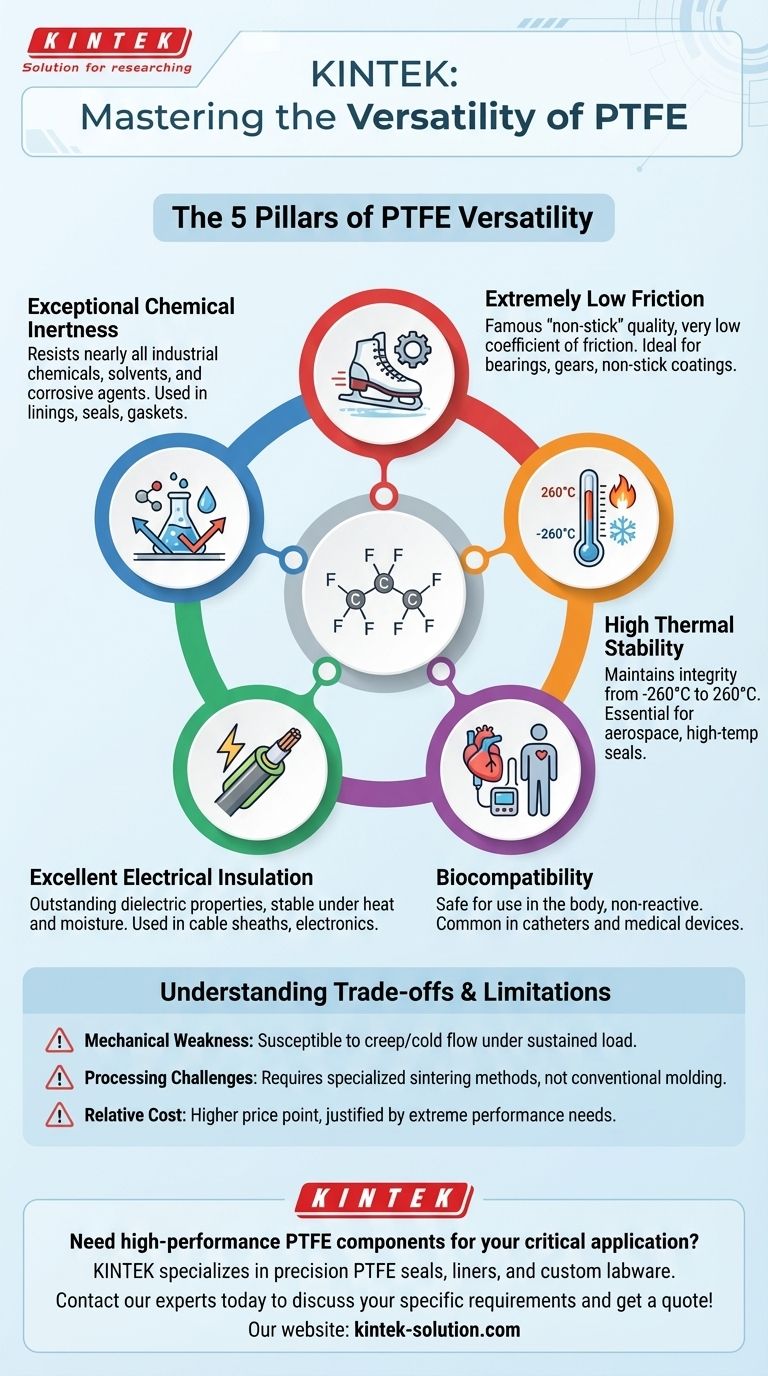
At its core, the versatility of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) across industries stems from a unique combination of five key properties: exceptional chemical resistance, an extremely low coefficient of friction, high thermal stability, excellent electrical insulation, and biocompatibility. This powerful set of characteristics allows it to perform reliably in extreme environments where most other materials would degrade or fail.
The true source of PTFE's power lies in its molecular structure. The incredibly strong bond between its carbon and fluorine atoms is what gives rise to its near-total chemical inertness, non-stick surface, and thermal resilience, making it a definitive problem-solving material for engineering's toughest challenges.

The Foundation: Unmatched Chemical Inertness
One of PTFE's most valuable properties is its ability to resist attack from nearly all industrial chemicals, solvents, and corrosive agents. This makes it an essential material for harsh-environment applications.
Why It's So Resistant
The fluorine atoms in PTFE create a protective, non-reactive sheath around the carbon backbone of the polymer. This stable molecular structure prevents chemicals from finding a weak point to initiate a reaction, rendering the material almost completely inert.
Common Industrial Applications
This inertness is critical in the chemical, petrochemical, and oil and gas industries. It is used for linings in pipes and vessels, seals, and gaskets that handle aggressive acids, bases, or solvents without degrading.
The Hallmark Trait: Extremely Low Friction
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any known solid material, with a static coefficient around 0.08 and a dynamic one as low as 0.01. This is the source of its famous "non-stick" quality.
Understanding the "Non-Stick" Effect
The material's surface energy is exceptionally low, meaning other substances have a very difficult time adhering to it. This anti-adhesion property ensures that materials slide off its surface with minimal resistance.
Applications in Motion and Flow
This property is leveraged in coated mechanical parts like bearings and gears to reduce wear and energy consumption. It is also essential for non-stick cookware and is used in medical devices like catheters to ensure smooth passage within the body.
Reliability Across Extreme Temperatures
PTFE maintains its structural integrity and performance characteristics over an exceptionally wide temperature range, typically from -260°C to 260°C (-436°F to 500°F).
How It Maintains Stability
Unlike many plastics that become brittle in extreme cold or melt in high heat, PTFE's strong internal bonds allow it to remain flexible and durable. It does not lose its core properties within this broad operating window.
Where Thermal Range is Critical
This makes it indispensable for aerospace and automotive applications, where components are exposed to severe temperature fluctuations. It's also used for high-temperature seals in industrial processing equipment.
Superior Electrical Insulation
PTFE is an outstanding electrical insulator, characterized by a low dielectric constant and high dielectric strength. Its performance remains stable even when exposed to heat and moisture.
The Dielectric Advantage
Its properties prevent the flow of electricity, making it ideal for isolating electrical components from each other and their surroundings. This resistance does not degrade significantly over a wide range of frequencies.
Applications in Electronics
It is widely used for insulating cables and wires (cable sheaths), especially in high-performance or high-frequency applications. It also serves as an insulator in connectors, transformers, and semiconductor manufacturing.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While its primary properties are exceptional, PTFE is not the solution for every problem. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Mechanical Weakness
Compared to other engineering plastics, PTFE has relatively low mechanical strength. It is susceptible to creep, or "cold flow," meaning it can deform over time when subjected to a sustained load.
Processing Challenges
PTFE cannot be processed using conventional melt-processing techniques like injection molding. It requires specialized methods like sintering, which can add complexity and cost to manufacturing.
Relative Cost
As a high-performance polymer, PTFE is generally more expensive than commodity plastics like polyethylene or polypropylene. Its use is typically justified by the severity of the application's demands.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting PTFE is a strategic decision based on overcoming a specific environmental challenge that commodity materials cannot handle.
- If your primary focus is sealing against aggressive chemicals: PTFE is the industry standard for gaskets, liners, and tubing in chemical processing.
- If your primary focus is reducing friction and wear: PTFE coatings or solid bearings provide a self-lubricating surface ideal for moving parts.
- If your primary focus is insulating critical electronics: PTFE's dielectric properties ensure reliable signal integrity, especially in high-frequency or high-temperature applications.
- If your primary focus is performance in extreme temperatures: PTFE provides unmatched stability and reliability in both cryogenic and high-heat environments where other materials fail.
Ultimately, PTFE's versatility makes it the go-to material for applications where failure is not an option.
Summary Table:
| Property | Key Characteristic | Primary Application |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | Resists nearly all industrial chemicals | Chemical processing seals & liners |
| Low Friction | Extremely low coefficient of friction | Non-stick coatings & bearings |
| Thermal Stability | Performs from -260°C to 260°C | High-temperature seals & aerospace parts |
| Electrical Insulation | Excellent dielectric properties | Cable insulation & semiconductor manufacturing |
| Biocompatibility | Safe for use in the body | Medical devices like catheters |
Need high-performance PTFE components for your critical application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise in custom fabrication ensures you get the exact solution, from prototypes to high-volume orders, that leverages PTFE's unique properties to solve your toughest engineering challenges.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements and get a quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications



















