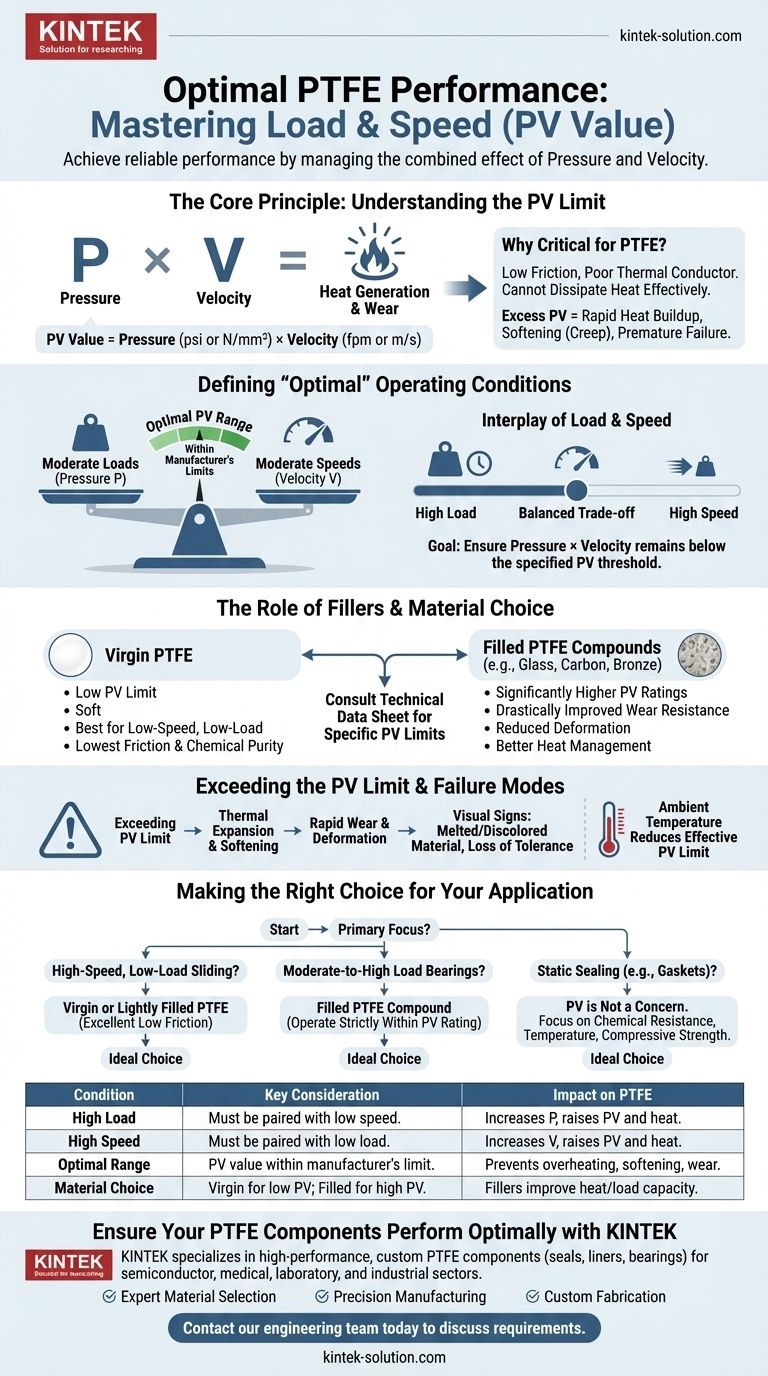
To achieve optimal performance, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) must be operated under moderate loads and speeds. The most critical factor is ensuring the combined effect of pressure and velocity—known as the PV value—remains within the specific manufacturer's limits for the material grade you are using. Exceeding this value will cause rapid heat buildup and premature failure.
The performance of PTFE is not determined by load or speed in isolation, but by their product (Pressure × Velocity). The primary goal is to manage this PV value to prevent frictional heat from exceeding the material's thermal limits, which is the root cause of wear and deformation.

The Core Principle: Understanding the PV Limit
What is the PV Value?
The PV value is a critical performance metric for bearing materials, calculated by multiplying the surface pressure (P, in psi or N/mm²) by the sliding velocity (V, in fpm or m/s).
This value represents the rate of energy being dissipated as heat at the contact surface. A higher PV value means more heat is being generated.
Why PV is Critical for PTFE
PTFE has an exceptionally low coefficient of friction, but it is also a very poor thermal conductor. It cannot dissipate heat effectively.
If the PV value is too high, heat is generated faster than the material can shed it. This causes the PTFE to soften, deform under load (a phenomenon known as "creep"), and wear away quickly.
The Role of Fillers
Pure, or virgin, PTFE has a relatively low PV limit. To overcome this, fillers like glass, carbon, bronze, or graphite are added to create PTFE compounds.
These fillers drastically improve wear resistance, reduce deformation under load, and increase the material's ability to manage heat, thereby allowing for significantly higher PV ratings.
Defining "Optimal" Operating Conditions
Moderate Loads (Pressure)
The term "moderate" is relative to the specific PTFE grade. A load that is excessive for virgin PTFE might be perfectly acceptable for a bronze-filled compound.
Pressure is the "P" in the PV equation. For any given speed, increasing the pressure will increase the PV value and the associated heat generation.
Moderate Speeds (Velocity)
Velocity is the "V" in the PV equation. Frictional heat increases directly with sliding speed.
Even under a very light load, an extremely high velocity can generate enough heat to exceed the thermal limit and cause failure.
The Interplay of Load and Speed
You must always consider the trade-off between pressure and velocity. A system with a high load must operate at a very low speed. Conversely, a high-speed system must operate under a very low load.
The goal is to ensure their combined product remains below the material's specified PV threshold.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Failure Modes
Exceeding the PV Limit
The primary failure mode for PTFE in dynamic applications is exceeding the PV limit. This results in thermal expansion, softening, and a rapid increase in wear rate.
Visually, this can appear as melted or discolored material and a complete loss of dimensional tolerance.
The Limitation of Pure PTFE
While offering the lowest friction and highest chemical purity, virgin PTFE is very soft. It is best suited for low-speed, low-load applications where its exceptional slipperiness is the main requirement.
Environmental Temperature
The ambient operating temperature reduces the effective PV limit. A hotter environment means the PTFE starts closer to its maximum temperature limit, leaving less "room" for frictional heating before failure occurs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To ensure reliable performance, you must select a material grade whose capabilities match the demands of your system.
- If your primary focus is high-speed, low-load sliding: Virgin or lightly filled PTFE is an excellent choice due to its extremely low friction.
- If your primary focus is moderate-to-high load bearings: You must use a filled PTFE compound (e.g., glass, carbon, or bronze-filled) and operate strictly within the manufacturer's specified PV rating.
- If your primary focus is static sealing (e.g., gaskets): PV is not a concern; instead, focus on the material's chemical resistance, temperature limits, and compressive strength.
Always consult the manufacturer's technical data sheet to find the specific PV limit for the exact material you are using.
Summary Table:
| Condition | Key Consideration | Impact on PTFE |
|---|---|---|
| High Load | Must be paired with low speed. | Increases pressure (P), raising PV value and heat. |
| High Speed | Must be paired with low load. | Increases velocity (V), raising PV value and heat. |
| Optimal Range | PV value within manufacturer's limit. | Prevents overheating, softening, and rapid wear. |
| Material Choice | Virgin PTFE for low PV; Filled PTFE for high PV. | Fillers (glass, carbon, bronze) improve heat resistance and load capacity. |
Ensure Your PTFE Components Perform Optimally
Selecting the right PTFE grade and operating within its precise PV limit is critical to preventing premature failure in demanding applications. KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-performance, custom PTFE components—including seals, liners, and bearings—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
We provide:
- Expert Material Selection: Guidance on choosing between virgin or filled PTFE compounds to perfectly match your load, speed, and environmental conditions.
- Precision Manufacturing: Components built to exact specifications for reliable, long-lasting performance.
- Custom Fabrication: From initial prototypes to high-volume production runs.
Don't let thermal failure compromise your system. Contact our engineering team today to discuss your application requirements and get a quote for durable, custom PTFE solutions.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability



















