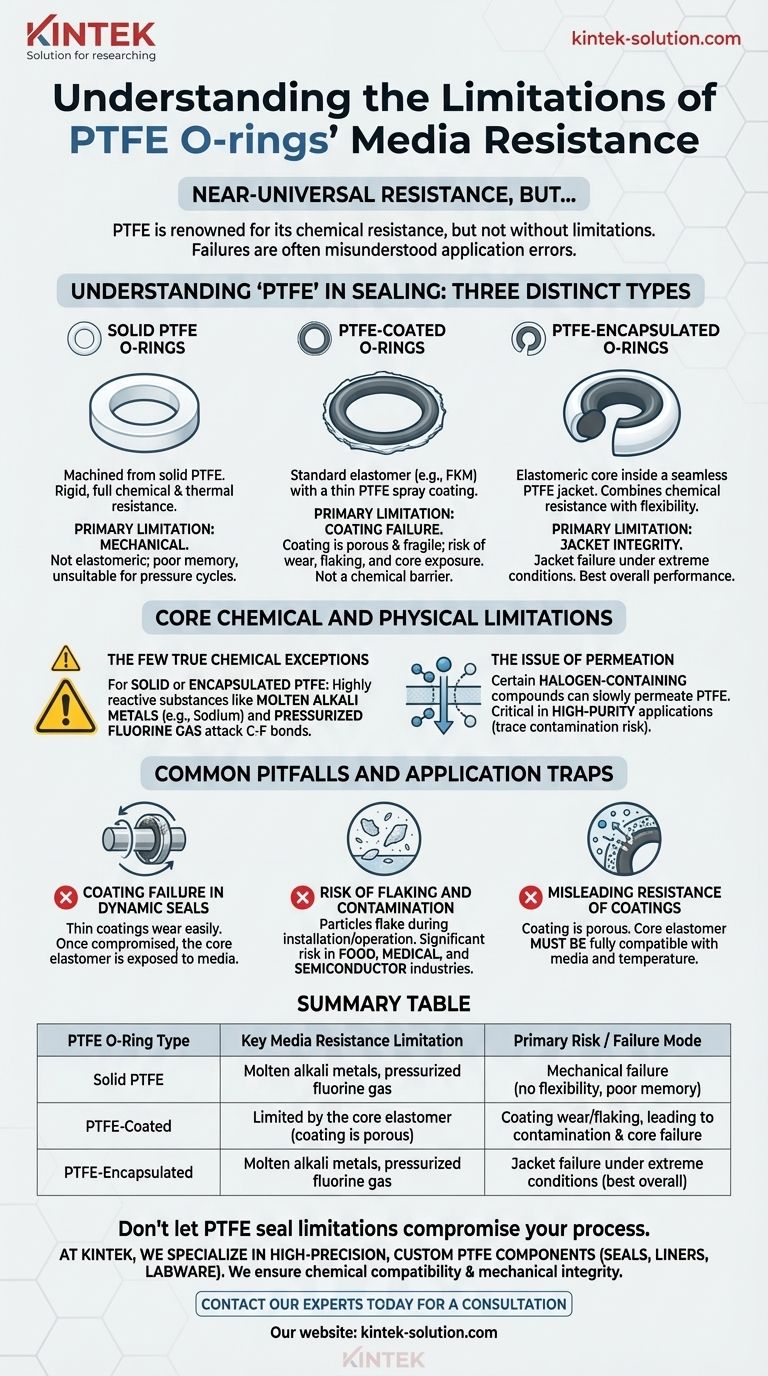
While PTFE is renowned for its near-universal media resistance, it is not without its limitations. The primary chemical vulnerabilities of solid PTFE O-rings are to highly reactive substances, specifically molten or liquid alkali metals (like sodium) and pressurized elemental fluorine gas. For most industrial and laboratory applications, these limitations are rarely encountered.
The most significant limitations of PTFE seals often stem not from chemical incompatibility, but from a misunderstanding of the different types available. The failures of PTFE-coated O-rings—due to wear, flaking, and porosity—are frequently and incorrectly attributed to the PTFE material itself.

Understanding "PTFE" in Sealing
The term "PTFE O-ring" can refer to three distinct products with vastly different mechanical properties and failure modes. Choosing the correct one is critical.
Solid PTFE O-Rings
These are machined from solid PTFE stock. They are rigid, white, and offer the material's full chemical and thermal resistance.
Their primary limitation is mechanical; they are not elastomeric. They have poor memory and do not rebound well after being compressed, making them unsuitable for applications with pressure cycles or thermal expansion.
PTFE-Coated O-Rings
This type consists of a standard elastomer O-ring (like FKM or Silicone) that is sprayed with a thin layer of PTFE.
The coating acts primarily as a low-friction surface lubricant for installation or single-use applications, not as a chemical barrier.
PTFE-Encapsulated O-Rings
These seals have an elastomeric core that is completely enclosed within a seamless PTFE jacket.
This design combines the chemical resistance and low friction of PTFE with the flexibility and memory of an elastomeric core, making it suitable for a wider range of applications than solid PTFE.
Core Chemical and Physical Limitations
While the chemical exceptions are few, they are absolute. Furthermore, subtle physical interactions can impact performance in sensitive systems.
The Few True Chemical Exceptions
For solid or encapsulated PTFE, the only commonly cited incompatible media are liquid alkali metals and pressurized fluorine gas. These highly reactive agents can attack the carbon-fluorine bonds that give PTFE its stability.
The Issue of Permeation
Certain halogen-containing compounds may slowly migrate, or permeate, through PTFE material.
While this typically does not cause swelling or damage to the seal itself, it can be a critical limitation in high-purity applications where even trace amounts of cross-contamination are unacceptable.
Common Pitfalls and Application Traps
Most perceived "failures" of PTFE seals are actually application errors stemming from a misunderstanding of PTFE-coated products.
Coating Failure in Dynamic Seals
PTFE coatings are extremely thin and can be easily scratched or worn away in dynamic applications with rubbing or rotating parts.
Once the coating is compromised, the seal's performance relies entirely on the underlying elastomer, negating the low-friction benefit and exposing a potentially incompatible material to the media.
Risk of Flaking and Contamination
The thin coating on PTFE-coated O-rings can flake off during installation or operation.
These microscopic PTFE particles can contaminate sterile or high-purity systems, making them a significant risk in food, medical, and semiconductor manufacturing.
Misleading Resistance of Coatings
A PTFE coating does not add significant chemical or thermal resistance to an O-ring. The coating is porous.
The core elastomer must be fully compatible with the application's chemicals and temperature range. Assuming the PTFE coating will protect an incompatible core material is a common and critical design error.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the appropriate seal requires matching the product type to the primary challenge you are solving.
- If your primary focus is ultimate chemical purity in a static seal: A solid PTFE O-ring is an excellent choice, but you must account for its mechanical inflexibility and potential for leaks under fluctuating pressure.
- If your primary focus is reducing installation friction for a static O-ring: A PTFE-coated elastomer can be effective, but you must verify that the core material is fully resistant to your media.
- If your primary focus is a dynamic seal with aggressive chemicals: Avoid PTFE-coated O-rings entirely. A PTFE-encapsulated O-ring provides a much more robust solution by combining chemical resistance with mechanical resilience.
- If your primary focus is avoiding all particulate contamination: Do not use PTFE-coated O-rings. The risk of flaking is too high for medical, food, or other clean-room applications.
Understanding these critical distinctions allows you to leverage the exceptional properties of PTFE without falling victim to common application traps.
Summary Table:
| PTFE O-Ring Type | Key Media Resistance Limitation | Primary Risk / Failure Mode |
|---|---|---|
| Solid PTFE | Molten alkali metals, pressurized fluorine gas | Mechanical failure (no flexibility, poor memory) |
| PTFE-Coated | Limited by the core elastomer (coating is porous) | Coating wear/flaking, leading to contamination & core failure |
| PTFE-Encapsulated | Molten alkali metals, pressurized fluorine gas | Jacket failure under extreme conditions (best overall performance) |
Don't let PTFE seal limitations compromise your process. The right seal type is critical for success in semiconductor, medical, and laboratory applications.
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-precision, custom PTFE components (seals, liners, labware) for demanding industries. We help you select or fabricate the perfect seal—from prototypes to high-volume orders—ensuring chemical compatibility and mechanical integrity.
Contact our experts today for a consultation and ensure your application's reliability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support



















