At their core, PTFE envelope gaskets are valued for their exceptional chemical resistance, wide temperature tolerance, and non-contaminating properties. They are composite gaskets, designed to combine the chemical resilience of PTFE with the mechanical sealing capabilities of a more compressible core material.
The central challenge with solid PTFE gaskets is their rigidity and susceptibility to "creep" under load. The PTFE envelope gasket solves this by using a protective, inert PTFE shell over a flexible inner core, delivering chemical immunity without sacrificing a reliable, tight seal.
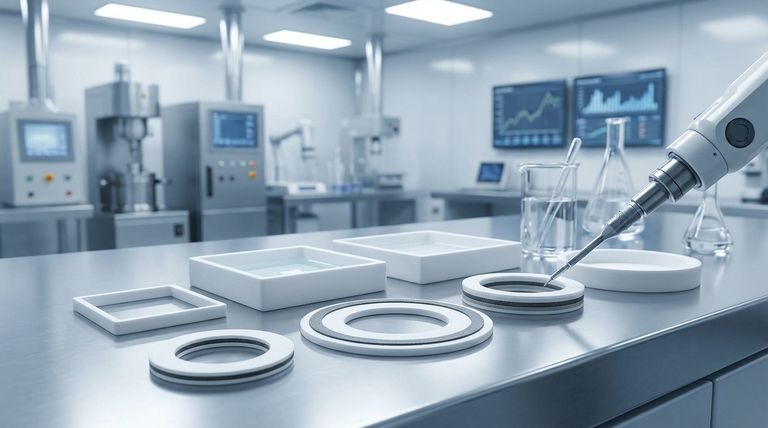

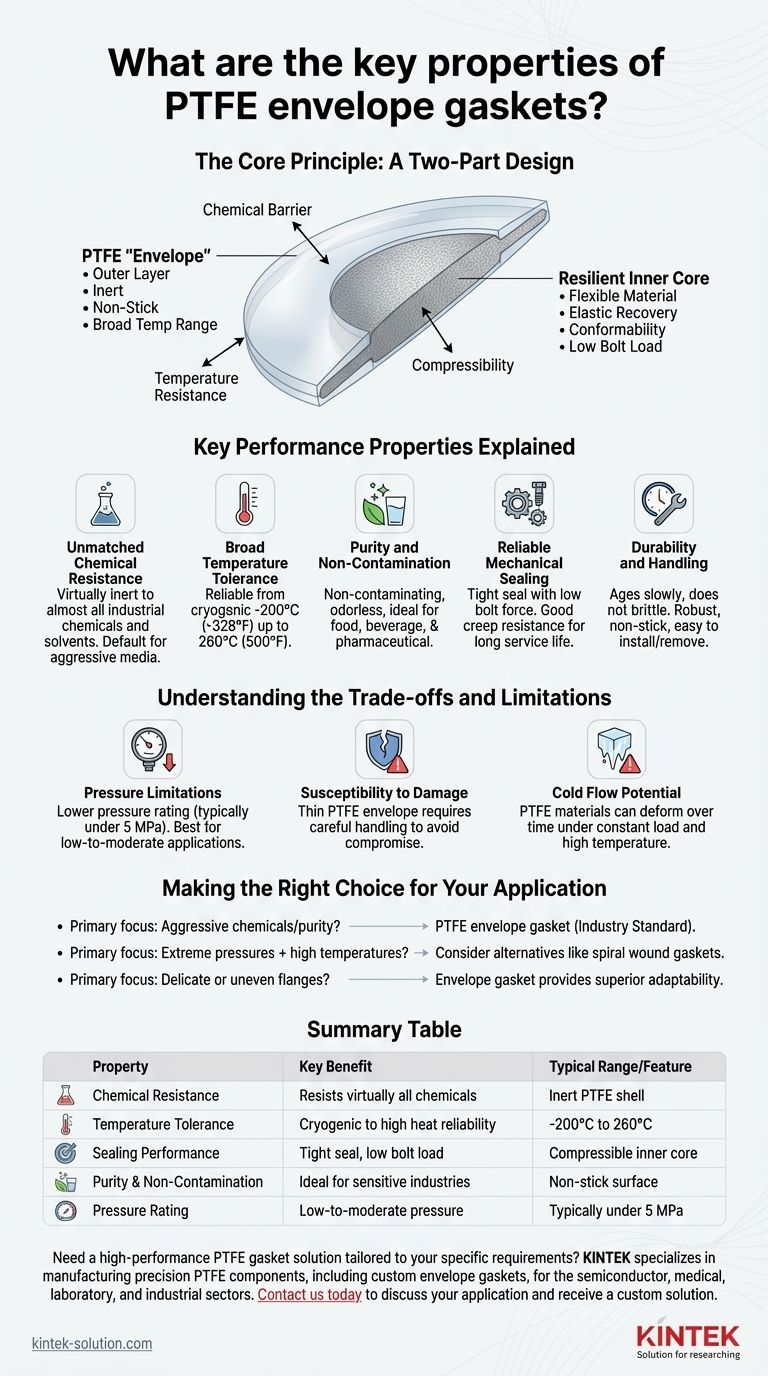
The Core Principle: A Two-Part Design
The unique properties of a PTFE envelope gasket come from its intelligent, two-part construction. It leverages the strengths of two different materials to create a superior sealing solution.
The PTFE "Envelope"
The outer layer is a thin "envelope" or jacket made from pure polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE).
This shell provides the gasket's signature properties: near-universal chemical resistance and a very wide operating temperature range.
Its famously non-stick surface also prevents material adhesion, resists product contamination, and simplifies cleaning during disassembly.
The Resilient Inner Core
Inside the PTFE envelope is a core made from a more compressible material, such as rubber or a non-asbestos fiber.
This inner core provides the elastic recovery and flexibility that a solid PTFE gasket lacks. It allows the gasket to conform to flange imperfections and maintain a tight seal even with fluctuations in pressure and temperature.
This design enables the gasket to seal effectively under low surface pressure, reducing the stress required on the flange bolts.
Key Performance Properties Explained
The combination of a protective shell and a flexible core results in a set of highly desirable performance characteristics for demanding industrial applications.
Unmatched Chemical Resistance
PTFE is virtually inert to almost all industrial chemicals and solvents. This makes envelope gaskets a default choice for sealing aggressive or corrosive media.
Broad Temperature Tolerance
These gaskets perform reliably across a vast temperature spectrum, typically from cryogenic lows of -200°C (-328°F) up to 260°C (500°F).
Purity and Non-Contamination
Because PTFE is non-contaminating, non-wetting, and odorless, these gaskets are ideal for high-purity applications in the food, beverage, and pharmaceutical industries.
Reliable Mechanical Sealing
The soft core allows the gasket to achieve a tight seal without excessive bolt force. This design also provides good creep resistance, ensuring the seal remains strong and consistent throughout its long service life.
Durability and Handling
PTFE ages very slowly and does not become brittle over time. The robust, non-stick nature of the gasket makes it easy to install and remove, reducing maintenance time.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While highly effective, PTFE envelope gaskets are not a universal solution. Understanding their limitations is critical for proper application.
Pressure Limitations
The primary trade-off for their chemical resistance and conformability is a lower pressure rating compared to metallic or spiral wound gaskets. They are best suited for low-to-moderate pressure applications, typically under 5 MPa.
Susceptibility to Damage
The PTFE envelope is relatively thin. Care must be taken during installation to avoid scratching or damaging the envelope, which would compromise its chemical resistance and create a potential leak path.
Cold Flow Potential
While the design minimizes this, all PTFE materials are subject to some degree of "cold flow" or creep, which is the tendency of the material to deform over time under a constant load. This must be considered in applications with high bolt loads or sustained elevated temperatures.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct gasket requires matching its properties to your specific operational demands.
- If your primary focus is handling aggressive chemicals or maintaining product purity: The PTFE envelope gasket is an industry standard due to its inert shell.
- If your primary focus is sealing at extreme pressures combined with high temperatures: You may need to evaluate alternatives like spiral wound gaskets, which are engineered for those specific conditions.
- If your primary focus is sealing delicate or slightly uneven flange surfaces: The compressible core of an envelope gasket provides superior adaptability and a better seal compared to a rigid, solid PTFE gasket.
Understanding this balance between chemical resilience and mechanical function is the key to selecting the right seal for your operational needs.
Summary Table:
| Property | Key Benefit | Typical Range/Feature |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Resists virtually all industrial chemicals and solvents | Inert PTFE shell |
| Temperature Tolerance | Operates reliably from cryogenic to high heat | -200°C to 260°C (-328°F to 500°F) |
| Sealing Performance | Maintains tight seal under low bolt load | Compressible inner core for creep resistance |
| Purity & Non-Contamination | Ideal for food, beverage, and pharmaceutical industries | Non-stick, non-contaminating surface |
| Pressure Rating | Best for low-to-moderate pressure applications | Typically under 5 MPa |
Need a high-performance PTFE gasket solution tailored to your specific requirements? KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE components, including custom envelope gaskets, for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise ensures you get a seal that combines superior chemical resistance with reliable mechanical performance. Contact us today to discuss your application and receive a custom solution from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Volumetric Flasks for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Use
People Also Ask
- When and by whom was PTFE discovered? A Tale of Accidental Innovation
- Why is dimensional stability a concern when machining PTFE? Ensure Accurate, Stable PTFE Components
- What is the hardness range of PTFE on the Shore D scale? Leveraging Its Softness for Superior Performance
- What are some applications of CNC machined PTFE parts? Critical Components for Medical, Electrical & Food Industries
- How does PTFE compare to other low-friction plastics like UHMW-PE and Nylon? A Guide to Material Selection



















