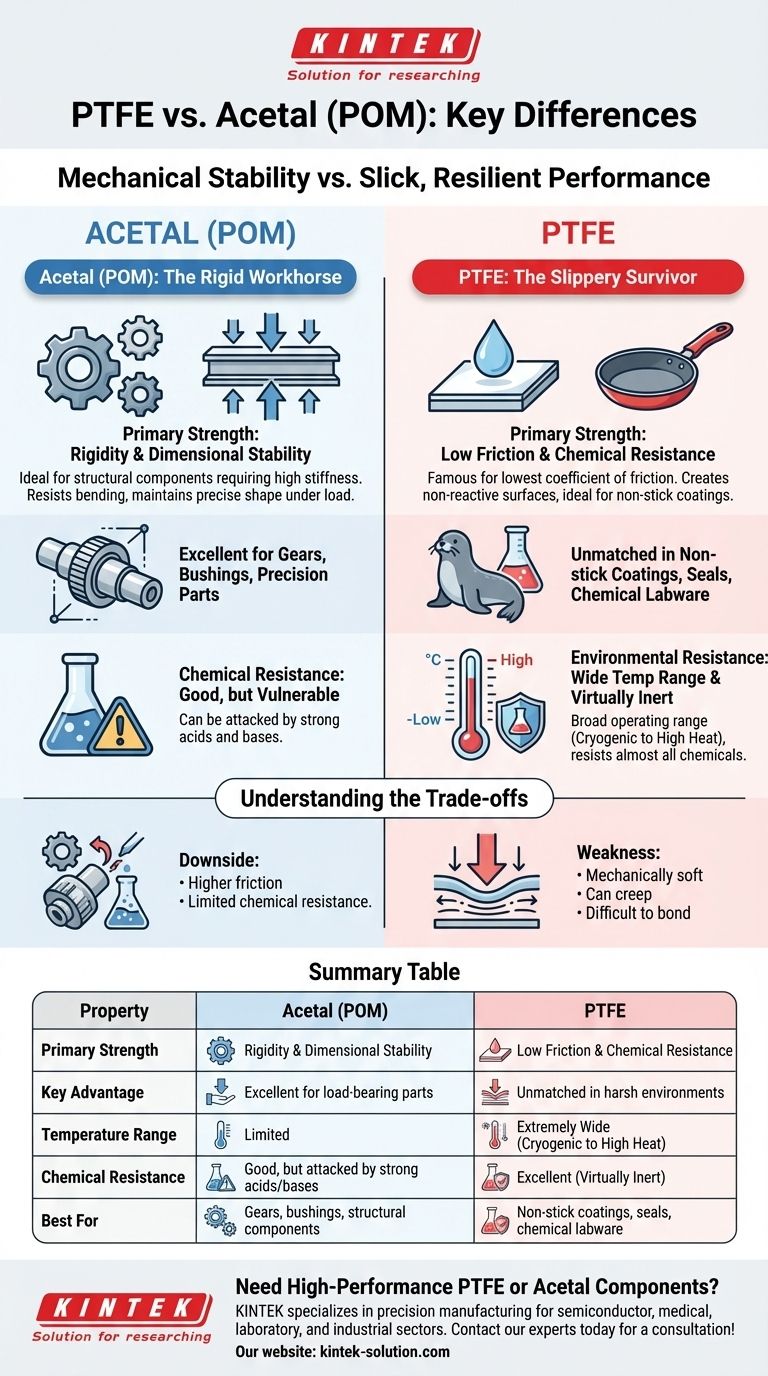
Choosing between PTFE and Acetal (POM) is a choice between mechanical stability and slick, resilient performance. Acetal, also known as Polyoxymethylene (POM), is a rigid, dimensionally stable engineering thermoplastic ideal for structural components that require high stiffness. In contrast, PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene) is a fluoropolymer prized for its exceptionally low friction, wide temperature tolerance, and superior chemical resistance.
Your decision hinges on a single question: Is the primary need for structural integrity or for unparalleled surface performance? Acetal provides the structure, while PTFE provides the performance against friction, chemicals, and heat.

The Core Difference: Mechanical Strength vs. Surface Performance
The fundamental distinction between these two materials lies in what they are engineered to do. Acetal is designed to bear loads and hold its shape, whereas PTFE is designed to survive extreme environments and reduce friction.
Acetal (POM): The Rigid Workhorse
Acetal's primary advantage is its excellent rigidity and dimensional stability. This means it resists bending under load and maintains its precise shape across a range of conditions.
This makes it an ideal material for high-performance engineering components like gears, bushings, and precision mechanical parts that demand stiffness and predictability.
PTFE: The Slippery Survivor
PTFE is famous for having one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any known solid. It is exceptionally "slippery," which is why it's used as a non-stick coating.
Unlike the rigid Acetal, PTFE is softer and more flexible. Its value is not in its strength, but in its ability to create low-friction, non-reactive surfaces.
Comparing Environmental Resistance
How a material behaves when exposed to heat and chemicals is often a critical factor in selection. Here, PTFE has a significant advantage over Acetal.
Temperature Tolerance: PTFE's Clear Advantage
PTFE has a much broader operating temperature range than Acetal. It remains functional at extremely low cryogenic temperatures and can withstand high temperatures far better than POM.
This makes PTFE the only choice for applications involving extreme temperature swings or consistent high-heat exposure.
Chemical Resistance: PTFE's Near-Universal Inertness
PTFE is virtually inert and will not react with the vast majority of industrial chemicals. It can withstand highly aggressive substances without degrading.
Acetal, while generally robust, has a known vulnerability. It can be attacked and degraded by strong acids and bases, making it unsuitable for applications involving these chemicals.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither material is perfect for every situation. Choosing one means accepting the inherent limitations of the other. Understanding these trade-offs is crucial for avoiding material failure.
The Downside of Acetal's Strength
While strong and rigid, Acetal has a higher coefficient of friction than PTFE. For applications where minimizing drag is the top priority, Acetal is the inferior choice.
Its most significant trade-off is its limited chemical resistance. A design that works perfectly in a neutral environment could fail catastrophically if exposed to the wrong chemical substance.
The Weakness of PTFE's Slipperiness
PTFE's greatest strength is also a source of weakness. It is a mechanically soft material that can "creep" or deform under sustained pressure, making it unsuitable for high-load structural parts.
Furthermore, its non-stick properties make it notoriously difficult to bond to other materials. This can complicate assembly processes.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To make a definitive decision, identify the single most critical property your application demands.
- If your primary focus is mechanical precision and load-bearing: Choose Acetal (POM) for its superior rigidity and dimensional stability.
- If your primary focus is the lowest possible friction: Select PTFE for its unmatched slickness in applications like non-stick coatings or slide bearings.
- If your primary focus is resistance to harsh chemicals or extreme temperatures: PTFE is the clear winner due to its chemical inertness and wide operating range.
Ultimately, understanding the core trade-off between Acetal's structural strength and PTFE's specialized surface performance is the key to successful material selection.
Summary Table:
| Property | Acetal (POM) | PTFE |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Strength | Rigidity & Dimensional Stability | Low Friction & Chemical Resistance |
| Key Advantage | Excellent for load-bearing parts | Unmatched in harsh environments |
| Temperature Range | Limited | Extremely Wide (Cryogenic to High Heat) |
| Chemical Resistance | Good, but attacked by strong acids/bases | Excellent (Virtually Inert) |
| Best For | Gears, bushings, structural components | Non-stick coatings, seals, chemical labware |
Need High-Performance PTFE or Acetal Components?
KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you require the unmatched chemical resistance of PTFE or the structural integrity of Acetal, we provide custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Let us help you select the perfect material and deliver the precise component your application demands.
Contact our experts today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What medical applications does PTFE have? Discover Its Critical Role in Implants and Devices
- What significant discovery about PTFE was made in the 1990s? Unlock Enhanced Performance with Radiation Cross-Linking
- Why is PTFE used in medical and pharmaceutical applications? The Ultimate Guide to Safety and Performance
- How is PTFE used in the medical field? Discover the Key to Biocompatible Medical Devices
- How does the composition of PTFE differ from other plastics? Unlocking Its Unique Chemical & Friction Properties
- How does PTFE contribute to environmental benefits? Durability, Efficiency, and Contamination Prevention
- What are the limitations of PTFE materials? Understand the Key Trade-Offs Before You Spec
- Why is flow regulation important in control systems? Ensure Stability, Safety, and Efficiency



















