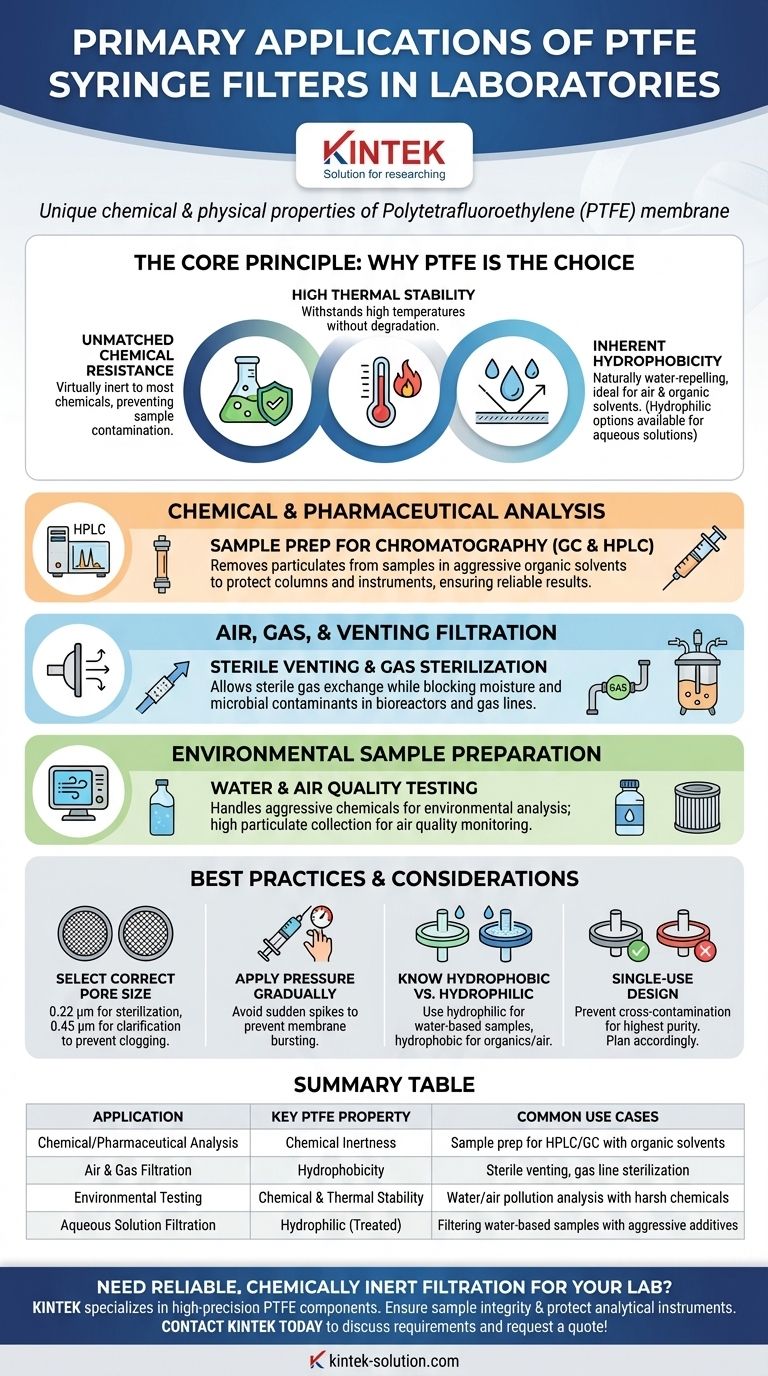
In the modern laboratory, PTFE syringe filters are primarily used for three key applications: preparing samples with aggressive organic solvents for chemical analysis like chromatography, sterilizing or filtering air and gases, and preparing samples for environmental testing. Their utility stems directly from the unique chemical and physical properties of the Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) membrane.
The core reason laboratories depend on PTFE syringe filters is their exceptional chemical inertness and thermal stability. This guarantees that the filter itself will not react with or contaminate the sample, ensuring the purity and accuracy of results, especially when working with harsh solvents or high temperatures.
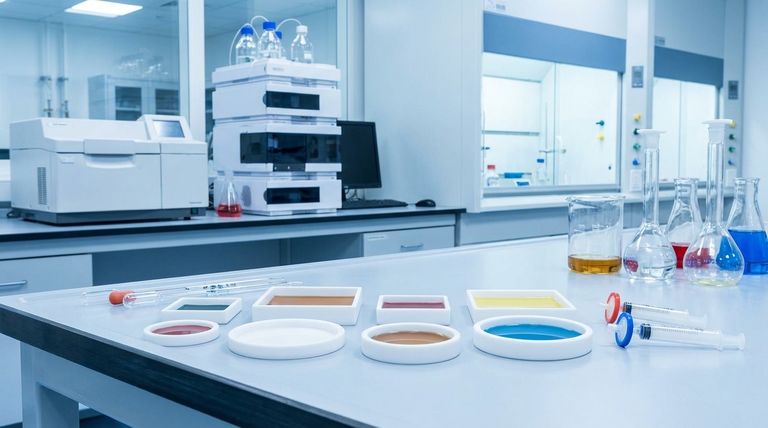

The Core Principle: Why PTFE is the Material of Choice
To understand the applications of PTFE filters, we must first understand the material itself. Its properties make it an indispensable tool for protecting sensitive instruments and ensuring sample integrity in demanding environments.
Unmatched Chemical Resistance
PTFE is virtually inert, meaning it does not react with most chemicals. This makes it the ideal choice for filtering samples containing strong acids, aggressive solvents, and other corrosive substances that would degrade other filter materials.
This chemical stability ensures that the filter does not leach contaminants into the filtrate, which is critical for sensitive analyses.
High Thermal Stability
The material can withstand high temperatures without degrading or losing its structural integrity. This allows for its use in applications involving hot liquids or gases where other polymers would fail.
Inherent Hydrophobicity
Standard PTFE is naturally hydrophobic, or water-repelling. This property makes it extremely effective for filtering air and gases, as it allows the gas to pass through while blocking aqueous aerosols and moisture.
It is also the primary reason PTFE is the default choice for non-aqueous, organic-based solvents used in High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC).
Versatility Through Hydrophilic Options
While naturally hydrophobic, PTFE membranes can be treated to become hydrophilic (water-attracting). This modification expands their utility, allowing them to be used for filtering aqueous solutions while retaining the material's broad chemical resistance.
Primary Laboratory Applications in Detail
The unique properties of PTFE translate directly into its most common uses, where purity and durability are non-negotiable.
Chemical and Pharmaceutical Analysis
PTFE filters are a mainstay in sample preparation for chromatography (both GC and HPLC). They are used to remove particulate matter from samples dissolved in strong organic solvents before injection.
This simple filtration step is critical for preventing clogs and damage to expensive chromatography columns and instrument components, thereby extending their lifespan and ensuring reliable results.
Air, Gas, and Venting Filtration
The hydrophobic nature of PTFE membranes makes them perfect for sterile venting of containers and bioreactors. They allow sterile air to enter or exit while preventing microbial contaminants and moisture from getting in.
They are also used for sterilizing gas lines and degassing solvents, contributing to the accuracy of experiments in microbiology and molecular biology.
Environmental Sample Preparation
In environmental science, PTFE filters are used for analyzing water pollution and testing air quality. They can handle the aggressive chemicals often required to prepare environmental samples for analysis.
For air quality monitoring, their high particulate collection efficiency makes them suitable for collecting and analyzing airborne particulate matter.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Best Practices
While highly effective, using PTFE filters correctly is key to achieving the best outcomes and avoiding common pitfalls.
Selecting the Correct Pore Size
Choosing the right pore size (e.g., 0.22 µm for sterilization or 0.45 µm for general clarification) is essential. Using a pore size that is too small for a high-particulate sample can lead to rapid clogging and slow filtration rates.
Applying Pressure Correctly
Pressure should always be applied to the syringe plunger gradually and evenly. A sudden increase in pressure can easily exceed the filter's pressure limit, causing the membrane to burst and ruining the sample.
Hydrophobic vs. Hydrophilic Confusion
A common error is attempting to filter an aqueous solution with a standard (hydrophobic) PTFE filter. This will result in extremely high backpressure and little to no flow. Always verify you are using a hydrophilic PTFE filter for water-based samples.
Single-Use by Design
PTFE syringe filters are designed for single use to prevent cross-contamination between samples. While this ensures the highest level of purity for each sample, it is a factor to consider in lab budgets and waste management.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct filter type is the first step toward reliable and reproducible results.
- If your primary focus is HPLC with organic solvents: Use a standard hydrophobic PTFE filter to clarify your sample and protect your analytical column from particulates.
- If your primary focus is sterile air filtration or venting: A hydrophobic PTFE filter is the ideal choice to allow gas exchange while blocking airborne moisture and microbes.
- If your primary focus is filtering aqueous solutions with harsh additives: Choose a specially treated hydrophilic PTFE filter to ensure compatibility and prevent membrane failure.
Understanding the fundamental properties of PTFE empowers you to select the right tool, protecting your instruments and ensuring the integrity of your analytical data.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key PTFE Property Used | Common Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical/Pharmaceutical Analysis | Chemical Inertness | Sample prep for HPLC/GC with organic solvents |
| Air & Gas Filtration | Hydrophobicity | Sterile venting, gas line sterilization |
| Environmental Testing | Chemical & Thermal Stability | Water/air pollution analysis with harsh chemicals |
| Aqueous Solution Filtration | Hydrophilic (Treated) | Filtering water-based samples with aggressive additives |
Need reliable, chemically inert filtration for your lab?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components, including custom syringe filters, seals, liners, and labware. Our products are designed for the demanding environments of the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
We ensure your sample integrity and protect your sensitive analytical instruments by providing components with exceptional chemical resistance and thermal stability. From prototypes to high-volume orders, our custom fabrication services deliver the exact solution you need.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific filtration requirements and request a quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What types of products are related to headspace septa? Essential Components for Leak-Proof Analysis
- What are the key properties that make PTFE shovels ideal for laboratory use? Ensure Sample Integrity with Chemically Inert Tools
- What role do sealing properties play in the effectiveness of PTFE/silicone septums? Ensure Sample Integrity and Data Accuracy
- What is the primary function of PTFE/silicone septa in HPLC autosampler vials? Ensure Sample Integrity and Accuracy
- What are the advantages of the PTFE bottle's non-stick surface? Ensure Purity and Efficiency in Your Lab
- What are the key properties of PTFE that make it suitable for labware applications? Ensure Lab Integrity with Superior Material
- Why is PTFE particularly valuable in laboratory settings? Achieve Unmatched Purity and Safety
- What are PTFE lined caps made of? A Guide to Their Inert, Protective Construction



















