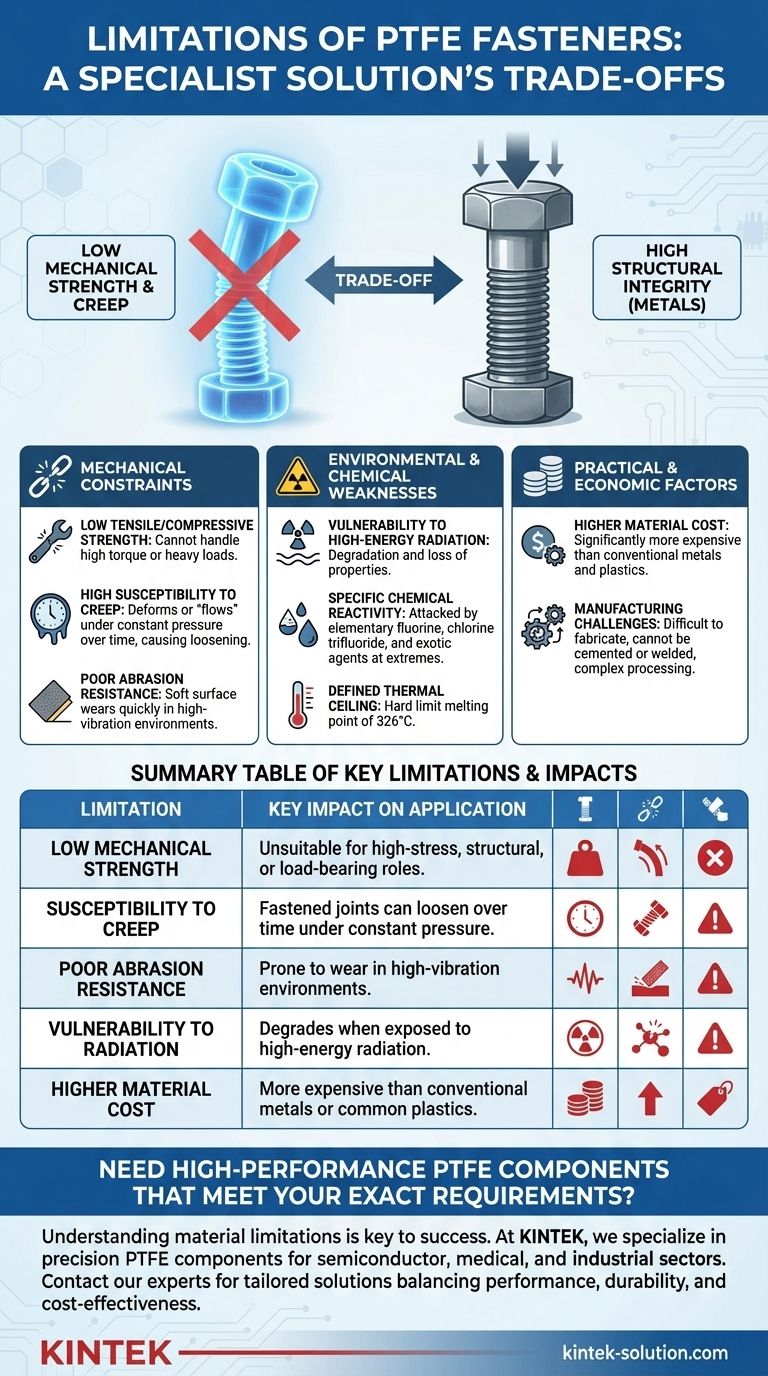
The primary limitations of PTFE fasteners are their low mechanical strength compared to metals, their susceptibility to deformation under load (creep), their vulnerability to high-energy radiation, and a higher material cost. While offering elite chemical and thermal resistance, they are fundamentally unsuited for high-stress, structural applications.
PTFE fasteners are a specialist solution, not a general-purpose one. Their value is in their chemical inertness and low-friction surface, but this comes at the direct trade-off of mechanical strength and resistance to physical deformation.

Deconstructing the Mechanical Limitations
The most significant factor limiting the use of PTFE fasteners is their physical performance under stress. They are a soft polymer, not a rigid metal, which dictates their appropriate use cases.
Low Tensile and Compressive Strength
PTFE fasteners cannot be torqued to high values and cannot support heavy structural loads. They lack the sturdiness of metal and even many other polymers, making them unsuitable for environments where high clamping force is required.
Susceptibility to Creep and Deformation
A critical limitation is creep. Under constant pressure, even if that pressure is well below its breaking point, PTFE will slowly deform or "flow" over time. This means a fastened joint can loosen on its own as the material gives way.
Poor Abrasion Resistance
The famous low-friction surface of PTFE is also soft and sensitive to abrasion. Contact with harder materials, especially in a high-vibration environment, can quickly wear down the fastener, compromising its integrity.
Understanding the Environmental and Chemical Constraints
While known for its resilience, PTFE has specific environmental weaknesses that can lead to catastrophic failure if overlooked.
Vulnerability to High-Energy Radiation
PTFE does not have good resistance to high-energy radiation. This type of radiation can cause the material's molecular structure to break down, leading to a complete loss of its beneficial properties.
Specific Chemical Reactivity
Despite its outstanding and broad chemical resistance, PTFE is not completely inert. It can be attacked by highly reactive chemical agents, particularly elementary fluorine, chlorine trifluoride, and other exotic fluorinating agents, especially at high temperatures and pressures.
Defined Thermal Ceiling
PTFE performs exceptionally well across a wide temperature range (from –200°C to +260°C). However, it has a definitive melting point of 326°C, which acts as a hard limit for any application.
The Practical and Economic Trade-offs
Beyond performance characteristics, practical considerations can also limit the feasibility of using PTFE fasteners in a project.
Higher Material Cost
PTFE is a premium specialty polymer. Fasteners made from it are significantly more expensive than those made from conventional materials like steel or more common plastics.
Manufacturing and Fabrication Challenges
The same properties that make PTFE useful also make it difficult to manufacture. Its non-stick surface means it cannot be cemented or welded, and its unique processing requirements can make mass production more complex and costly compared to other polymers.
Making the Right Choice: When to Avoid PTFE
Use this guidance to determine if PTFE's limitations make it the wrong choice for your application.
- If your primary need is high clamping force or structural support: Avoid PTFE. Its low strength and high potential for creep make it unsuitable and unsafe for load-bearing roles.
- If your environment involves significant abrasion or vibration: Choose a harder material. The softness of PTFE will lead to premature wear and failure.
- If your application will be exposed to high-energy radiation: Do not use PTFE. The material will degrade and fail.
- If your budget is a primary constraint: Look to more conventional materials first. PTFE is a high-cost solution for very specific problems.
Understanding these limitations is key to using PTFE effectively, ensuring you leverage its unique strengths only in the applications where it can safely excel.
Summary Table:
| Limitation | Key Impact on Application |
|---|---|
| Low Mechanical Strength | Unsuitable for high-stress, structural, or load-bearing roles. |
| Susceptibility to Creep | Fastened joints can loosen over time under constant pressure. |
| Poor Abrasion Resistance | Prone to wear in high-vibration environments. |
| Vulnerability to Radiation | Degrades when exposed to high-energy radiation. |
| Higher Material Cost | More expensive than conventional metals or common plastics. |
Need High-Performance PTFE Components That Meet Your Exact Requirements?
Understanding material limitations is the first step to a successful project. At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, and labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We prioritize precision production and offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, ensuring your components perform reliably even in demanding environments.
Let's discuss your specific application needs and material challenges. Contact our experts today for a tailored solution that balances performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
People Also Ask
- What is PTFE commonly known as and what are its unique properties? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What are the key benefits of PTFE in custom fabrication? Unlock Performance in Extreme Conditions
- What are the primary applications of PTFE fasteners and custom parts? Critical Solutions for Extreme Environments
- What are the base characteristics of PTFE? Unlocking Extreme Performance in Friction, Temperature, and Chemical Resistance
- What are the material advantages of machining Teflon? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance



















