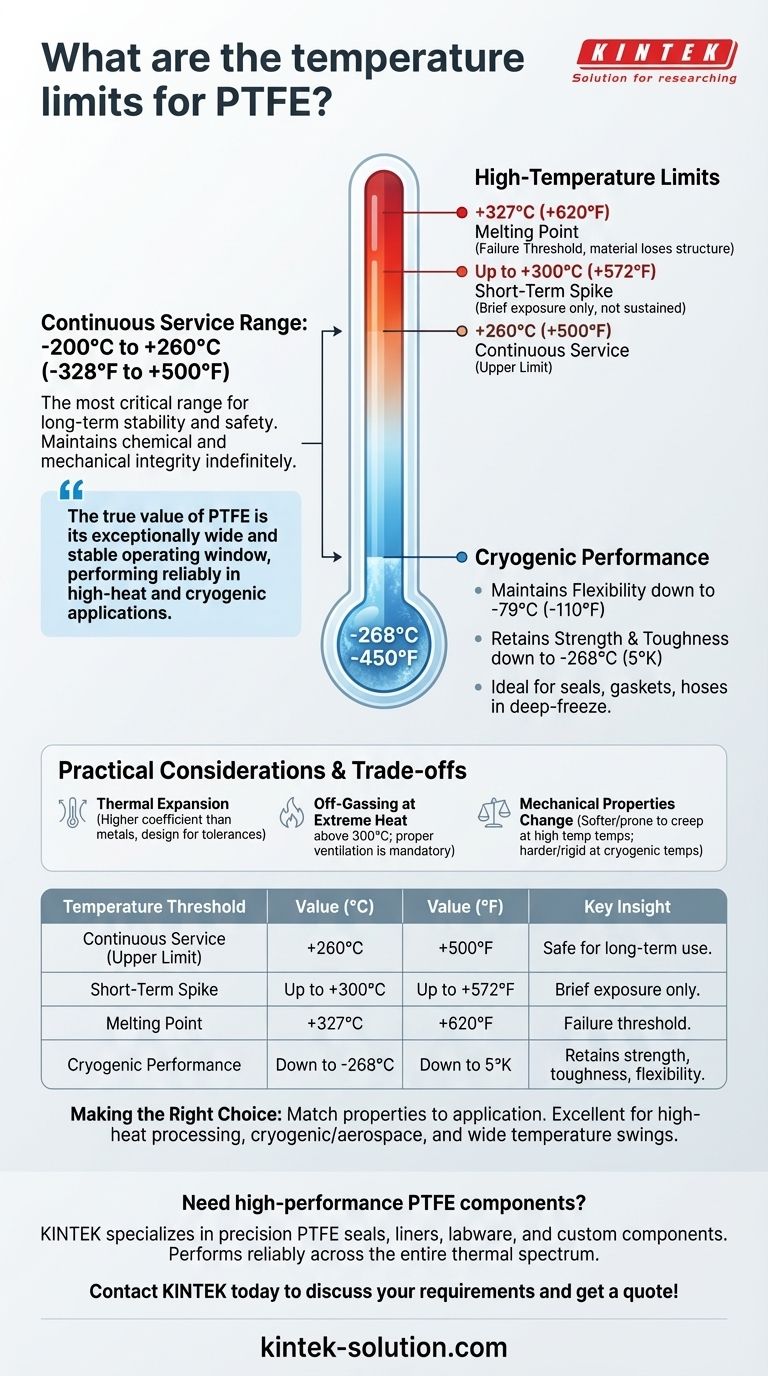
For practical engineering purposes, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) has a continuous service temperature range from approximately -200°C to +260°C (-328°F to +500°F). While its actual melting point is significantly higher at 327°C (620°F), and it retains useful properties at cryogenic temperatures near absolute zero, the 260°C limit is the critical threshold for long-term stability and safety.
The true value of PTFE is not just its high-temperature resistance but its exceptionally wide and stable operating window. Few materials can perform reliably in both high-heat industrial processes and cryogenic applications, making PTFE a uniquely versatile polymer for extreme environments.

Understanding PTFE's High-Temperature Limits
The upper temperature limit is often the first consideration for engineers, but it's important to distinguish between different thermal thresholds.
The Continuous Service Temperature
The most critical number for reliability is the continuous service temperature, which is universally cited as 260°C (500°F). At or below this temperature, PTFE maintains its chemical and mechanical integrity indefinitely without significant degradation.
Short-Term Temperature Spikes
For brief periods, PTFE can withstand slightly higher temperatures. Some sources indicate it can handle intermittent exposure up to 290-300°C (554-572°F), but this is not recommended for sustained operation.
The Melting Point
PTFE's physical melting point is approximately 327°C (620°F). Approaching this temperature causes the material to lose its solid structure. It is crucial to understand that the melting point is a failure threshold, not an operating limit.
PTFE's Performance in Cryogenic Conditions
PTFE's performance at low temperatures is just as remarkable as its resistance to heat. This makes it a go-to material for cryogenic applications where other plastics and elastomers would become brittle and fail.
Maintaining Flexibility
While many materials become rigid and fragile in the cold, PTFE maintains good flexibility at temperatures as low as -79°C (-110°F). This is essential for seals, gaskets, and hoses that must function in deep-freeze conditions.
Retaining Strength and Toughness
Even at extreme cryogenic temperatures, PTFE exhibits high strength and toughness. It remains a functional, self-lubricating material at temperatures as low as -268°C (5°K), which is incredibly close to absolute zero.
Practical Considerations and Trade-offs
While its thermal range is impressive, relying on datasheet numbers alone can be misleading. Understanding the practical limitations is key to successful implementation.
Thermal Expansion
PTFE has a relatively high coefficient of thermal expansion. This means it will expand and contract more than metals with temperature changes, a critical design consideration for components with tight tolerances.
Off-Gassing at Extreme Heat
This is a critical safety consideration. As PTFE approaches and exceeds its maximum service temperature, it begins to decompose and can release toxic fumes. This process accelerates significantly above 300°C, well before its melting point. Proper ventilation is mandatory in any application where PTFE could be overheated.
Mechanical Properties Change with Temperature
While PTFE functions across its thermal range, its mechanical properties are not static. It becomes softer and more prone to creep at its upper temperature limits, while becoming harder and more rigid at cryogenic temperatures. These changes must be factored into any mechanical design.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a material requires matching its properties to the specific demands of your application.
- If your primary focus is high-heat industrial processing: PTFE is an excellent choice for continuous use up to 260°C (500°F) in applications like seals, gaskets, and non-stick coatings.
- If your primary focus is cryogenic or aerospace applications: PTFE is one of the few polymers that retains its strength, toughness, and self-lubricating properties at temperatures approaching absolute zero.
- If your primary focus is an application with wide temperature swings: PTFE's incredible stability from deep cold to high heat makes it a reliable choice for components that must perform across a vast thermal spectrum.
By understanding both the impressive range and the practical limits of PTFE, you can confidently select it for the most demanding thermal environments.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Threshold | Value (°C) | Value (°F) | Key Insight |
|---|---|---|---|
| Continuous Service (Upper Limit) | +260°C | +500°F | Safe for long-term use; maintains integrity. |
| Short-Term Spike | Up to +300°C | Up to +572°F | Brief exposure only; not for sustained operation. |
| Melting Point | +327°C | +620°F | Failure threshold; material loses structure. |
| Cryogenic Performance | Down to -268°C | Down to 5°K | Retains strength, toughness, and flexibility. |
Need high-performance PTFE components that can handle your most extreme temperature challenges?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE seals, liners, labware, and custom components for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise ensures your parts perform reliably across the entire thermal spectrum, from cryogenic applications to high-heat processes.
We offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, prioritizing the precision and material integrity your critical applications demand.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific requirements and get a quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Customizable PTFE Crucibles for Laboratory and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are some exceptional properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Extreme Environments
- Why are PTFE vials considered environmentally friendly? Reduce Lab Waste with Durable Reusables
- What are the common characteristics of Teflon? Unlocking Extreme Chemical and Thermal Resistance
- What are the primary applications of PTFE? Unlocking High-Performance Solutions
- What are the unique properties of PTFE that make it commercially valuable? Unlock Unmatched Performance



















