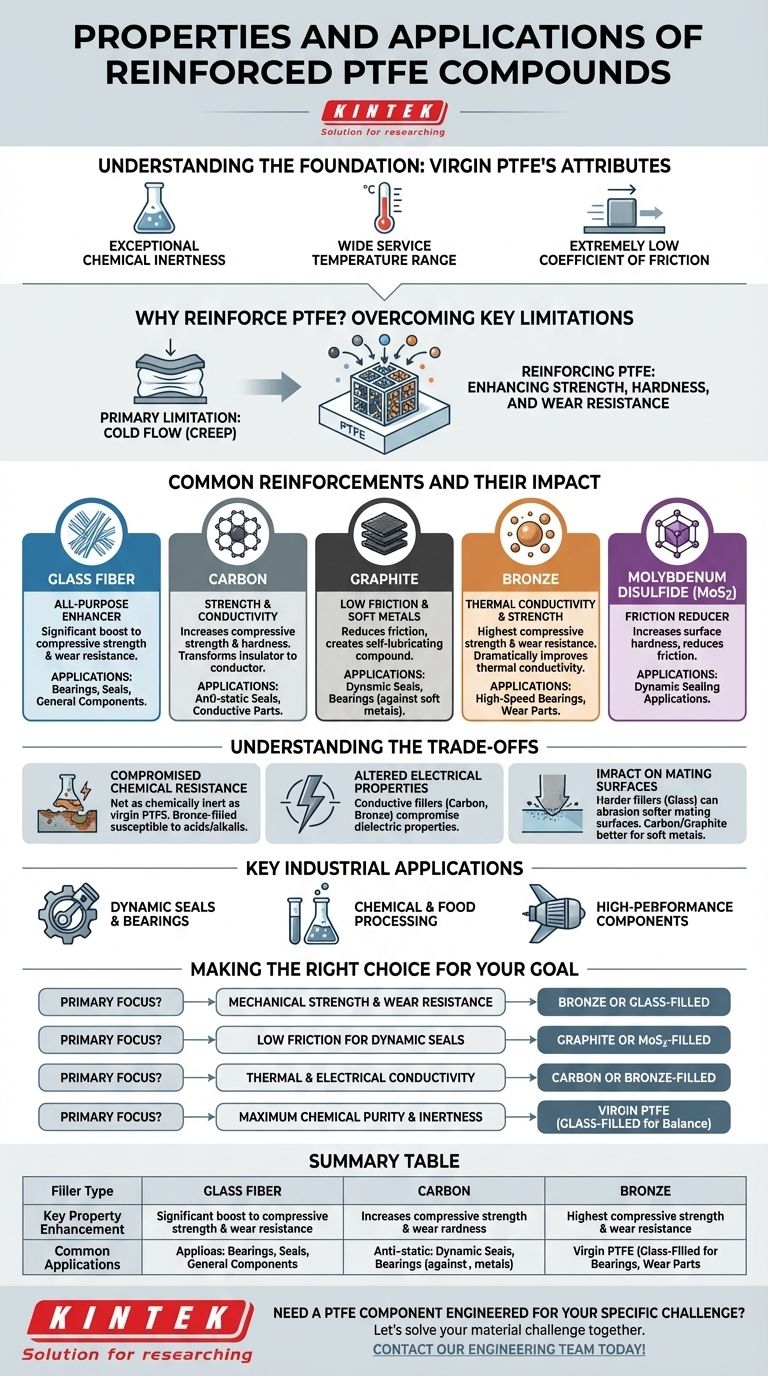
Reinforced Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) compounds are engineered materials that enhance the excellent inherent properties of virgin PTFE by adding specific fillers. This process dramatically improves mechanical characteristics like compressive strength and wear resistance, making the material suitable for demanding industrial applications where virgin PTFE would fail due to its softness.
The core purpose of reinforcing PTFE is to overcome its primary weakness—a tendency to deform or "creep" under load. By adding fillers like glass, carbon, or bronze, you gain significant mechanical strength and wear resistance while retaining PTFE's exceptional chemical inertness and low-friction surface.
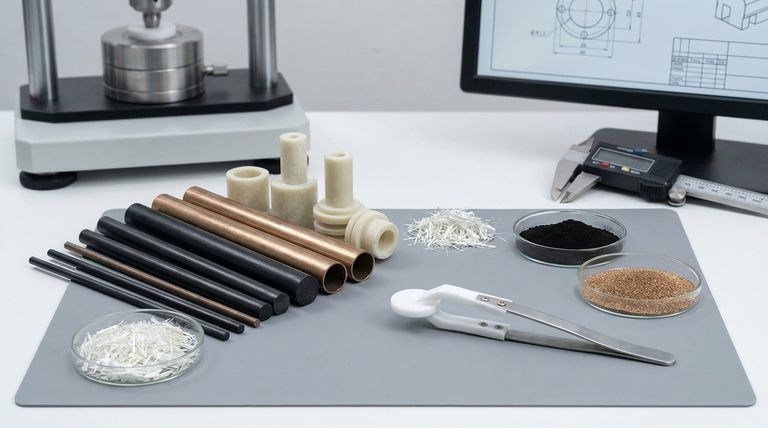

Understanding the Foundation: Virgin PTFE's Attributes
Before exploring reinforcements, it's essential to understand the baseline properties that make PTFE a valuable material. Virgin PTFE is a highly stable linear polymer known for several key attributes.
Exceptional Chemical Inertness
PTFE is resistant to nearly all industrial chemicals and solvents. This makes it an ideal choice for corrosion-resistant linings, seals, and components used in chemical processing and handling.
Wide Service Temperature Range
The material maintains its properties across an extreme range of temperatures. It does not become brittle at low temperatures or degrade at the high temperatures seen in many industrial processes.
Extremely Low Coefficient of Friction
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material, giving it its famous "non-stick" quality. This property is invaluable for creating low-friction surfaces in dynamic applications.
Why Reinforce PTFE? Overcoming Key Limitations
While its core attributes are excellent, virgin PTFE is a relatively soft material. Its primary limitation is cold flow, or creep—a tendency to permanently deform when subjected to a sustained compressive load.
Reinforcing PTFE with fillers directly addresses this weakness. The fillers act as a structural matrix within the PTFE, significantly increasing its compressive strength, hardness, and overall wear and abrasion resistance.
Common Reinforcements and Their Impact
The choice of filler is determined by the specific performance enhancement required for the end application. Each filler imparts a unique combination of properties to the PTFE base.
Glass Fiber: The All-Purpose Enhancer
Glass fiber is one of the most common fillers. It provides a significant boost to compressive strength and general wear resistance, making it a good all-around choice for components like bearings and seals.
Carbon: For Strength and Conductivity
Adding carbon increases compressive strength and hardness even more than glass. Critically, it also transforms PTFE from an electrical insulator into a conductive material, which is useful for anti-static applications.
Graphite: For Low Friction and Soft Metals
Graphite is often combined with other fillers like carbon. Its primary benefit is reducing the coefficient of friction, creating a self-lubricating compound ideal for dynamic seals or bearings that run against softer metal surfaces.
Bronze: For Thermal Conductivity and Strength
Bronze fillers provide the highest increase in compressive strength and wear resistance. They also dramatically improve thermal conductivity, helping to dissipate heat in high-speed bearing and wear applications.
Molybdenum Disulfide (MoS2): A Friction Reducer
Similar to graphite, MoS2 is used to increase the surface hardness and further reduce friction. It creates a highly lubricious compound suitable for dynamic sealing applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Adding fillers is not a universal upgrade; it involves specific trade-offs that are critical to consider during material selection.
Compromised Chemical Resistance
While filled PTFE compounds still offer excellent chemical resistance, they are not as inert as virgin PTFE. Bronze-filled compounds, in particular, are susceptible to attack by certain acids and alkalis.
Altered Electrical Properties
The outstanding dielectric (insulating) properties of virgin PTFE are compromised by conductive fillers. Carbon and bronze fillers will make the compound conductive, which may be undesirable for electrical insulation applications.
Impact on Mating Surfaces
Harder fillers like glass fiber can be abrasive to softer mating surfaces (e.g., aluminum or brass). For these applications, a compound filled with carbon and graphite is often a better choice.
Key Industrial Applications
The enhanced properties of reinforced PTFE make it a problem-solving material across many sectors.
Dynamic Seals and Bearings
This is the primary application area for reinforced PTFE. Its low friction, high strength, and wear resistance are ideal for piston rings, bearings, valve seats, and dynamic seals where durability is paramount.
Chemical and Food Processing
The combination of chemical resistance and structural integrity makes reinforced PTFE suitable for pump components, valve parts, and filters in corrosive or high-purity environments, including food, beverage, and pharmaceutical processing.
High-Performance Components
In aerospace, automotive, and industrial equipment, reinforced PTFE is used for components that require reliable performance under high heat, high impact, or vacuum conditions.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct compound requires matching the filler to the primary demand of your application.
- If your primary focus is mechanical strength and wear resistance: A bronze-filled or glass-filled PTFE compound is the most effective choice.
- If your primary focus is low friction for dynamic seals: A compound filled with graphite or molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) will deliver the best performance.
- If your primary focus is thermal and electrical conductivity: A carbon or bronze-filled PTFE is necessary for dissipating heat or static electricity.
- If your primary focus is maximum chemical purity and inertness: Virgin PTFE may be the best option, but if strength is needed, a glass-filled compound offers a good balance.
By understanding these filler-property relationships, you can specify a PTFE compound precisely engineered for your unique challenge.
Summary Table:
| Filler Type | Key Property Enhancement | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Glass Fiber | Compressive Strength, Wear Resistance | Bearings, Seals, General Components |
| Carbon | Compressive Strength, Electrical Conductivity | Anti-static Seals, Conductive Parts |
| Graphite | Low Friction, Self-Lubrication | Dynamic Seals, Bearings (soft mating surfaces) |
| Bronze | High Compressive Strength, Thermal Conductivity | High-Speed Bearings, Wear Parts |
| Molybdenum Disulfide (MoS2) | Reduced Friction, Surface Hardness | Dynamic Sealing Applications |
Need a PTFE Component Engineered for Your Specific Challenge?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE components—from custom seals and liners to complex labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you require the unmatched strength of bronze-filled PTFE for a high-load bearing or the low-friction properties of a graphite-filled compound for a dynamic seal, our expertise in custom fabrication ensures a perfect fit for your application, from prototypes to high-volume production.
Let's solve your material challenge together. Contact our engineering team today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials



















