The material options for PTFE seals are not about choosing different types of PTFE, but rather about selecting the right filler material to blend with the virgin PTFE base. Unlike traditional rubber O-rings, pure, unfilled PTFE is rarely used for sealing because it lacks the elasticity needed to maintain a constant force. Instead, high-performance seals use a composite of PTFE and specific additives to enhance properties like wear resistance, compressive strength, and thermal conductivity.
The term "PTFE O-ring" can be misleading. For demanding applications, the solution is almost never a simple ring of pure PTFE, but a precisely engineered seal made from a filled PTFE compound, often energized with a metal spring to provide the necessary sealing force.

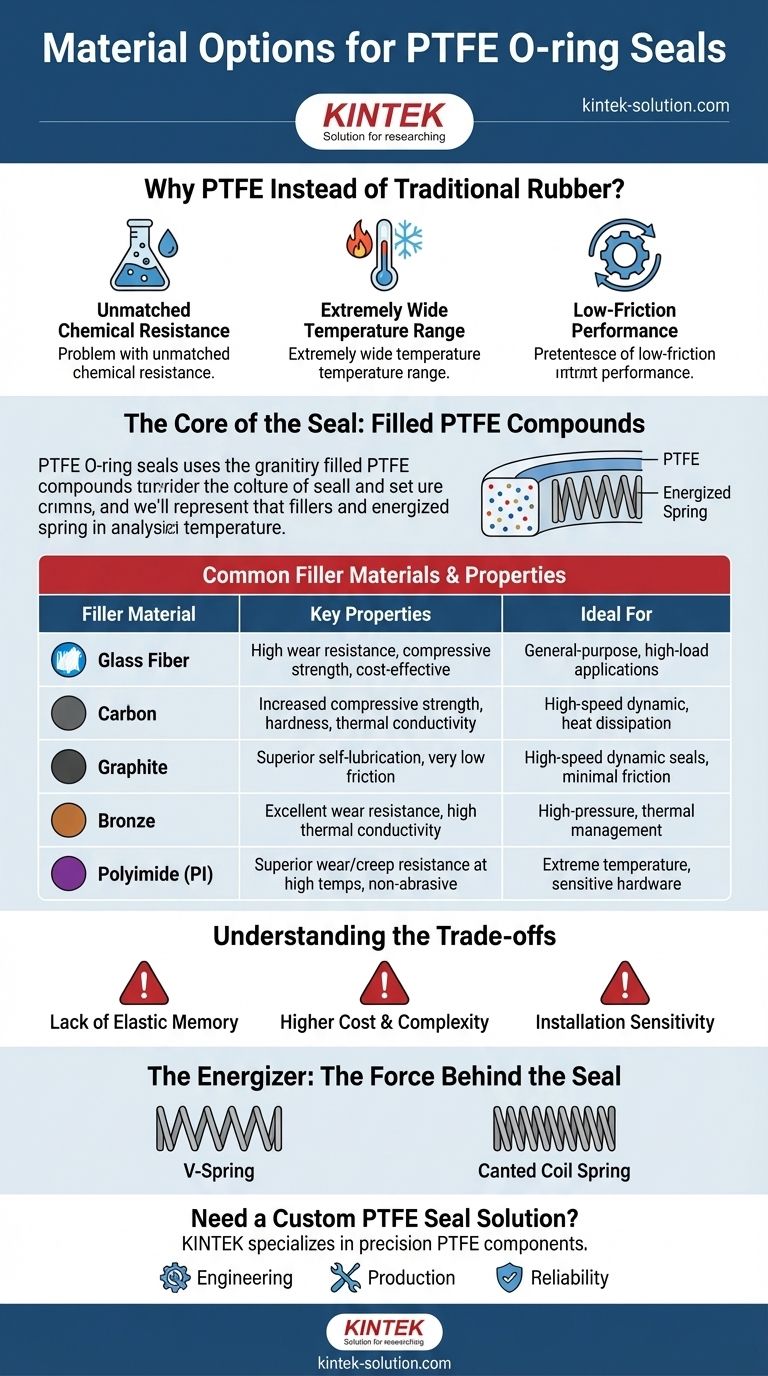
Why PTFE Instead of Traditional Rubber?
Before examining the filler materials, it's crucial to understand why you would choose a PTFE-based seal over a standard elastomer like NBR, EPDM, or FKM. The decision comes down to performance in extreme conditions.
Unmatched Chemical Resistance
PTFE is virtually inert to almost all industrial chemicals and solvents. This makes it the default choice for aggressive media where traditional rubber seals would quickly degrade.
Extremely Wide Temperature Range
PTFE seals maintain their integrity in conditions far beyond the limits of most elastomers, performing reliably in both cryogenic applications and at high temperatures.
Low-Friction Performance
With one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material, PTFE is ideal for dynamic applications like rotating shafts or reciprocating pistons, minimizing wear and energy loss.
The Core of the Seal: Filled PTFE Compounds
The true versatility of PTFE seals comes from the blending of additives or fillers into the base PTFE resin. Each filler imparts specific characteristics to the final product.
The Purpose of Fillers
Fillers are added to counteract PTFE's inherent softness and its tendency to deform under load (a characteristic known as "creep"). They dramatically improve wear resistance, load-bearing capacity, and thermal conductivity.
Common Filler Materials and Their Properties
- Glass Fiber: A common, cost-effective filler that significantly increases wear resistance and compressive strength, but it can be abrasive to softer metal hardware.
- Carbon: Increases compressive strength and hardness. Carbon-filled compounds are also more conductive, which helps dissipate heat in high-speed dynamic applications.
- Graphite: A self-lubricating filler that enhances low-friction properties, making it excellent for high-speed dynamic seals where minimal friction is critical.
- Bronze: Provides excellent wear resistance and high thermal conductivity. Bronze-filled PTFE can handle high pressures but has lower chemical resistance compared to other fillers.
- Polyimide (PI): Offers superior wear and creep resistance, especially at high temperatures, without being abrasive to hardware.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, PTFE-based seals are not a universal solution. Understanding their limitations is key to using them successfully.
Lack of Elastic Memory
A PTFE seal, once compressed, does not spring back to its original shape like a rubber O-ring. This is why an energizer is almost always required to maintain a consistent sealing force.
Higher Cost and Complexity
The manufacturing process for PTFE seals is more involved than for molded rubber O-rings. It requires machining the material from molded tubes, which is a more costly and precise operation.
Installation Sensitivity
Because they are more rigid than elastomers, PTFE seals require more care during installation to avoid scratching or gouging the sealing surface, which could create a leak path.
The Energizer: The Force Behind the Seal
The "secret ingredient" in many high-performance PTFE seals is a metal spring energizer, which provides the physical force that the PTFE material itself lacks.
What is a Spring Energizer?
A spring energizer is a metal spring, typically made of stainless steel or another corrosion-resistant alloy, that is fitted into a groove inside the PTFE seal jacket. It acts as a constant outward force, pushing the seal lips against the hardware.
Common Spring Designs
- V-Spring (Cantilever Spring): A common design that offers a good balance of force and flexibility, suitable for a wide range of static and dynamic applications.
- Canted Coil Spring: Provides a very consistent force across a wide range of deflection. This makes it ideal for applications with hardware inconsistencies, high pressure, or extreme temperatures.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your choice of a specific filled PTFE compound depends entirely on the demands of your application.
- If your primary focus is high wear resistance and pressure: A bronze-filled or glass-filled PTFE compound is likely the best choice.
- If your primary focus is low-friction in a dynamic seal: A graphite or specialized polymer-filled PTFE will deliver the best performance.
- If your primary focus is broad chemical compatibility and high temperatures: A carbon or polyimide-filled compound offers a robust solution.
Ultimately, selecting the right PTFE seal is about matching a specific compound and energizer design to the unique challenges of your operating environment.
Summary Table:
| Filler Material | Key Properties | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Glass Fiber | High wear resistance, compressive strength, cost-effective | General-purpose, high-load applications |
| Carbon | Increased compressive strength, hardness, thermal conductivity | High-speed dynamic applications, heat dissipation |
| Graphite | Superior self-lubrication, very low friction | High-speed dynamic seals, minimal friction critical |
| Bronze | Excellent wear resistance, high thermal conductivity | High-pressure applications, good thermal management |
| Polyimide (PI) | Superior wear/creep resistance at high temps, non-abrasive | Extreme temperature applications, sensitive hardware |
Need a Custom PTFE Seal Solution for Your Demanding Application?
Choosing the right filled PTFE compound is critical for performance in semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial equipment. KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE components—from custom seals and liners to complex labware.
We partner with you to:
- Engineer the perfect compound for your specific chemical, temperature, and pressure requirements.
- Deliver precision production with custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders.
- Ensure reliability in the most demanding environments.
Contact us today to discuss your project and get a quote: Get in Touch
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support



















