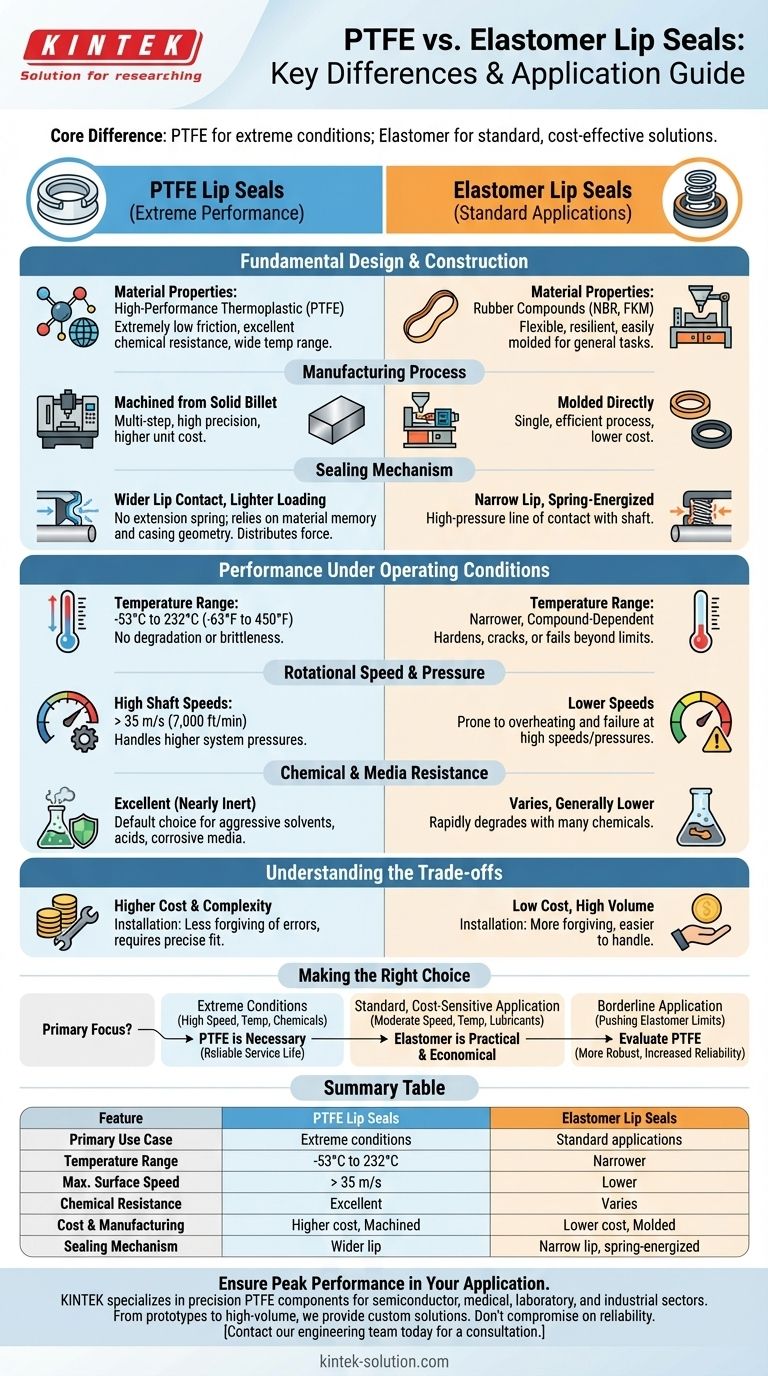
At their core, the key difference is application-driven: PTFE lip seals are engineered for extreme operating conditions where traditional elastomer seals would fail. PTFE excels due to its superior material properties and a distinct design that favors high speeds, extreme temperatures, and aggressive chemicals, while elastomer seals are a versatile and cost-effective solution for more standard applications.
The choice between PTFE and elastomer seals is not about which is universally superior, but about matching the seal's fundamental design and material capabilities to the specific demands of your operating environment.

Fundamental Design and Construction Differences
The performance gap between these two seal types originates in their material properties, manufacturing methods, and the resulting sealing mechanics.
Material Properties
PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) is a high-performance thermoplastic renowned for its extremely low friction, exceptional chemical resistance, and a very wide operating temperature range.
Elastomers (rubber compounds like NBR or FKM) are prized for their flexibility, resilience, and ability to be molded, which makes them suitable for a vast range of general-purpose sealing tasks.
Manufacturing Process
An elastomer lip seal is typically molded directly onto its metal casing in a single, efficient process. This makes it a cost-effective solution for high-volume production.
A PTFE lip cannot be molded this way. It must be machined from a solid billet of material and then press-fitted into its metal casing. This multi-step process requires high precision and contributes to a higher unit cost.
Sealing Mechanism and Contact
Elastomer seals typically use a spring-energized, narrow lip that creates a high-pressure line of contact with the shaft to prevent leaks.
PTFE seals operate differently. They do not use an extension spring, relying instead on the material's memory, the seal's inherent elasticity, and a precisely engineered casing. They feature a wider lip contact pattern with lighter unit loading, distributing force over a larger area to manage friction and wear at high speeds.
Performance Under Operating Conditions
These design differences translate directly into distinct performance capabilities, which is the most critical factor in selection.
Temperature Range
PTFE seals can operate in extreme temperatures, typically from -53°C to 232°C (-63°F to 450°F), without degrading or becoming brittle.
Elastomer seals have a much narrower temperature range that varies by compound. Exceeding these limits can cause them to harden, crack, or lose their sealing ability.
Rotational Speed and Pressure
PTFE's low-friction properties allow it to handle significantly higher shaft speeds, often exceeding 35 m/s (7,000 ft/min), where an elastomer seal would quickly overheat and fail.
PTFE seals also bridge the gap between standard lip seals and more complex mechanical seals, operating effectively at higher system pressures than most elastomer designs can withstand.
Chemical and Media Resistance
PTFE is nearly chemically inert, making it the default choice for applications involving aggressive solvents, acids, or other corrosive media that would rapidly degrade most rubber compounds.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right seal requires acknowledging the compromises inherent in each design.
Cost and Complexity
The primary advantage of elastomer seals is their low cost, driven by efficient, high-volume molding processes.
PTFE seals are significantly more expensive. This is a direct result of higher raw material costs and the precision machining required for their manufacture.
Installation Sensitivity
While both seals require careful installation, the design of a PTFE seal, which relies on a precise press-fit and casing geometry for its sealing force, can be less forgiving of installation errors or shaft imperfections.
Wear Characteristics
The wider, lower-pressure footprint of a PTFE seal is specifically designed to manage wear in high-speed applications. However, in abrasive media, the performance can vary, and proper material selection is critical.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct seal is a matter of aligning its capabilities with your specific operational needs.
- If your primary focus is extreme conditions (high shaft speeds, wide temperature ranges, or aggressive chemicals): PTFE is the necessary choice as elastomer seals will not provide reliable service life.
- If your primary focus is a standard, cost-sensitive application (moderate speeds, temperatures, and common lubricants): An elastomer seal is the most practical and economical solution.
- If your application is borderline (pushing the limits of a high-performance elastomer): Evaluate PTFE as a more robust alternative that can offer a significant increase in reliability and seal longevity.
Ultimately, a well-informed seal selection is a foundational step in ensuring the reliability and performance of your equipment.
Summary Table:
| Feature | PTFE Lip Seals | Elastomer Lip Seals |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use Case | Extreme conditions (high temp, speed, chemicals) | Standard, cost-sensitive applications |
| Temperature Range | -53°C to 232°C (-63°F to 450°F) | Narrower, compound-dependent |
| Max. Surface Speed | > 35 m/s (7,000 ft/min) | Lower, prone to overheating |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent (nearly inert) | Varies, generally lower |
| Cost & Manufacturing | Higher cost, precision machined | Lower cost, high-volume molded |
| Sealing Mechanism | Wider lip, lighter unit loading | Narrow lip, spring-energized |
Ensure Peak Performance in Your Application
Choosing the wrong seal can lead to equipment failure and costly downtime. The experts at KINTEK specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, and labware—for the most demanding environments in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
We provide custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, ensuring you get a seal perfectly matched to your specific operating conditions, whether you need the extreme capabilities of PTFE or a high-performance elastomer solution.
Don't compromise on reliability. Contact our engineering team today for a consultation to optimize your sealing solution.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What is the working temperature range of PTFE? Master Extreme Heat and Cryogenic Applications
- What are the material advantages of machining Teflon? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- Why is PTFE suitable for cryogenic or high-temperature applications? Unmatched Thermal Stability from -450°F to 500°F
- What are the base characteristics of PTFE? Unlocking Extreme Performance in Friction, Temperature, and Chemical Resistance
- What are some common applications of machined PTFE? Leverage its Unique Properties for Demanding Applications



















