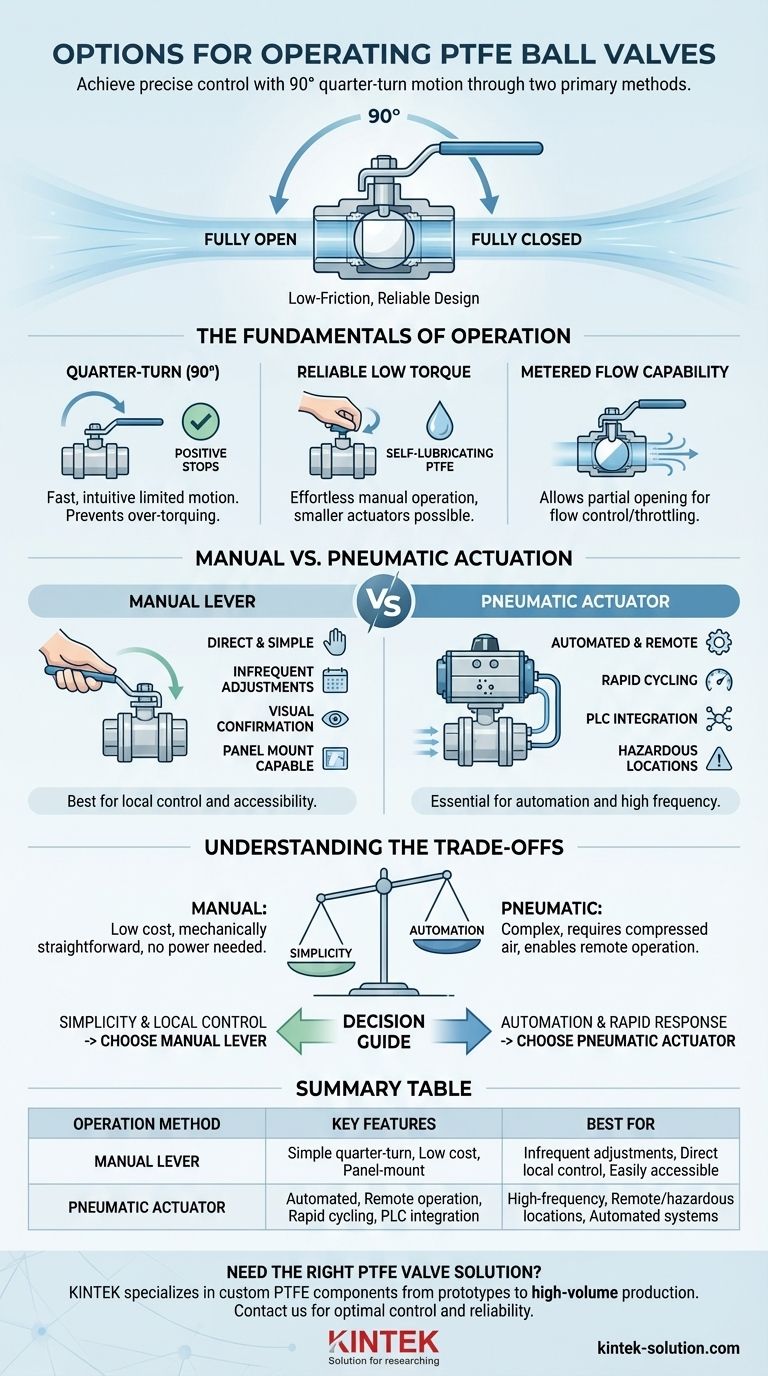
Operating a PTFE ball valve is achieved through two primary methods. These valves are designed for a simple quarter-turn (90-degree) motion to go from fully open to fully closed, and can be operated either directly by hand with a lever or automated with a pneumatic actuator connected via an adapter.
The choice between manual and pneumatic operation is a strategic decision based on your need for control, speed, and system integration. Both methods, however, leverage the inherent low-friction, reliable design of the PTFE valve itself.

The Fundamentals of PTFE Valve Operation
To choose the right method, you must first understand the core mechanical principles that make these valves effective and easy to operate.
Quarter-Turn with Positive Stops
A key design feature is the quarter-turn operation. This means the valve handle only needs to move 90 degrees to cycle between the fully open and fully closed positions.
This limited motion is fast and intuitive. Furthermore, the inclusion of positive stops provides a clear, physical confirmation when the valve has reached its fully open or closed state, preventing over-torquing.
Reliable Low Torque
PTFE, the material used for all media-wetted surfaces, has an extremely low coefficient of friction. This self-lubricating property means very little force is required to turn the ball inside the valve.
This low-torque requirement is what makes manual operation so effortless and allows for the use of smaller, more efficient pneumatic actuators in automated systems.
Metered Flow Capability
While designed for on/off service, many PTFE ball valves can be positioned partially open. This allows for the metering or throttling of flow, giving operators more granular control over their process beyond a simple binary state.
Manual vs. Pneumatic Actuation: A Comparison
Your choice of operator will fundamentally change how the valve interacts with your system and personnel.
Manual Lever Operation
This is the most direct and simple method. A lever is attached directly to the valve stem, allowing an operator to open or close it by hand.
This approach is ideal for applications where adjustments are infrequent, direct visual confirmation is needed, or the valve is easily accessible. Many models also include panel mount capability, simplifying installation in control panels or enclosures.
Pneumatic Actuator Operation
For automation, a pneumatic actuator is mounted to the valve. This device uses compressed air to generate the rotational force needed to turn the valve stem.
This method is essential for remote operation, integration into a PLC or other automated control system, or in applications requiring rapid or frequent cycling where manual operation would be impractical.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between manual and pneumatic operation involves balancing cost, complexity, and performance.
Simplicity vs. Automation
Manual operation is the definition of simplicity. It is mechanically straightforward, has the lowest initial cost, and requires no external power infrastructure.
Pneumatic actuation introduces complexity and cost. It requires a compressed air supply, control solenoids, and tubing, but in return, it provides automation, precision, and the ability to operate valves in hazardous or hard-to-reach locations.
Speed and Cycling Frequency
Pneumatic actuators can open or close a valve almost instantly and can perform thousands of cycles without fatiguing. This makes them the only viable choice for high-frequency applications.
Manual operation is, by its nature, slower and dependent on an operator's presence and physical ability.
Installation and Maintenance
A manually operated valve is lightweight and simple to install. With no required lubrication and a long service life, it is virtually maintenance-free.
A pneumatic system adds more components that must be installed and maintained, including the air supply system, filters, regulators, and the actuator itself.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision should be guided by the specific demands of your process.
- If your primary focus is simplicity and direct local control: Choose manual lever operation for its straightforward, low-cost, and reliable performance.
- If your primary focus is automation or remote operation: Opt for a pneumatic actuator to integrate the valve seamlessly into a larger control system.
- If your primary focus is frequent cycling or rapid response: A pneumatic actuator is the only practical choice to meet the demands of high-frequency applications.
By understanding these core operational principles, you can confidently select the valve configuration that best serves your system's goals.
Summary Table:
| Operation Method | Key Features | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Manual Lever | Simple quarter-turn, low cost, panel-mount capable | Infrequent adjustments, direct local control, easily accessible locations |
| Pneumatic Actuator | Automated, remote operation, rapid cycling, PLC integration | High-frequency applications, remote/hazardous locations, automated control systems |
Need the right PTFE valve solution for your application?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-performance, custom PTFE components—including seals, liners, labware, and ball valves—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you require simple manual valves or complex automated systems with pneumatic actuators, we deliver precision-engineered solutions from prototypes to high-volume production.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific requirements and let our experts help you select or fabricate the perfect PTFE ball valve for optimal control, reliability, and performance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What is PTFE, and why is it used in expansion joints? Superior Chemical & Thermal Stability
- What are the key features of PTFE gaskets? Unlock Superior Chemical & Thermal Sealing
- How are PTFE bushes designed and manufactured? A Guide to Custom Engineered Components
- What role do Teflon rods play in the electrical and electronics industry? Ensure Superior Insulation and Reliability
- What are the main differences between PTFE lined butterfly valves and hard seal butterfly valves? Choose the Right Seal for Your Application
- How are PTFE diaphragms manufactured? Achieve Optimal Performance for Your Application
- What are some applications of PTFE in the food processing industry? Improve Efficiency and Safety
- What are the advantages of PTFE diaphragms? Achieve Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance



















