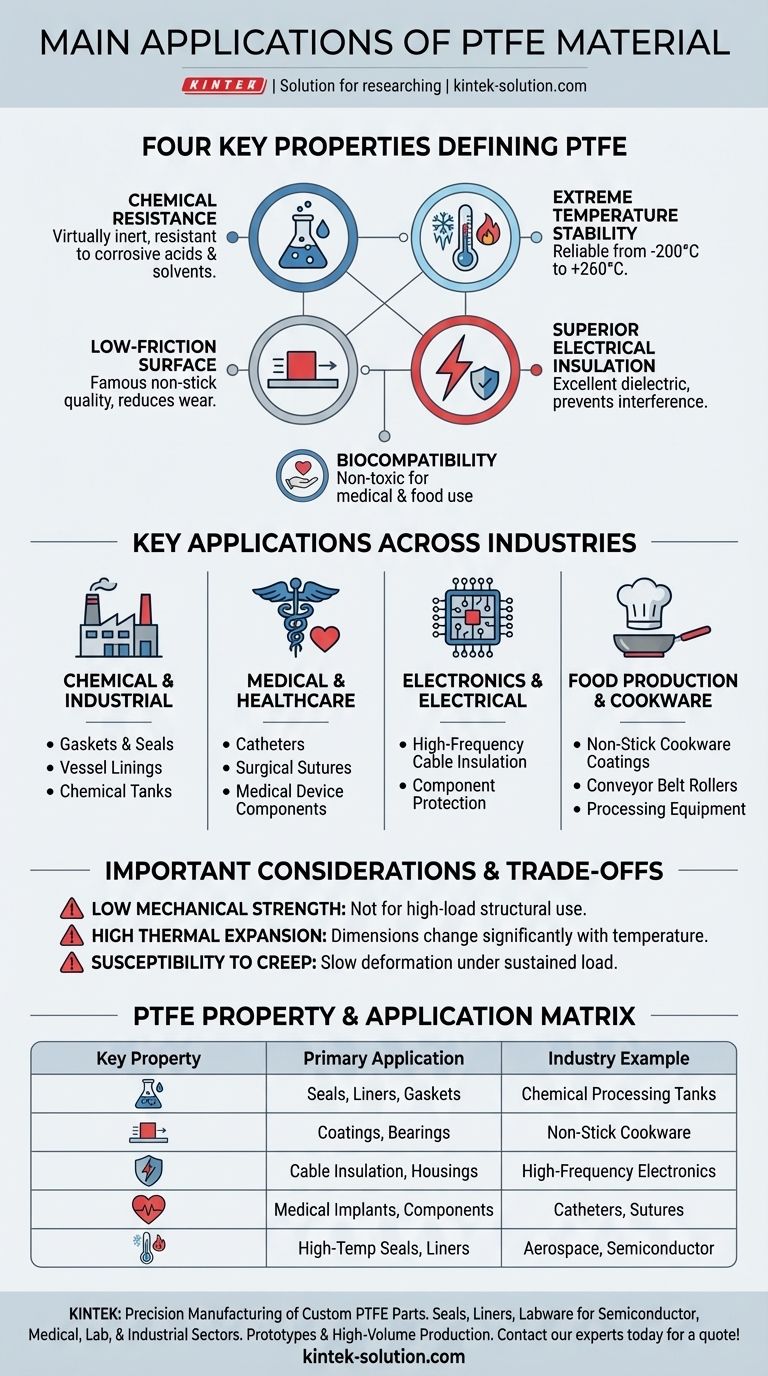
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a high-performance polymer used across an exceptionally wide range of demanding industries. Its primary applications are found in the chemical processing, medical, electrical, and food production sectors, where it serves as everything from non-stick coatings and chemical-resistant linings to electrical insulation and biocompatible implants.
The core reason for PTFE's widespread use is its unique and powerful combination of four key properties: near-total chemical inertness, extreme temperature stability, an incredibly low-friction surface, and excellent electrical insulation.

The Properties That Define PTFE
To understand where PTFE is used, you must first understand why. Its applications are a direct result of its remarkable material characteristics.
Unmatched Chemical Resistance
PTFE is virtually inert and resistant to almost all chemicals, including aggressive acids, solvents, and alkalis. This makes it an ideal material for containing or coming into contact with corrosive substances.
Extreme Temperature Stability
The material performs reliably across a vast temperature range, typically from -200°C to +260°C (-328°F to +500°F). It maintains its properties in cryogenic conditions and at temperatures that would degrade most other polymers.
The 'Non-Stick' Low Friction Surface
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material. This gives it its famous non-stick quality, which is crucial for applications involving sliding parts, easy-release surfaces, and reducing wear.
Superior Electrical Insulation
As a fantastic electrical insulator with a low dielectric constant, PTFE is used to prevent electrical interference and protect sensitive electronic components. It effectively blocks the flow of electricity.
Biocompatibility and Purity
PTFE is non-toxic and biocompatible, meaning it does not react with bodily tissues or fluids. This purity is critical for its use in the medical and food and beverage industries.
Key Applications Across Industries
These fundamental properties make PTFE an essential problem-solver in sectors where standard materials would fail.
In the Chemical and Industrial Sector
The material's chemical inertness is paramount here. It is fabricated into gaskets, seals, vessel linings, and tanks to safely handle and store highly corrosive chemicals.
In Medical and Healthcare
Because it is biocompatible and has low friction, PTFE is used for catheters, surgical sutures, and medical device components. Its non-stick surface helps prevent bacterial buildup and ensures smooth operation.
In Electronics and Electrical Engineering
Its excellent dielectric properties make PTFE a top choice for insulating high-frequency cables and wires. It is also used to protect sensitive electronic components from environmental factors.
In Food Production and Cookware
Best known for its use as the non-stick coating on pans, PTFE is also used for conveyor belt rollers and other food processing equipment. Its high-temperature resistance and easy-to-clean surface are invaluable.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While exceptionally capable, PTFE is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is critical for proper application.
Mechanical Strength and Rigidity
PTFE is a relatively soft material with low tensile strength and rigidity compared to engineering plastics or metals. It is not suitable for high-load structural applications on its own.
High Thermal Expansion
The material has a high coefficient of thermal expansion, meaning its dimensions change more significantly with temperature fluctuations than other materials. This must be accounted for in precision engineering designs.
Susceptibility to Creep
Under a sustained load, PTFE can slowly deform over time, a phenomenon known as "creep." This makes it less suitable for applications requiring long-term dimensional stability under constant pressure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting PTFE depends entirely on whether its unique strengths align with your primary engineering challenge.
- If your primary focus is harsh environment survival: PTFE's unmatched chemical and thermal resistance is its defining feature.
- If your primary focus is reducing friction: Its non-stick, low-friction surface is ideal for sliding parts, bearings, and coatings.
- If your primary focus is electrical insulation: Its superior dielectric properties make it a top choice for high-frequency or sensitive electronic applications.
- If your primary focus is purity and safety: Its biocompatibility and inertness are indispensable in medical and food-grade equipment.
Ultimately, PTFE is the material of choice for solving engineering problems in environments where performance and reliability are non-negotiable.
Summary Table:
| Key Property | Primary Application | Industry Example |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | Seals, Liners, Gaskets | Chemical Processing Tanks |
| Low Friction / Non-Stick | Coatings, Bearings | Non-Stick Cookware, Conveyor Belts |
| Electrical Insulation | Cable Insulation, Component Housings | High-Frequency Electronics |
| Biocompatibility | Medical Implants, Device Components | Catheters, Surgical Sutures |
| High-Temp Stability | High-Temp Seals, Liners | Aerospace, Semiconductor Manufacturing |
Need high-performance PTFE components tailored to your specific challenges?
At KINTEK, we specialize in the precision manufacturing of custom PTFE parts—including seals, liners, labware, and complex components—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you require prototypes or high-volume production, our expertise ensures your components meet the highest standards for chemical resistance, purity, and durability.
Contact our experts today to discuss your project requirements and get a quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? The 3 Pillars Driving Demand for High-Performance Parts
- What fabrication services are available for PTFE? Shearing, Stamping, Laser Cutting, Molding & Machining
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Demanding Applications
- What design considerations are important for custom PTFE parts? Design for Performance & Reliability
- What chemical processing applications involve PTFE-machined parts? Essential Components for Corrosive & High-Purity Systems



















