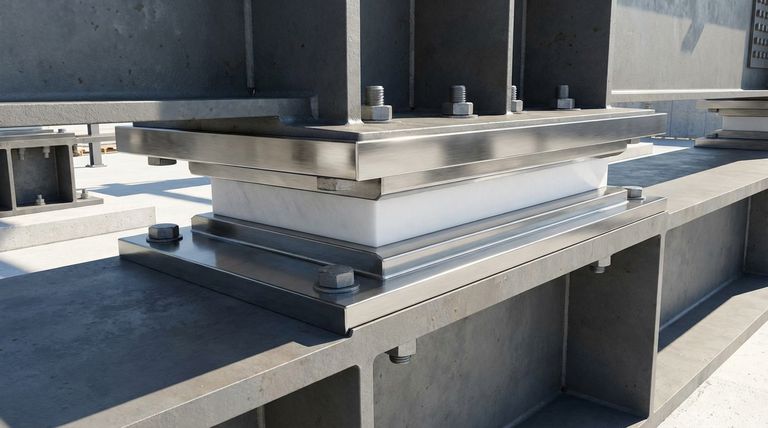
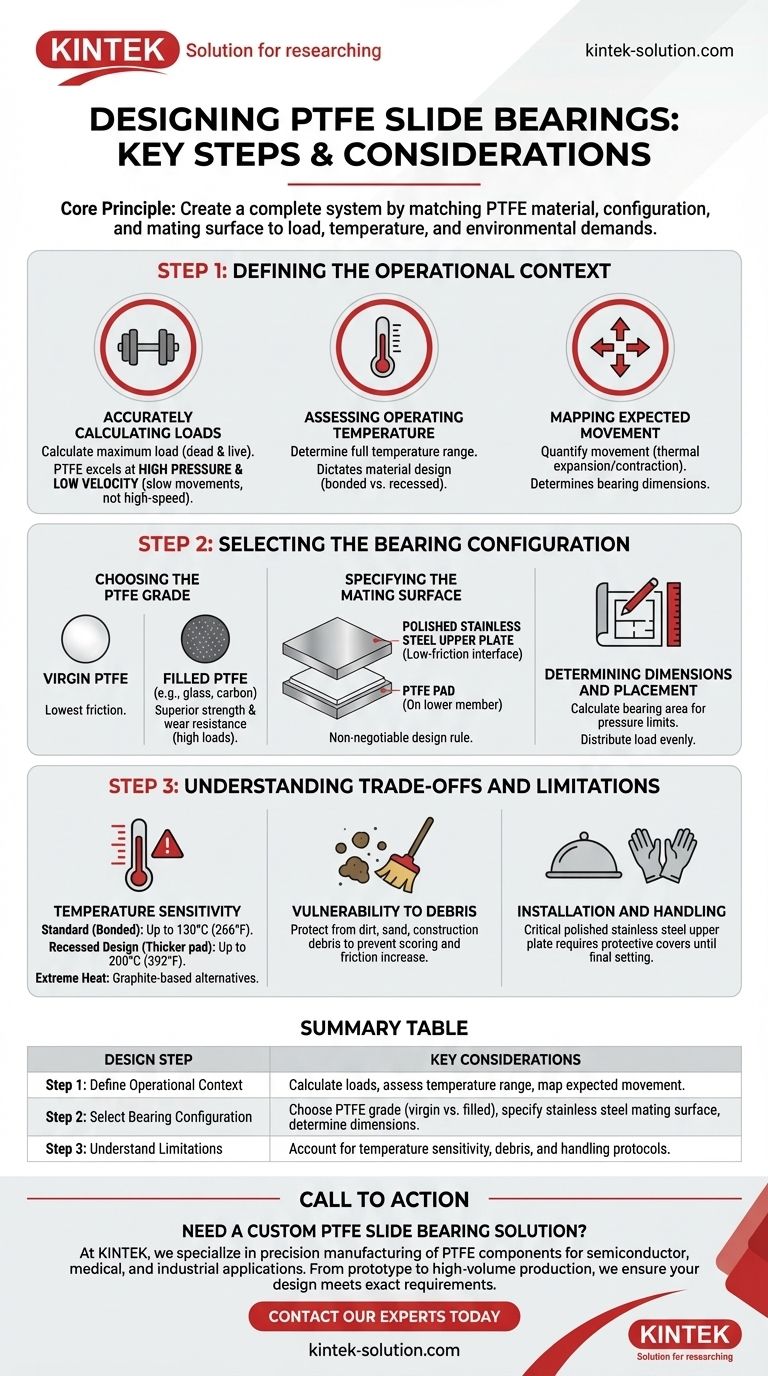
To design a PTFE slide bearing, you must first define the load, movement, and temperature requirements of your application. This analysis directly informs the selection of the bearing's material grade, physical dimensions, mounting method, and the critical specification of its mating surface.
The core principle of designing a PTFE slide bearing is not just about calculating size, but about creating a complete system. Success depends on correctly matching the PTFE material, its configuration, and its mating surface to the specific load, temperature, and environmental demands of the application.

Step 1: Defining the Operational Context
Before selecting any components, you must establish the fundamental parameters the bearing will operate under. This is the most critical phase, as all subsequent decisions depend on the accuracy of this data.
Accurately Calculating Loads
The design process begins with a precise calculation of the maximum load the bearing will support. This includes dead loads (the structure's own weight) and live loads (variable forces).
PTFE bearings excel under conditions of high pressure and low velocity. Their low-friction properties are most effective when managing slow movements, such as thermal expansion, not high-speed rotational motion.
Assessing the Operating Temperature
Temperature has a direct and significant impact on material selection. You must determine the full range of temperatures the bearing will experience during its service life.
This assessment will dictate whether a standard bonded PTFE is sufficient or if a more robust recessed or alternative material design is required.
Mapping Expected Movement
Quantify the anticipated movement in all directions. For structural applications, this is often thermal expansion and contraction, but can also include movement from other sources.
The total expected travel distance influences the required dimensions of the sliding surfaces to ensure the components remain in contact throughout their full range of motion.
Step 2: Selecting the Bearing Configuration
With the operational context defined, you can specify the physical components of the bearing assembly.
Choosing the PTFE Grade
The choice between virgin PTFE and a filled grade is critical. Virgin PTFE offers the lowest coefficient of friction.
Filled PTFE grades (reinforced with glass, carbon, or other materials) provide superior mechanical strength and wear resistance. This makes them better suited for applications with higher loads or where durability is the primary concern.
Specifying the Mating Surface
This is a non-negotiable design rule. The bearing assembly must consist of a PTFE pad sliding against a dissimilar, harder surface.
For optimal performance, the PTFE pad should be on the lower member of the assembly. The upper member must be a polished stainless steel plate to ensure a low-friction interface.
Determining Dimensions and Placement
Using your load calculations, determine the required bearing area to keep surface pressure within the material's limits. This calculation will define the length and width of the PTFE pad.
Next, decide on the number and position of the bearings to distribute the load evenly across the structure's support points.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
An effective design acknowledges the inherent constraints of the material and protects against common failure modes.
Temperature Sensitivity
Standard PTFE bearings, typically a 3mm pad bonded to a steel backing plate, are generally suitable for service temperatures up to 130°C (266°F).
For higher temperatures up to 200°C (392°F), a recessed design is necessary. Here, a thicker 5mm PTFE pad is set into a pocket in the backing plate, which protects the edges and prevents creep. For extreme heat, graphite-based bearings are an alternative.
Vulnerability to Debris
While PTFE bearings are essentially maintenance-free, their performance depends on a clean sliding interface. The design must protect the bearing from dirt, sand, and other construction debris.
Failure to keep the interface clean can lead to scoring of the surfaces, a significant increase in the coefficient of friction, and premature failure.
Installation and Handling
The polished stainless steel upper plate is critical to performance and can be easily damaged during transit or installation. The design specification should include requirements for protective covers that are only removed immediately before the final setting of the structure.
Finalizing Your Design Specification
Use these guidelines to translate your operational requirements into a clear and effective bearing specification.
- If your primary focus is a standard building or bridge application: A standard bonded PTFE pad sliding against polished stainless steel is the most common and cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is a high-temperature environment like industrial piping: You must specify a recessed PTFE design or a graphite-based bearing for temperatures exceeding 200°C.
- If your primary focus is durability under very high compressive loads: A filled or reinforced PTFE grade will provide the necessary wear resistance and mechanical strength.
By systematically addressing these key principles, you can design a PTFE slide bearing solution that is safe, reliable, and perfectly suited to its purpose.
Summary Table:
| Design Step | Key Considerations |
|---|---|
| Step 1: Define Operational Context | Calculate loads (dead & live), assess temperature range, and map expected movement. |
| Step 2: Select Bearing Configuration | Choose PTFE grade (virgin vs. filled), specify polished stainless steel mating surface, and determine dimensions. |
| Step 3: Understand Limitations | Account for temperature sensitivity (up to 200°C with recessed design) and vulnerability to debris. |
Need a custom PTFE slide bearing solution for your semiconductor, medical, or industrial application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in the precision manufacturing of PTFE components, including custom slide bearings. We work with you from prototype to high-volume production to ensure your design meets exact load, temperature, and movement requirements.
Contact our experts today to discuss your project and receive a tailored solution that delivers superior performance and reliability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support



















