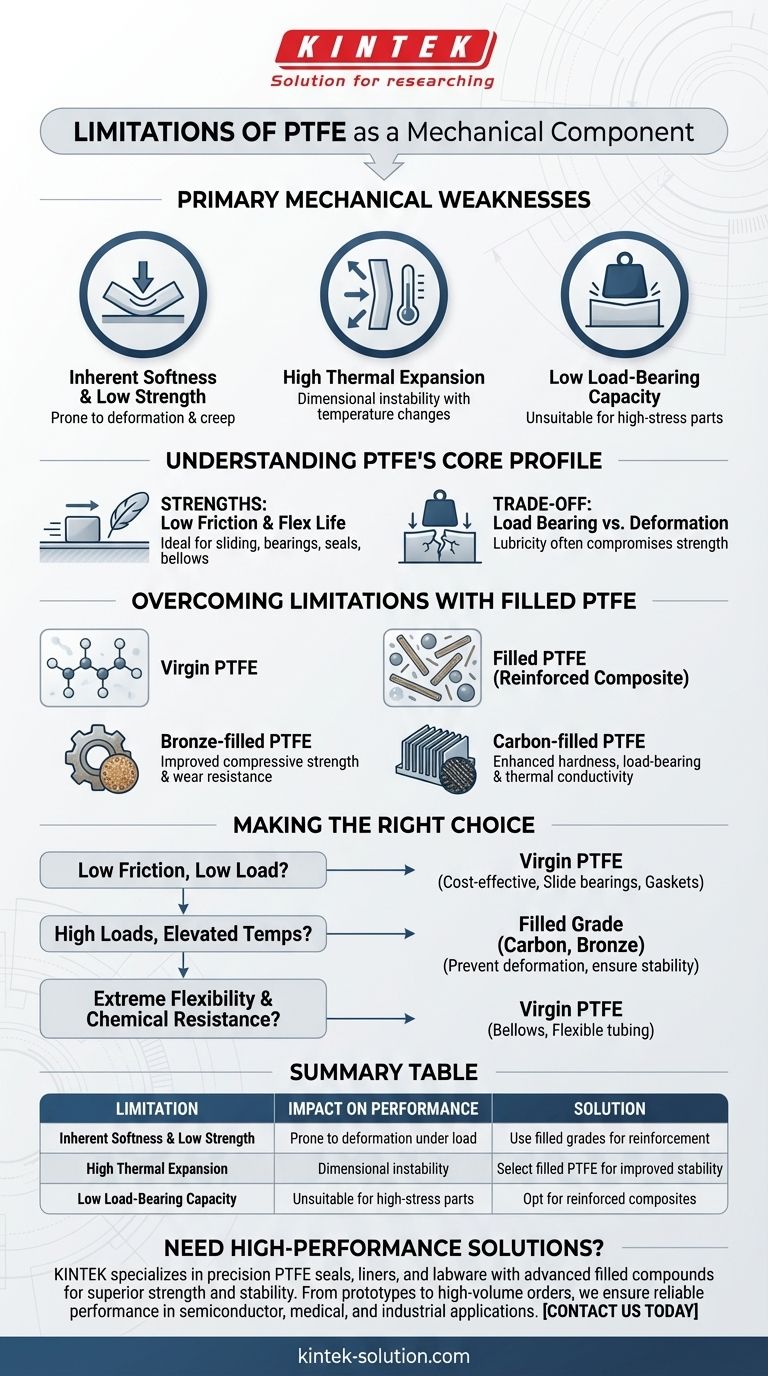
The primary mechanical limitations of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) are its inherent softness, low strength, and high thermal expansion. These characteristics can lead to dimensional instability and deformation under load, making it unsuitable for applications requiring high rigidity or tight tolerances across a range of temperatures.
While pure PTFE is renowned for its unmatched low friction, its effectiveness as a mechanical component is often limited by its softness and poor dimensional stability. The solution for demanding applications lies in using filled grades of PTFE, which significantly enhance strength and rigidity.

Understanding PTFE's Core Mechanical Profile
To effectively use PTFE, you must first understand its inherent, and sometimes contradictory, mechanical properties. It is a material defined by a unique combination of strengths and weaknesses.
Inherent Softness and Low Strength
Pure, or "virgin," PTFE is a relatively soft material. It can be easily indented or scratched, sometimes even with just a fingernail.
This softness means it has low tensile and compressive strength compared to other engineering plastics, making it prone to deforming under significant mechanical stress.
High Thermal Expansion
PTFE has a high coefficient of thermal expansion. This means its dimensions change significantly with temperature fluctuations.
For components that require precise tolerances, this can be a major drawback, as the part may not fit or function correctly as operating temperatures change.
Key Strengths: Low Friction and Flex Life
The defining advantage of PTFE is its extremely low coefficient of friction, one of the lowest of any solid material. This makes it an exceptional choice for self-lubricating bearings, seals, and slide plates.
It also possesses excellent durability and a long flex life, which is why it is often used for critical components like bellows that must endure repeated movement.
Common Pitfalls and Trade-offs
Choosing PTFE requires a clear-eyed assessment of its trade-offs. Its benefits in one area often create challenges in another.
Load Bearing vs. Material Deformation
The primary trade-off is its lubricity versus its strength. While ideal for sliding parts, its softness means it can easily creep or deform under constant, heavy loads.
This makes unfilled PTFE a poor choice for static structural components that must bear significant weight without changing shape over time.
Precision vs. Temperature Fluctuation
The benefits of its chemical inertness can be undermined by its thermal instability. A PTFE part machined to a perfect tolerance at room temperature may be too loose or too tight at its operating temperature.
This requires careful engineering consideration, especially in systems that experience thermal cycling.
Overcoming Limitations with Filled PTFE
For mechanically demanding applications, the weaknesses of virgin PTFE are often mitigated by adding filler materials to the polymer matrix.
How Fillers Enhance Performance
Fillers like carbon, bronze, or glass fibers are compounded with PTFE resin to create a new material. These fillers act as a reinforcing structure within the soft PTFE matrix.
This results in a composite material that is harder, stronger, and more dimensionally stable under load and at elevated temperatures, while still retaining much of PTFE's desirable low-friction characteristic.
The Impact of Common Fillers
Bronze-filled PTFE offers significantly improved compressive strength and wear resistance.
Carbon-filled PTFE enhances hardness, load-bearing capabilities, and thermal conductivity, helping to dissipate heat in high-speed applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct grade of PTFE is essential for mechanical success. Your decision should be based directly on the primary demands of your application.
- If your primary focus is low friction in a low-load environment: Virgin (unfilled) PTFE is an excellent and cost-effective choice for slide bearings, gaskets, and seals.
- If your component must withstand high loads or elevated temperatures: A filled grade of PTFE, such as carbon or bronze-filled, is necessary to prevent deformation and ensure stability.
- If you require extreme flexibility and chemical resistance: Virgin PTFE remains the ideal material for applications like chemical bellows and flexible tubing.
By understanding these fundamental trade-offs, you can harness the unique advantages of PTFE while mitigating its inherent mechanical limitations.
Summary Table:
| Limitation | Impact on Performance | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Inherent Softness & Low Strength | Prone to deformation under load | Use filled grades (e.g., carbon, bronze) for reinforcement |
| High Thermal Expansion | Dimensional instability with temperature changes | Select filled PTFE for improved stability |
| Low Load-Bearing Capacity | Unsuitable for high-stress structural parts | Opt for reinforced composites for strength |
| Trade-off: Lubricity vs. Strength | Excellent low friction but weak under pressure | Balance with filled PTFE for combined benefits |
Need high-performance PTFE components that overcome these limitations? KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE seals, liners, and labware with advanced filled compounds for superior strength and stability. Whether you're in the semiconductor, medical, or industrial sector, our custom fabrication—from prototypes to high-volume orders—ensures your mechanical parts perform reliably under load and temperature variations. Contact us today to discuss your specific requirements and let our expertise enhance your application's success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability



















